
Q:Which combinations of antihypertensivemedications are most effective-and which arebest avoided?

Q:Which combinations of antihypertensivemedications are most effective-and which arebest avoided?

ABSTRACT: Diuretics remain a mainstay of heart failure therapy. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and ß-blockers inhibit activation of neurohormonal systems; these agents are recommended for most patients with symptomatic systolic heart failure. Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) are alternatives for patients who are unable to tolerate ACE inhibitors. Recent trials suggest that ARBs are also useful when added to the regimen of patients with a low ejection fraction. Although digoxin can provide long-term inotropic support in men, it significantly increases the risk of mortality in women; because of the risk of toxicity, use digoxin with caution in older persons and patients with renal dysfunction. Consider an aldosterone antagonist in patients who remain symptomatic at rest despite the use of a diuretic, digoxin, an ACE inhibitor or an ARB, and a ß-blocker. Lifestyle modifications such as dietary restriction and exercise are helpful in all patients.
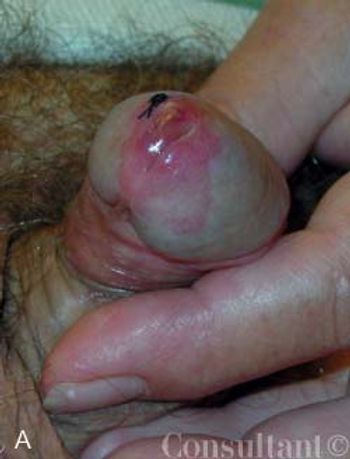
An uncircumcised 58-yearold man presented with a persistent “rash” on his penis of 5 years’ duration. He complained of localized irritation with coitus. Over-the-counter ointments and corticosteroid preparations had failed to clear the eruption. The patient had hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and coronary artery disease. He had been monogamous for the last decade and denied any risk factors for sexually transmitted diseases.

ABSTRACT: In high-risk patients with vascular disease, blockade of the renin- angiotensin system (RAS) can help prevent cardiac remodeling that ultimately results in left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) and heart failure. Optimal treatment of these patients, who often have diabetes or renal disease, usually involves a combination of agents-1 of which should be a thiazide diuretic-to reduce blood pressure, control the comorbid condition, and prevent end-stage organ damage. The manner in which the RAS is interrupted may be important. For example, although a thiazide diuretic and an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor are recommended for hypertensive patients with LVH, an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) in combination with a diuretic was recently found to reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in these patients to a greater degree than a ß-blocker/diuretic. Both ACE inhibitors and ARBs delay the progression of diabetic nephropathy and reduce albuminuria. ARBs were recently shown to reduce progression from microalbuminuria to macroalbuminuria. In patients with systolic heart failure who cannot tolerate ACE inhibitors, an ARB can be used with a ß-blocker.

Uncontrolled hypertension is a major health problem among African Americans. Obesity, high sodium and low potassium intake, and inadequate physical activity have been identified as barriers to cardiovascular health in many African Americans. Thus, it is important to educate and counsel patients about lifestyle modifications, such as a low-sodium, DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension)-type diet; regular aerobic exercise; moderation of alcohol consumption; and smoking cessation. All classes of antihypertensive agents lower blood pressure in African Americans, although some may be less effective than others when used as monotherapy. Most patients require combination therapy. Both patient barriers (such as lack of access to health care and perceptions about health and the need for therapy) and physician barriers (such as poor communication styles) contribute to the low rates of hypertension control in African Americans. Patient-centered communication strategies can help overcome these barriers and can improve compliance and outcomes. Such strategies include the use of open-ended questions, active listening, patient education and counseling, and encouragement of patient participation in decision making.

