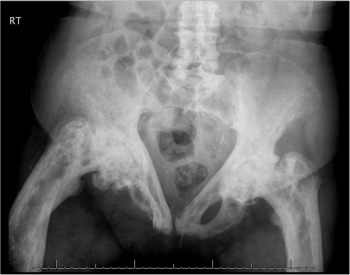
Oral etidronate, IV pamidronate, and then zoledronate caused bone markers to normalize in this 80-year-old woman-temporarily. What’s going on? Answer this and questions on 3 other topics in this week’s quiz.

Oral etidronate, IV pamidronate, and then zoledronate caused bone markers to normalize in this 80-year-old woman-temporarily. What’s going on? Answer this and questions on 3 other topics in this week’s quiz.
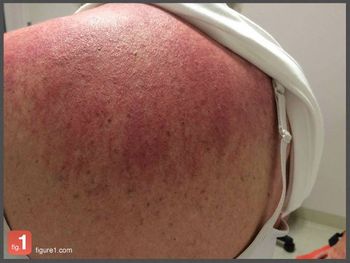
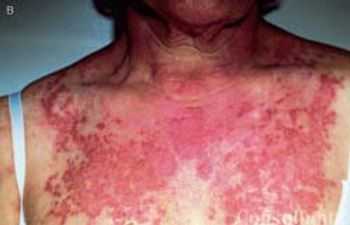
The “shawl sign” and the heliotrope rash: two skin signs that are pathognomonic of dermatomyositis. Here: a close-up look.
Polycystic ovary syndrome, “dermatoses of pregnancy,” systemic sclerosis, subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus, gallbladder agenesis, sarcoidosis-a close look at medical problems seen frequently in women.
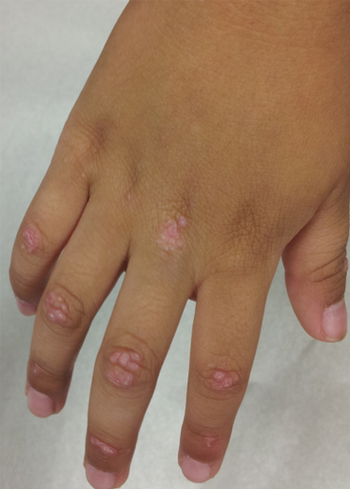
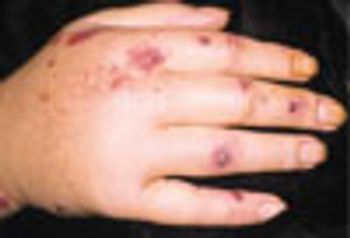
A 5-year-old boy had pain and weakness in his legs and had trouble climbing stairs. He had a dramatic rise in CPK followed by erythematous papules on the hands, as shown, and a rash around the eyelids. Which diagnosis is most likely?
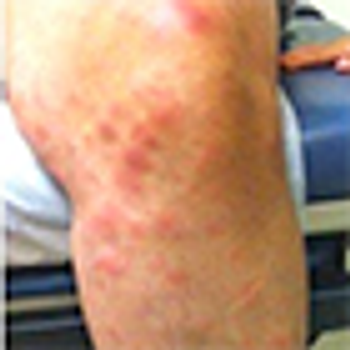
Test yourself on symptoms of Löfgren syndrome, comorbdities of Down syndrome; complications of diabetes, and more in this week’s quiz.
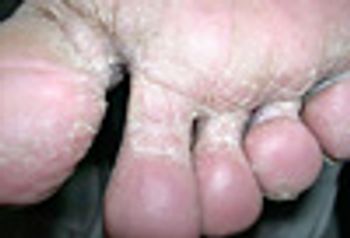
A wide range of disorders show up in the feet, and patients often turn to their primary care physician to find the diagnosis. This week's photo quiz offers several presentations to test your knowledge.

The FDA today advised physicians prescribing rituximab to screen and monitor all patients taking the drug for evidence of hepatitis B infection.
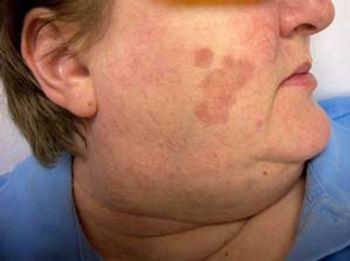
This week’s questions challenge your dermatologic and radiologic skills, and then some. See how you fare…

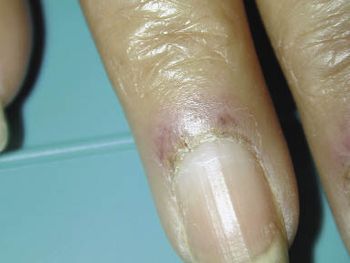
The diagnosis of juvenile dermatomyositis can be challenging when proximal muscle weakness develops without characteristic skin manifestations. In this patient, rash appeared 2 months after the onset of muscle weakness. As a result, the initial diagnosis was viral myositis, which led to delayed therapy.

Approval of a blood test that identifies the genotype of hepatitis C virus that has infected a patient can be expected to improve the effectiveness of treatment for chronic hepatitis C with new antivirals.
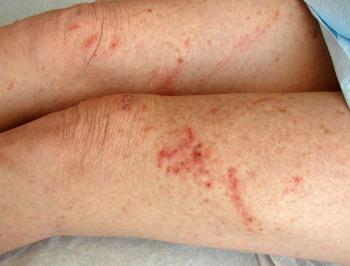
Images of acute allergic contact dermatitis, Lyme disease, southern tick–associated rash illness, tick-borne babesiosis, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, and brown recluse spider bites.
Images of guttate, small-plaque, and chronic plaque psoriasis; systemic lupus erythematosus; pityriasis rubra pilaris; and secondary syphilis.
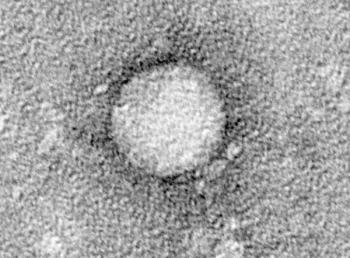
A new era in hepatitis C treatment began in May 2011, with approval of telaprevir and boceprevir. They are effective only for some patients, but new and better options are well on their way to the clinic.
See clinical features of rheumatologic diseases including rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis, psoriatic arthritis, scleroderma

Much like HIV/AIDS, RA is associated with a higher risk of cardiovascular disease and consequent death. How might inflammation add to the risk?
Does this look like melanoma? Which is not true of Löfgren syndrome? Yoga and Afib; what cause of mental confusion? Skin lesions and HIV.. . . See if you can answer this week's quiz questions.
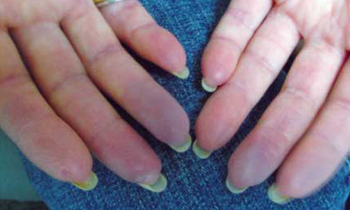
Edema of the hands has numerous etiologies: leukocytoclastic vasculitis, puffy hands from HCV infection, DVT, lymphedema, trauma

Löfgren syndrome is a form of acute sarcoidosis characterized by a triad of symptoms: hilar adenopathy, erythema nodosum, and arthralgias.

About 70% of patients with gout are treated exclusively in the primary care setting. Because the prevalence of gout is rising, particularly among older patients, you are increasingly likely to encounter this disease in your practice.

In the third podcast in this 3-part series, Dr Lieberman describes the options for treatment of an acute flare and for long-term urate-lowering therapy. The first step is lifestyle modification, and he discusses the challenges of motivating patients to institute and adhere to dietary changes.

The gold standard for diagnosis is joint aspiration and synovial fluid analysis; however, compensated polarized light microscopy is not available in most primary care practices. In part 2 of his 3-part podcast, Dr Lieberman discusses the diagnosis of gout in real-world practice.

Gout is a primary care disease. About 70% of patients with gout are treated exclusively in the primary care setting. And because the prevalence of gout is increasing, particularly in older patients, you are increasingly likely to encounter this disease in your practice.

How effective is antimalarial therapy in patients with lupus?

How effective is antibiotic therapy for long-standing reactive arthritis?

How safe and effective is combination therapy for rheumatoid arthritis?