
17-Year-old girl with a 7-month history of small, red papules on her arms and thighs. Rash is not painful or itchy. Otherwise in good health.

17-Year-old girl with a 7-month history of small, red papules on her arms and thighs. Rash is not painful or itchy. Otherwise in good health.

A 16-year-old boy with asymptomatic, hyperpigmented, hairy lesion on his left upper back. The pigmentation, first noted 5 years earlier, had progressively spread across his torso. The coarse and dark hair confined to the hyperpigmented area had appeared at age 13 years. Medical history uneventful. Review of systems showed no abnormalities. No family history of similar skin lesions.
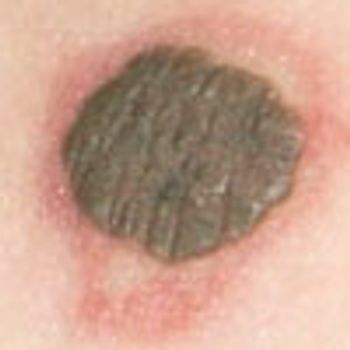
This darkly pigmented lesion on the left arm of a 27-year-old man had been present since birth and had slowly enlarged over the past 2 months. Two days earlier, another physician had diagnosed a wart and treated the lesion with liquid nitrogen, which caused erythema of the surrounding skin.

A 50-year-old woman had a 6-month history of severe generalized itchiness and fatigability. There was no associated fever, abdominal pain, or joint pain. A cholecystectomy had been performed 20 years earlier. She had no family history of hypercholesterolemia or liver disease.

A 52-year-old man presented with asymptomatic papules on his scrotum. The lesions had first appeared 1 year earlier. He had not sustained local trauma to the scrotum, and his medical history was unremarkable. There was no family history of similar skin lesions.

A 45-year-old man sought medical advice after suffering for 6 months with recurrent pain and a purulent discharge at the sacrococcygeal region. Two weeks before this consultation, an abscess on the patient's right buttock had been drained by another physician. The patient had type 1 diabetes mellitus for 5 years; his medical history was otherwise unremarkable.

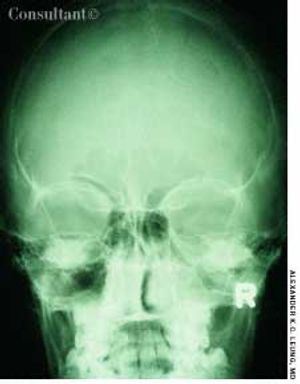
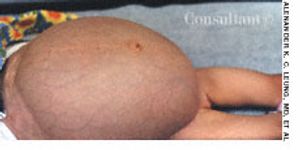
The parents of this 5-month-old boy were concerned that his eyes wereturned in toward the nose. The infant was otherwise healthy. Physical findingswere normal. In particular, when a light source was projected onto theeyes, the light reflex was centered in both eyes.
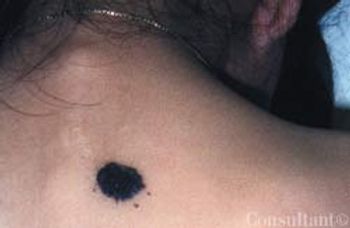
This black lesion had been present on the upper back of a 5-year-old girl since birth. The lesion had gradually enlarged to its current size of 1.5 cm. In the past year, 3 satellite black macules had developed in the surrounding area.
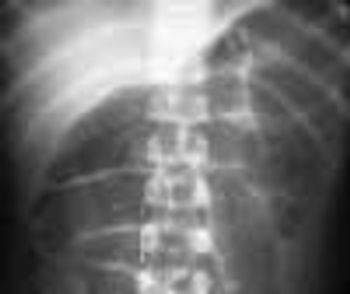
This obstruction is caused by a failure of intestinal peristalsis; there is no evidence of mechanical obstruction. Paralytic ileus is common after abdominal surgery, especially if anticholinergic drugs are given preoperatively and/or narcotics are used postoperatively. It usually lasts 2 to 3 days. Paralytic ileus may also be caused by peritonitis; ischemia or surgical manipulation of the bowel; retroperitoneal hemorrhage; spinal fracture; systemic sepsis; shock; hypokalemia; uremia; pharmacologic agents (eg, vincristine, loperamide, and calcium channel blockers); diabetic ketoacidosis; and myxedema.
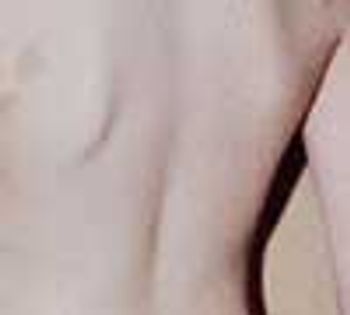
These are hyperpigmented, regularly bordered, sharply demarcated macules that are usually tan or light brown in whites and dark brown in dark-skinned persons. The lesions are characterized by an increased number of melanocytes and an increased amount of melanin in the epidermis.
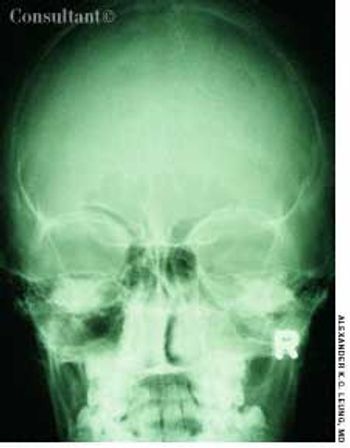
A 10-year-old boy had a headache, fever, cough, and nasal discharge for 2 days. His temperature was 38°C (100.4°F). Mucopurulent, yellow nasal discharge, fetid breath, and tenderness over the maxillary area were noted.
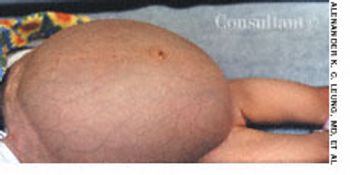
This 8-month-old girl presented with chronic constipation, which had begun during the neonatal period. She had her first bowel movement at 72 hours of age. Since then, she has had bowel movements once every 3 to 4 days. Her stools are pelletlike. Results of thyroid function tests done when she was a neonate were normal.
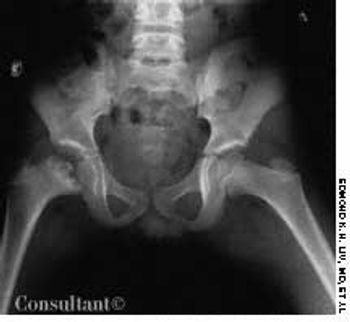
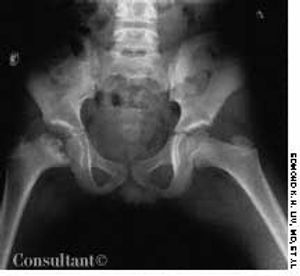
A 10-year-old boy presented with a limp and occasional pain in the right knee of 2 years' duration. A roentgenogram of the pelvis revealed fragmentation of the right capital femoral epiphysis with an irregular acetabulum.

