Articles by Marti Jill Rothe, MD

In recent years, the role of the immunesystem in the pathogenesis of psoriasishas been extensively delineated. Thisresearch has spawned a new classof medications that target specific immunefactors and hold great promiseas psoriasis therapies. The Table highlightsthe significant features of 4 ofthese biologic agents.

These benign tumors made up of nevus cells may be flat or raised, pigmented (Figure A) or nonpigmented.
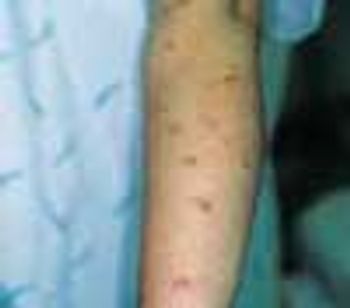
Pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy (PUPPP). This cutaneous eruption usually occurs in the last trimester. It is seen only rarely in the postpartum period. PUPPP is more common in primigravidas but can occur in any pregnant patient.

Benign skin tumors seen in pregnant patients as well as those who are not pregnant include acrochordons, seborrheic keratoses, pyogenic granulomas, and spider angiomas. There have been reports that melanocytic nevi develop or change during pregnancy; however, a pilot study at our institution was unable to confirm this finding.

These benign vascular tumors are sometimes seen in pregnancy.
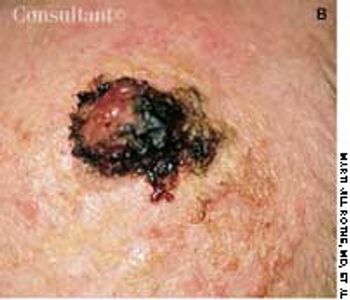
An 82-year-old man with Alzheimer's disease and atrial fibrillation was referred for evaluation of a lesion present for an undetermined period. It was initially noted 1 week earlier, at his first office visit with a geriatrician.
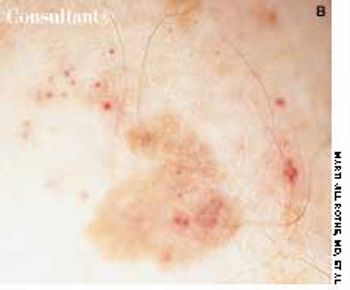
A 69-year-old man with a history of basal cell carcinoma of the face and back presented for a 6-month skin cancer evaluation. Physical examination revealed an asymmetric, irregularly pigmented, thin brown plaque of the anterior chest. A 3-mm punch biopsy specimen was obtained from a deeply pigmented area at the inferior border of the lesion to rule out melanoma.

A 75-year-old man complained of the sudden appearance of multiple “moles” on his back. He had no history of skin cancer. Past medical history was significant for prostate cancer, which had been diagnosed and treated 2 years previously.
Some cutaneous conditions are unique to pregnancy and the postpartum period. Others may affect both pregnant and nonpregnant women. Familiarity with these conditions is important in the evaluation of a pregnant patient with a rash or cutaneous lesion.
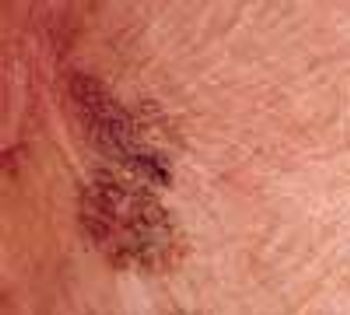
Recurring blisters on the sides of the fingers brought a 72-year-old man to his physician. He was asked to change into a gown for a full-skin examination. Physical examination demonstrated minute papulovesicles affecting the medial and lateral aspects of the fingers, consistent with dyshidrosis. The patient's skin was severely sun-damaged, and there was an irregularly pigmented, asymmetric patch affecting the posterolateral neck.
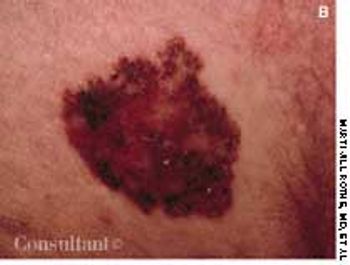
A 60-year-old woman was referred by her gynecologist because of a lesion on the buttocks of which the patient first became aware when she noticed blood on her underwear. Physical examination revealed an irregularly pigmented and slightly eroded asymmetric plaque. Examination with a magnifier highlighted a slightly rolled border, from which a shave biopsy was performed.

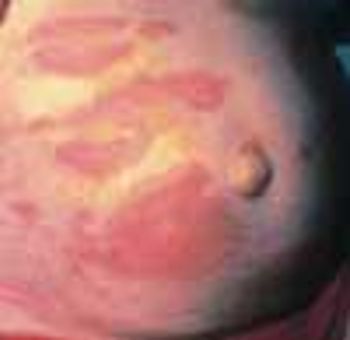
A 70-year-old man who had just completeda course of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazolefor a urinary tract infectionpresented with palpable purpuraand cutaneous erosions of acute onseton his legs (A). He also had massivescrotal edema and purpura (B).

Painful blue toes developed in a 72-year-old woman with coronary artery andperipheral vascular disease after she underwent angiography.

A middle-aged man with"jock itch" that has failed torespond to antifungal creams.An older woman who has diffusehyperkeratosis of predominantlyweight-bearing surfaces.A young man with mildlypruritic, small, salmon pinkpapules and thick white scaleon his trunk and arms.













