
Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) is the most common cause of sporadic encephalitis worldwide. In the California Encephalitis Project, 24% of the cases of viral encephalitis were caused by HSV-1 and 3% were caused by HSV-2.1

Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) is the most common cause of sporadic encephalitis worldwide. In the California Encephalitis Project, 24% of the cases of viral encephalitis were caused by HSV-1 and 3% were caused by HSV-2.1

The death rate for HIV-infected patients who miss scheduled clinic appointments during their first year of treatment is more than double that for patients with perfect attendance, according to a recent study (Douglas D. Reuters Health. February 11, 2009).

In 2005, members of the Group of Eight (G8)-an international forum for the governments of Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Russia, the United Kingdom, the United States, and the European Union-along with the African Union and the heads of state attending the 2005 United Nations World Summit, joined with the UNAIDS Secretariat in committing themselves to providing universal access to HIV care, prevention, and treatment for all those in need by 2010.

Although children can usually inhale very well during lung auscultation, typically they do not exhale sufficiently. I ask them to “breathe in real big and then let all the air out without being noisy.” I place one hand on their chest and the other on their back; I let them inhale, and when they start to exhale, I gently compress the chest to accentuate the breath sounds and to obtain a full exhalation. Children tolerate this very well.

When a patient with iron deficiency anemia fails to respond to oral iron supplementation, consider whether foods he or she is consuming may be contributing to malabsorption. Such foods include coffee and tea (because they contain tannins) and cola drinks (a result of their phosphate content). In addition, because achlorhydria may interfere with iron absorption, encourage patients to eat foods rich in vitamin

In contrast to previous conferences, at this year’s Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI), held February 8 through 11 in Montreal, there were few presentations on major clinical trials of antiretroviral therapy and little news on investigational agents was reported. Nevertheless, there were a number of important studies dealing with the treatment of HIV infection, a few of which I’ll summarize here.

Here is a common clinical scenario. Your patient was admitted to the hospital with an acute myocardial infarction (MI). Intervention has been successful, and the patient's condition is now stable. The cardiologist is concerned about the patient's hemoglobin value of 9 g/dL. Active bleeding, hemolysis, and other potential causes of anemia (iron or vitamin B12 deficiency, for example) have been excluded. The decision is made to transfuse to raise the hemoglobin level above 10 g/dL.

When do a baby's eyes stop deviating? When is surgery indicated for a child with esotropia? Answers here.

A 50-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with severe dizziness, weakness, and dyspnea of 1 week’s duration. Ten days earlier, an upper respiratory tract infection (URTI) was diagnosed; over-the-counter cough syrup and acetaminophen were prescribed. However, the patient’s condition has steadily deteriorated since then. In addition, her urine has darkened over the past few days.
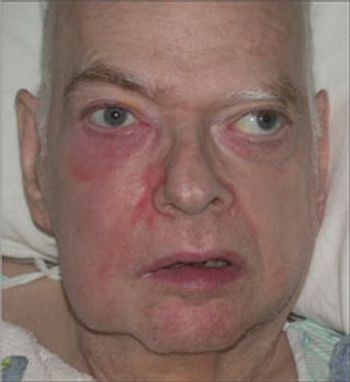
A 76-year-old man is seen because of redness below the right eye. Has long-standing “lazy eye” on the left, which is chronically deviated outward. Has lived in nursing home for some years due to self-care deficit from memory loss. No recent eye surgery, conjunctivitis, sinus infection, or periocular trauma.

Infective endocarditis (IE) starts as a vegetation on the valvular structures. The infection can extend to the adjacent periannular areas and erode into nearby cardiac chambers, leading to an aorto-cavitary fistula (ACF).1,2

Ebola virus and Marburg virus are responsible for Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF) and Marburg hemorrhagic fever (MHF), respectively.

Microbes collect on fabric, objects, and surfaces in the hospital environment, but what role do they play in disease transmission, and how can a more sterile environment be maintained? The current findings sometimes leave us with more questions than answers. Food for thought was presented at a poster session that focused on nosocomial infections and environmental contamination at the joint 48th Annual Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy and the Infectious Diseases Society of America 46th Annual Meeting, which convened October 25-28, 2008, in Washington, DC.

Delusional parasitosis and factitious disorder are psychiatric illnesses that are often encountered by clinicians. The differential diagnosis can be tricky, but treatment, which may include referral to a mental health specialist, may be trickier.

Ninety percent of adult cases of encephalitis are caused by herpes simplex virus (HSV) type 1, and HSV type 2 encephalitis is clinically indistinguishable from HSV-1 encephalitis.

Vaccination rates in adults are lower than those in children, but the consequences of lack of immunization in adults are just as significant. Barriers to adult immunization include patients’ lack of knowledge or misconceptions about vaccines and health care providers’ failure to recommend vaccination.1

The CDC recommends that sexually active adolescent girls be screened for Chlamydia trachomatis infection at least annually and that all sexually active women aged 20 to 25 years and women aged 25 years or older who have risk factors also receive an annual screening.1 How well are these screening practices being observed and what are the implications?

Emphysematous pyelonephritis (EPN) is a rare but life-threatening infection characterized by widespread necrosis and production of gas within the kidney.

A 70-year-old man was admitted with a change in mental status and shortness of breath. He had a history of carcinoma of the colon and status postcolectomy with ileostomy. He was receiving long-term total parenteral nutrition, including lipid emulsion, for short-gut syndrome. Other pertinent findings in the medical history included type 2 diabetes mellitus and enterocutaneous fistula.

Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) must be recognized now as one of the most common causes of infections acquired in the community. The majority of these infections involve the skin and soft tissue structures and confer significant morbidity on those affected.