
Extraintestinal manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease affect the musculoskeletal, dermatologic, ocular, renal and pulmonary systems.

Extraintestinal manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease affect the musculoskeletal, dermatologic, ocular, renal and pulmonary systems.

They are similar chronic inflammatory diseases with causes unknown, and recent clinical and genetic evidence supports an intertwined pathogenic relationship.

Patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease typically don’t receive preventive services at the same rate as general medical patients. Vaccination is a key area of confusion.

(AUDIO) According to the Centers for Disease Control, more than one-third of US adults are obese. The CDC also estimates that as many as 1.4 million Americans suffer from inflammatory bowel disorder. So is there a link?
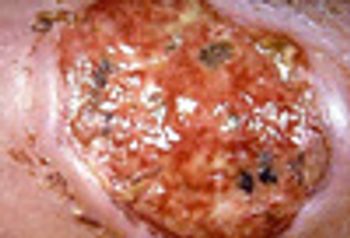
The location (pretibial surface) of this ulcer, its visibly rolled undermined border, and severe pain are all typical of pyoderma gangrenosum, which is typically associated with inflammatory bowel disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and hematologic malignancies.

Is the increased risk of IBD due to pollution, a too-clean home, or antibiotics? Or none of the above?

An association between non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and these two inflammatory bowel disorders has long been suspected but not, until now, documented.
Patients with IBD may have discomfort for 3 to 5 years before a diagnosis is made. Many are treated unsuccessfully with antibiotics, anti-spasmodics, or narcotics. Here, read 5 important tips, plus a bonus point, to help streamline diagnosis and management.

Like other chronic inflammatory conditions, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) has been revolutionized by the advent of biologic agents that fundamentally alter the inappropriate inflammatory response. The most potent of these are the biologic agents, infliximab, adalimumab, certolizumab pegol, and natalizumab. They also have the most dangerous side-effect profile.

Are persons with asthma at risk for other proinflammatory disorders? Yes, say researchers from the Mayo Clinic and Olmsted Medical Center in Rochester, Minn, who found that asthma is associated with the development of diabetes mellitus and coronary artery disease. However, there was no association between asthma and rheumatoid arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease.

A diet high in fats and protein increases the risk of developing ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease, researchers found. Hou and colleagues performed a systematic review to evaluate the association between diet and risk of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)

Despite a lower prevalence of traditional risk factors-such as hypertension and diabetes-patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) have a higher incidence of stroke, said researchers at the University of Miami.

Does upper endoscopy affect the diagnosis or management of adults with colitis? No, say investigators from Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles, although the procedure is routinely performed in children with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) of the colon.

Quality of life in children and adolescents with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a key focus of research presented at the 2010 Advances in IBD conference in Hollywood, Florida. Two of the top abstracts address social isolation and patient adherence to medication regimens among teenagers with IBD.

More than 1000 clinicians and researchers from all over the world will gather in Hollywood, Florida, this week for the 2010 Advances in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation’s Conference. The featured speaker is Jean-Frederic Colombel, MD, Professor of Hepatogastroenterology at Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Lille, France, who will discuss management strategies to improve the quality of care of patients with IBD.

Certain patients with inflammatory bowel disease are at heightened risk for the development of colorectal cancer. But researchers have not yet been able to discover markers that can identify these patients.

In this engaging session, 5 patients with complex and difficult cases of ulcerative colitis were presented to an expert panel, which consisted of Maria Abreu, MD, Edward Loftus, MD, and David Rubin, MD. The panel moderator was Jean-Paul Achkar, MD.

A 19-year-old woman presented with shortness of breath, dry cough, and pleuritic chest pain of unknown duration. Her medical history included endometriosis, a benign ovarian cyst,

A 35-year-old woman presented to the emergency department (ED) with vague abdominal complaints. The patient had a complex medical history that included diverticulosis and relapsing polychondritis. Initially, her polychondritis was limited to involvement of the ears and nose. Within the past few years, however, her polychondritis flares had been associated with progressive dyspnea, which prompted intermittent and then long-term use of high-dose oral corticosteroids.

Traveler's diarrhea (TD) occurs in persons traveling fromindustrialized countries to less developed regions of the world.Because of the growing ease of travel and an increasinglyglobalized economy, TD is becoming more common. Increasingantibiotic resistance among causative bacterial organisms andalso emergence of new pathogens are additional challenges inthe management of TD. Enterotoxigenic and enteroaggregativepathotypes of Escherichia coli are the principal causes of TD.This review discusses the epidemiology of these pathogens, aswell as elements of prevention, diagnosis, and management.[Infect Med. 2008;25:264-276]

MILWAUKEE -- A Clostridium difficile infection sharply increases the risk of death for patients with underlying inflammatory bowel disease, researchers here said.

abstract: Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) can have a variety of extraintestinal manifestations, including pulmonary disease. Bronchial involvement is the most common, but other manifestations include upper airway disease; parenchymal involvement, such as bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia (BOOP) and interstitial lung disease; and serositis, including pleural effusions and pericarditis. Patients with BOOP may present with fever, dyspnea, cough, and pleuritic chest pain. Chest radiographs show bilateral patchy airspace opacities or a diffuse process; CT scans often demonstrate the opacities to be pleural-based. Corticosteroids appear to be effective in the management of certain pulmonary manifestations of IBD, such as BOOP and pulmonary infiltrates with eosinophilia. (J Respir Dis. 2007;28(6):227-234)

ABSTRACT: Screening options for colorectal cancer (CRC) include colonoscopy every 10 years, annual fecal occult blood testing, flexible sigmoidoscopy every 5 years, or double contrast barium enema every 5 years. In white patients at average risk, screening should begin at age 50; in African American patients, at age 45. Colonoscopy is preferred to sigmoidoscopy because it can detect proximal neoplasms and has the longest protection interval. High-risk patients include those with a family history of CRC or adenomas. These persons should begin colonoscopic screening at age 40, or 10 years earlier than the age at which CRC or adenomas were diagnosed in a first-degree relative. Other high-risk patients are those with a personal history of CRC, a genetic syndrome, or inflammatory bowel disease. In patients with CRC, the first follow-up colonoscopy is performed 1 year after surgery. If results are normal, the interval can be extended to every 3 years.

As the population ages, physicians are seeing a greaternumber of patients with colorectal disorders. This book combinesan up-to-date survey of the latest basic and clinicalresearch in the field with practical advice for the day-to-daycare of patients with colonic diseases. The first section ofthe book covers current knowledge of normal colorectal physiology.Section 2 discusses the basic disease mechanismsinvolved in colonic disorders and reviews the uses of suchinvestigational tools as colonoscopy, colonic biopsy, anorectalmanometry, ultrasonography, motility measurement,defecography, CT, and MRI. The third section offers a fulldiscussion of the diagnosis and treatment of commoncolonic disorders, including colorectal neoplasia, inflammatorybowel disease, ulcerative colitis, diverticular disease,Crohn disease, constipation, and irritable bowel syndrome.In addition to currently recommended approaches to evaluationand treatment, chapters in this section include discussionof advanced and investigational therapies.

A 40-year-old man has had discomfort at the distal end of thefingers of both hands for several weeks. He has also noticed nail pitting andonycholysis. He denies any trauma or inciting event and has been otherwisehealthy. He has no family history of inflammatory bowel disease, althoughhe believes that some family members have had rashes.