
Clinicians often override electronic medication safety alerts, according to study findings published in the February issue of the Archives of Internal Medicine, indicating that such systems need to be more selective to be truly useful.

Clinicians often override electronic medication safety alerts, according to study findings published in the February issue of the Archives of Internal Medicine, indicating that such systems need to be more selective to be truly useful.

Adults in the United States spent more on medications for diabetes and high cholesterol and other metabolic disorders than on any other class of medications in 2006. Expenditures for metabolic agents totaled $38.1 billion, or 18.3% of total outpatient drug expenditures for noninstitutionalized adults 18 years and older. In all, outpatient drug spending totaled $208.1 billion in 2006. Expenditures for the top 5 therapeutic classes accounted for $130.8 billion, or 62.9% of total expenditures. Findings are from the ongoing Medical Expenditure Panel Survey conducted by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.

A health care reform strategy proposed by the Commonwealth Fund Commission on a High Performance Health System relies on insurance, payment, and system reforms that would purportedly improve access, enhance quality, and save $3 trillion in costs by 2020 (if undertaken by 2010). The 122-page report, titled “The Path to a High Performance US Health System,” was released last month and is available at www.commonwealthfund.org.

Although highly effective with a high benefit-to-risk ratio, highly active antiretroviral therapy has a variety of adverse effects, including metabolic, lipid, and bone toxicities. Importantly, renal toxicity has been associated with some of the more widely used agents, specifically from the NRTI and protease inhibitor classes.

The availability of highly active antiretroviral therapy has improved the survival and quality of life of patients infected with HIV. Clinicians are now focusing on the management of metabolic complications and previously unrecognized drug toxicities. The incidence and prevalence of kidney disease are increasing in older HIV-infected patients because of the widespread use of antiretroviral therapy.

In 1998, President Clinton declared HIV/AIDS to be a "severe and ongoing crisis" in the African American community and launched the

THE CASE: A 7-year-old boy has had left ankle pain for 2 days. Neither he nor his mother can recall any recent trauma to the joint. He is usually very active, but he has been unable to bear weight on the left foot and has been resting in bed. His mother reports that he had some tactile fevers, which were transiently relieved with ibuprofen, and that he has been eating and drinking normally. Despite the application of ice and elevation, the ankle has become red and swollen.
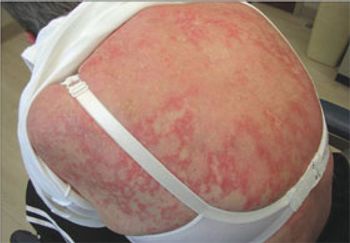
This rash erupted on the upper body of a 58-year-old woman in late August. It was mildly pruritic and nontender. The patient had not started any new medications and was not taking photosensitizing drugs. She had Sjögren syndrome; the rest of her history was noncontributory. Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (SCLE) was diagnosed. SCLE typically affects white women aged 30 to 40 years.1 It presents as nonindurated, nonscarring, erythematous plaques with or without a fine scale that may progress into a diffuse, widespread, papulosquamous or annular lesion with central hypopigmentation or telangiectasia.

A 51-year-old man is admitted to the hospital with painful ulcers on both lower extremities, severe anemia, and a 45-kg (100-lb) weight loss over the past year. Pain from the ulcers prevents him from walking. The ulcers developed about 5 years earlier, as a result of his wearing high boots for work; they began as small sores and grew over time.

An 83-year-old man examined on admission for end-of-life care due to profound dementia. His wife states that his penis has not changed in appearance, but knows that he always had concerns about it. To her knowledge he never had trouble voiding. Patient too impaired to discuss any topic coherently. Wife considers it unlikely he would have disclosed any symptom of this type to her.

Painful cracks in the fingertips are a common problem, especially during cold weather. A simple but effective remedy is to have the patient apply petroleum jelly to the crack, cover it with an adhesive bandage put on with a bit of tension, and then place a second adhesive bandage over the first at right angles for reinforcement. Instruct the patient to leave the bandages on overnight and to reapply 1 or 2 more nights if needed. If a patient’s daytime activities permit it, the bandages can also be worn during the day.

During a review of systems, I find it helpful and timesaving to ask the patient if he or she experiences symptoms that are out of the ordinary for the typical person. For example, instead of asking “Do you have fevers, chills, or night sweats?” I ask “Do you have fevers, chills, or night sweats more than the average person?” I find this approach yields more useful responses: they indicate whether the patient perceives the symptom as significant.
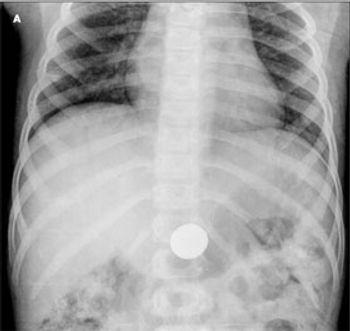
A 7-year-old girl was brought to the emergency department because of moderate pain on swallowing and mild upper abdominal discomfort. A few hours earlier, she had been given a piggy bank in order to save money for a family trip planned for the next day. On shaking the piggy bank upside down above her head, a few coins fell out. The child admitted to swallowing a coin. Physical examination findings were unremarkable. A plain abdominal radiograph showed what appeared to be 1 coin in the stomach (A)

This is the second part of a 2-part article on trends in HIV care.

Herpes simplex virus (HSV) is an enveloped double-stranded DNA virus that is a common pathogen in humans. There are 2 subtypes, HSV-1 and HSV-2,

One of the most highly discussed and publicized HIV-related presentations at the recent Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy/Infectious Diseases Society of America (ICAAC/IDSA)

A 19-year-old woman presented with shortness of breath, dry cough, and pleuritic chest pain of unknown duration. Her medical history included endometriosis, a benign ovarian cyst,

A 74-year-old woman with a history of breast cancer and cutaneous sarcoidosis was admitted after a fall from bed that resulted in a left hip fracture.

An estimated 62 million noninstitutionalized US adults 18 years and older, or approximately 30% of the adult population, have a disability that affects daily activity (Figure 1). About two-thirds (67%) of persons with basic actions difficulty (defined as difficulty with basic movement or sensory, cognitive, or emotional difficulties) are younger than 65 years, according to the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS), a CDC division.

When medical professionals think of the health consequences of obesity, we usually think of increased prevalence of coronary artery disease, stroke, some cancers, diabetes, and hypertension. If we think a bit more, osteoarthritis, gallstones, asthma, and sleep disorders come to mind.1 How many of us are aware of the connection between obesity and the increased risk of various mental illnesses and conditions?