An obese 55-year-old woman had intermittent dysuria and frequent urination for 4 days and fever, abdominal pain, and vomiting for 3 days. Her history included type 1 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and angina; her medications included insulin, nifedipine, and nitroglycerin.
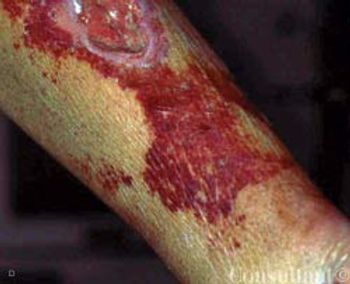
A 59-year-old man, who was unable to walk, was brought to the emergency department with severe leg pain, worsening weakness, increasing fatigue, chills, and fever of 3 days' duration. The symptoms began after a round of golf. In addition to the leg pain, which particularly affected the calf muscles, the lower extremities were red and swollen.

Persons with a systolic blood pressure (BP) of 120 to 139 mm Hg or a diastolic BP of 80 to 89 mm Hg are now considered, according to the latest Joint National Committee (JNC) report on hypertension.
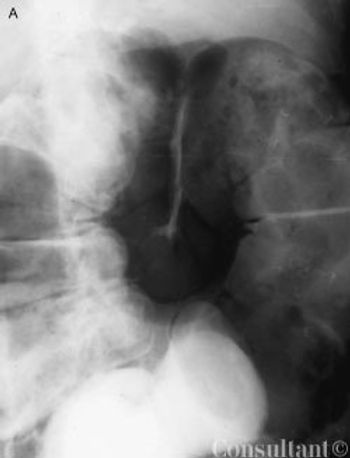
Progressive abdominal distention, nausea, constipation, and mild abdominal pain developed in an 82-year-old woman 5 days after she underwent surgical repair of a left hip fracture. Her medical history was significant for Parkinson disease, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and hypertension.

A 63-year-old woman presents withdiffuse hyperkeratosis of the solesand palms. She also has onycholysis-separation of the nail plate fromthe nail bed-and salmon-coloredplaques behind her ears. Biopsy ofone of the plaques confirms the suspecteddiagnosis of psoriasis.

A middle-aged man with"jock itch" that has failed torespond to antifungal creams.An older woman who has diffusehyperkeratosis of predominantlyweight-bearing surfaces.A young man with mildlypruritic, small, salmon pinkpapules and thick white scaleon his trunk and arms.

A 30-year-old man presents with scalingand erythema of the scalp that extendspast the anterior hairline. Thepatient has a family history of psoriasis.For the past 5 years, he has experiencedwintertime flares of the diseasethat affect his scalp and the extensorsurfaces of the extremities.

A 46-year-old man complains that his"jock itch" failed to respond to antifungalcreams. The patient has hadpsoriasis on his elbows and knees formany years.

A 72-year-old man presents with skinlesions and nail abnormalities. Erythematous,sharply defined, demarcatedpapules and rounded plaquescovered by silvery micaceous scaleare noted on the elbows, knees, andscalp. Involved areas appear to be bilaterallysymmetric. Localized psoriasisvulgaris is diagnosed.

4A:Small, slightly pruritic, salmonpink papules with thick white scalehave arisen over the past 5 days onthe trunk and arms of a 24-year-oldman. The patient has a history ofvery mild psoriasis vulgaris of the elbows,knees, and scalp; he deniesstreptococcal pharyngitis or other recentinfections. Guttate psoriasis isdiagnosed.

Focal, painless discoloration of theleft thumbnail (A) developed severalyears earlier in this 46-year-old man.Oral antifungal therapy had no effecton the lesion.

A 35-year-old man presents with extensiveplaques over much of thetrunk and extremities. This severeflare of psoriasis developed after astressful emotional experience.

A 60-year-old man with a long historyof psoriasis vulgaris required a systemiccorticosteroid for a severe exacerbationof asthma. Soon after theErythrodermic or Pustular Psoriasiscorticosteroid was discontinued, generalizederythema and scaling of theskin developed.

