A recent study found that obese or severely obese patients have a 60% higher risk of chronic diarrhea vs those who are within a normal weight range.

A recent study found that obese or severely obese patients have a 60% higher risk of chronic diarrhea vs those who are within a normal weight range.

Eating just half a serving more a day of nuts can help ward off weight gain and lower the risk of obesity, according to a recent study.

Findings: a heart-healthy lifestyle reduces DM risk; 1 egg a day may protect against T2DM; and a new genetic risk score may improve DM diagnosis.

A new study models the impact of 4 key public health interventions on global HCV burden to see if WHO elimination targets are realistic.
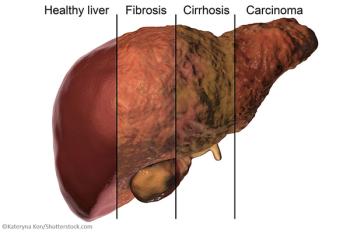
A first-of-its-kind study found that among cirrhosis patients with and without HIV-coinfection, liver function improved >50% in each cohort.

Fanciful flavors added to e-cigarettes react with vaping solvents (eg, polypropylene glycol) to create compounds that may persist and harm.
Authors speculate that this alteration of smooth airway muscle may imprint a unique signature that could help lead to highly targeted new asthma therapies.
Authors of a new study found that lifestyle factors, not a major air pollutant, play a more significant role in women developing asthma COPD overlap syndrome.

When using inhaled corticosteroids for the treatment of asthma, COPD, and other airways disease, authors of a new study warn to proceed with caution.
A new study found that post-hip fracture, less than 5% of elderly patients were started on osteoporosis medication despite high risk for recurrent fracture.

Results include: The metabolic dangers of neuroleptic Rx in youth; prevalence of T2DM in minorities with severe mental illness; and gaps in care for mentally ill with T2DM.
Dupilumab is shown to alleviate asthma symptoms and improve a patient's ability to breathe better than standard therapy, according to a new study.

New study highlights why males are more prone to respiratory disorders than females, especially during early life.
Treatment rates for dangerously high cholesterol levels remain low, according to a new study.

Routine fasting for cholesterol tests could be eliminated by adopting a newer method for determining LDL cholesterol, according to a new study.

The prevalence of asthma in children is on the decline, but researchers still stress the importance of asthma education to not only children, but to parents and others involved in their care.

A new study finds cases of acute HCV infection increasing on pace with the rise in numbers of opioid abusers who inject drugs.

In a new study, the combination of hands-on in school asthma therapy and telemedicine visits proved a successful model that could be scalable.
Fractional exhaled nitric oxide concentration is a helpful tool that aids in asthma diagnosis. But it's not the only piece of the diagnostic puzzle.
Read a concise review of a new real-world study that shows high efficacy for this all-oral combination against HCV GT2.

Highlights of 3 studies from 2017 that support the role of PCPs in HCV infection treatment, including prescribing direct-acting antiviral agents.
The lung microbiome may have a profound effect on many respiratory conditions and it plays a significant role in asthma severity and response to treatment.
This study sheds light on the interactive effects of atopic dermatitis and early allergic sensitization, and may help you predict which children may develop asthma and food allergies.

When it comes to cannabis use, one issue is when.

Children with comorbid asthma and obesity showed a 26% higher 30-day hospital readmission rate vs normal weight peers with asthma.
Even asthma patients without extra body weight may see as much as a 50% reduction in asthma symptom scores. It's really that simple.
A new study’s lead author notes, however, that lack of significant effect may have been secondary to important study limitations.
Lower respiratory infections in children seem to predispose to poor adult lung function, but causation and directionality have yet to be determined.
Study authors propose a new asthma patient “phenotype” in which a previous severe event is the sole predictor of another one.

Results of a recent study into the role of lipids in atopic asthma could help identify new targets for therapy.

Published: January 28th 2013 | Updated:

Published: March 5th 2013 | Updated:

Published: March 25th 2013 | Updated:

Published: April 9th 2013 | Updated:

Published: April 11th 2013 | Updated:

Published: April 10th 2013 | Updated: