Drs Tina Q. Tan and Rodney Rohde share final thoughts on addressing patient and parent concerns with COVID-19 vaccines.

Drs Tina Q. Tan and Rodney Rohde share final thoughts on addressing patient and parent concerns with COVID-19 vaccines.

Experts comment on the significance of mRNA (messenger RNA) technology in developing COVID-19 vaccines, as well as vaccines against other viral infections.

Rodney Rohde, PhD, MS, SM(ASCP)CM, shares his approach to initiating conversations around COVID-19 vaccination to patients and family members, highlighting the safety of administering multiple vaccines at during 1 visit.

Experts conclude their discussion on the efficacy and safety study of nirsevimab for Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) commenting on possible dosing strategies and key takeaways from this study.

Experts discuss the results of the safety and efficacy study of nirsevimab for Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) commenting on the adverse events observed in the test and placebo groups.

Experts discuss how infant weight related to efficacy outcomes of nirsevimab for Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV), providing their clinical expertise on why this may have occurred and what improvements can be made to mitigate these differences.

Experts discuss data relating to the strains of Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) and how clinicians should consider them in relation to the efficacy of nirsevimab.
Flor M. Munoz, MD, MSc, and Tina Tan, MD, FAAP, FIDSA, FPIDS, continue their discussion on the results of nirsevimab for Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) and offer insights on how this may change therapeutic approaches in the future.

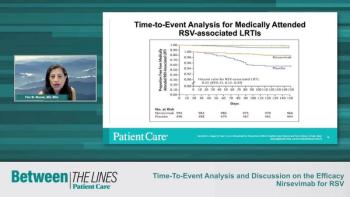
Tina Tan, MD, FAAP, FIDSA, FPIDS, and Flor M. Munoz, MD, MSc, discuss the initial efficacy data of the study on nirsevimab for Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) and how it compared to placebo.
Flor M. Munoz, MD, MSc, and Tina Tan, MD, FAAP, FIDSA, FPIDS, discuss the patient population of the safety and efficacy study on nirsevimab for Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV).

Tina Tan, MD, FAAP, FIDSA, FPIDS, presents the background, objectives, and methods of a recent study on the efficacy and safety of nirsevimab for Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) in late-preterm and term infants.
Flor M. Munoz, MD, MSc, and Tina Tan, MD, FAAP, FIDSA, FPIDS, discuss the prevalence of Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) and prior preventative gaps. They also discuss the recent FDA-approval of nirsevimab for late-preterm and term infants.
Tina Tan, MD, FAAP, FIDSA, FPIDS, and Flor M. Munoz, MD, MSc, introduce the objectives of their discussion and background information on Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) and nirsevimab.

Vaccines have substantially reduced the incidence ofpediatric pneumonias caused by Haemophilus influenzae type band certain serotypes of Streptococcus pneumoniae. However,other organisms are being identified more frequently, includingmethicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and serotypesof S pneumoniae that are not covered by the pneumococcalvaccine. Although chest radiographs are still a basic componentof the assessment of pneumonia, CT scans are increasinglybeing used to differentiate effusion from empyema and consolidationand to evaluate for pleural fluid loculations, lung abscesses,and lung necrosis. ß-Lactams, particularly extendedspectrumcephalosporins, remain an important cornerstone ofthe treatment of complicated pneumonia. In areas where community-acquired MRSA is a concern, empirical coverage for thispathogen should be considered in patients with a severe ornecrotizing pneumonia. (J Respir Dis. 2008;29(2):85-92)
Published: January 12th 2024 | Updated:

Published: January 12th 2024 | Updated:

Published: January 12th 2024 | Updated:

Published: April 7th 2008 | Updated: