Articles by D. Papaioannides, MD
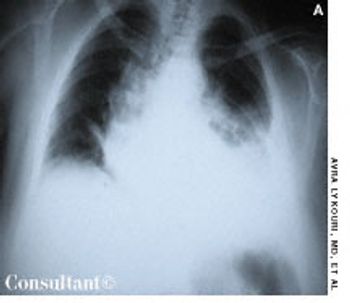
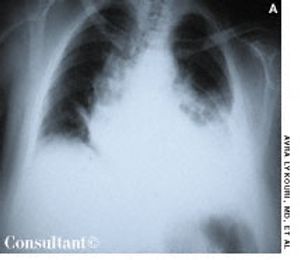
Traumatic hemothorax usually results from penetrating or contused thoracic injuries that lead to rib fracture and damage of intercostal or pulmonary vessels. Hemorrhagic shock can occur with massive blood loss into the pleural space. The shock state may be exacerbated by decreased venous return.
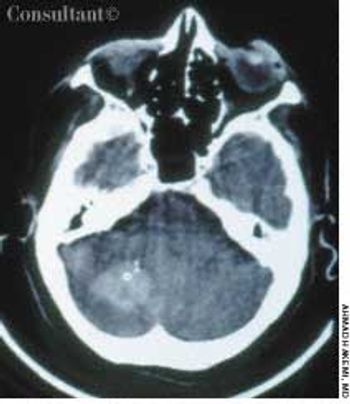
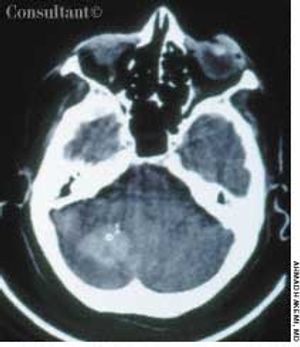
A 65-year-old woman with a long history of hypertension treated with metoprolol and felodipine complained of dizziness, headache, nausea, and vomiting of acute onset. Her blood pressure was 220/110 mm Hg. She was drowsy and unable to stand or walk.
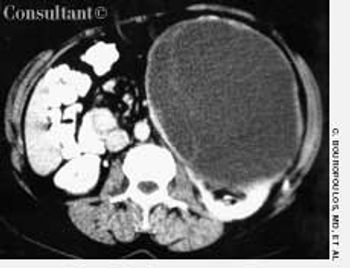
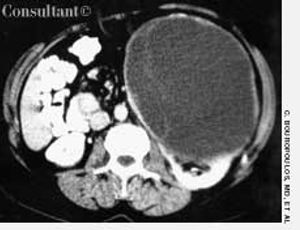
A 43-year-old woman was admitted to the hospital with left flank pain. The physical examination revealed a left abdominal mass. Laboratory test results identified normochromic-normocytic anemia (hematocrit, 33%; hemoglobin, 10.8 g/dL; and mean corpuscular volume, 88 fL) and microscopic hematuria (10 red blood cells per high-power field).

A 65-year-old woman experienced dyspnea, dizziness, and left pleuritic pain several hours after falling down a flight of stairs. Shallow breathing and increased tenderness of the left thoracic wall were evident with palpation. Decreased breath sounds on the left and dullness on percussion were also noted.