ABSTRACT: Indications for pulmonary function tests (PFTs) have widened substantially, ranging from screening smokers for early lung disease to determining the diagnosis and prognosis of pulmonary conditions. Current indications also include screening for drug-induced lung toxicity and preoperative screening for lung resection surgery. In the workup of respiratory symptoms, such as dyspnea, cough, and wheezing, PFTs can identify obstructive or restrictive patterns that may suggest a diagnosis such as asthma or interstitial lung disease. The ratio of FEV1 to forced vital capacity is very sensitive to the presence of airflow limitation, although bronchoprovocation testing may be needed to diagnose asthma, especially in patients with mild intermittent disease. Measurements of lung volumes and carbon monoxide-diffusing capacity (DLCO) provide crucial information in selected patients. For example, a reduced DLCO may be a sign of more advanced disease, such as emphysema or pulmonary hypertension.Since the first description of the spirometer by John Hutchinson in the late 1800s, pulmonary function tests (PFTs) have expanded to include spirometry; lung volumes; carbon monoxide-diffusing capacity (DLCO) (transfer factor); respiratory muscle performance; and exercise and functional testing, such as the 6-minute walk test (6MWT) and cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET).
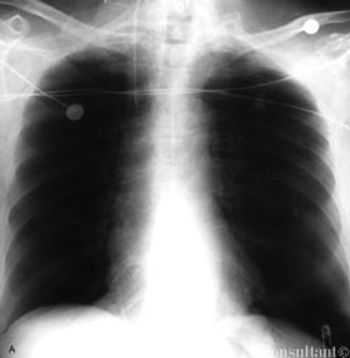
A 67-year-old woman, who had hypertension and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, presented to the emergency department with mild abdominal discomfort and shortness of breath.

ABSTRACT: Recent studies, although suggestive, do not yet support the routine use of angiotensin II receptor blockers in combination with angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors in patients with congestive heart failure (CHF). For CHF patients in normal sinus rhythm, consider digoxin when a regimen of diuretics, ACE inhibitors, and β-blockers at optimal dosages does not relieve symptoms completely. Anticoagulation may be warranted in CHF patients with atrial fibrillation, previous embolic events, severely reduced systolic performance, or potential chamber clots. β-Blockers are indicated for patients with mild to severe CHF, unless there is a specific contraindication, and therapy should be initiated once euvolemia has been achieved. Avoid NSAIDs and cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors in patients with CHF because the prostaglandin-blocking properties of these agents may promote fluid retention.

For several days, a 60-year-old woman has had fever, myalgias,fatigue, poor appetite, and diminished oral intake. Shedenies cough, sputum production, and urinary symptoms.
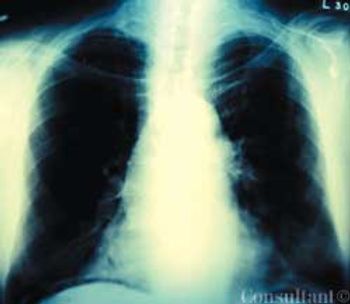
A 75-year-old man was brought to the emergency department with fever, cough, and abdominal pain of 2 days’ duration. The pain was most severe in the epigastric and umbilical regions. The patient’s history included type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and hypercholesterolemia. He had smoked cigarettes for 40 years and recently lost 50 lb. The patient was tachypneic and diaphoretic.
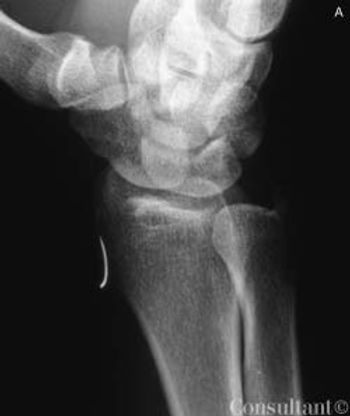
A 40-year-old man presented to the emergency department with moderate to severe pain over the left lateral wrist. Earlier in the day, an iron rod had accidentally struck his wrist. The patient’s history included chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, hypertension, and social anxiety disorder.

Three weeks after coronary artery bypass graft (CABG)surgery, a 52-year-old woman complained of pain at thesternal scar. The patient had a history of diabetes and hypertension.She had smoked cigarettes for many years.