This 8-year-old girl presented with bilateral ptosis, down-slanting palpebral fissures, malar hypoplasia, mild micrognathia, and mild webbing of the neck. She also had marked lumbar lordosis and a dextroconvex thoracic scoliosis with scapular winging. There was a generalized reduction in muscle mass with proximal limb weakness, short stature, diminished deep tendon reflexes, and an awkward waddling gait.
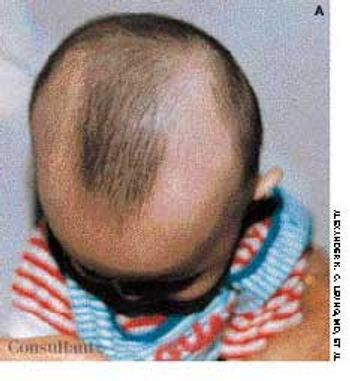
Concerned about their son's progressive hair loss during the last 6 months, his parents brought the 2-year-old into the office. The clinical appearance of hair loss extending in a band configuration around the temporal-occipital scalp margin confirmed the diagnosis of ophiasis.
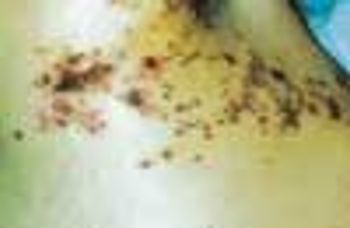
Ten days before presenting for evaluation, a 69-year-old man began to experience neuralgic pain and noticed the eruption of painful erythematous macules and papules on the right side of his chest. Within 24 to 72 hours, vesicles and pustules arose at the site. One week after onset, several of the lesions dried and crusted.
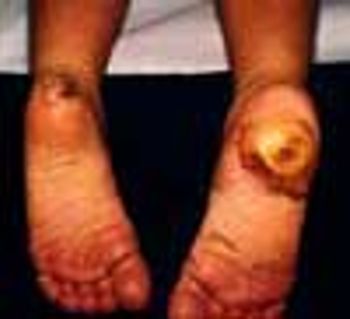
A 6-year-old girl presented with a huge ulcer on her right heel, seen here, that began as a minor laceration when she stepped on a rock several months earlier. On the left heel, there was a similar lesion in the process of healing that had also followed a minor injury. Her feet and hands were dry and hyperkeratotic.
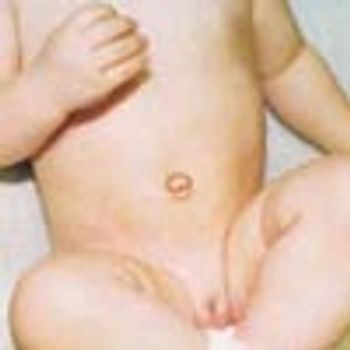
A 3-month-old female infant presented with a mass in the umbilical area. During the neonatal period, an infection of the umbilical cord had resulted in the formation of exuberant granulation tissue at the base of the umbilicus.
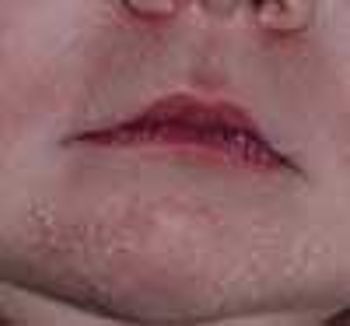
The whitish lesions on the nose and chin of this neonate are milia-tiny keratinous inclusion cysts that occur mainly on and around the nose.

This condition involves the invagination of a proximal segment of bowel (the intussusceptum) into a more distal segment (the intussuscipiens). It occurs most frequently in infants between the ages of 5 and 12 months and is a leading cause of intestinal obstruction in children aged 2 months to 5 years. Intrauterine intussusception is associated with the development of intestinal atresia. The male to female ratio is approximately 3:2. Intussusception is slightly more common in white than in black children and is often seen in children with cystic fibrosis.
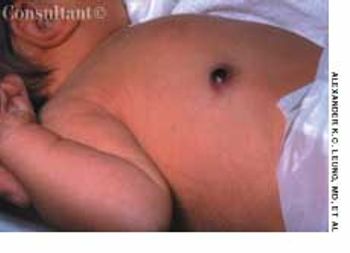
A male infant was born to a 29-year-old woman (gravida 3, para 2), following an uncomplicated pregnancy and normal vaginal delivery. At birth, a brownish 1-cm nodule was noted on the right side of the upper abdomen. The infant was otherwise healthy.
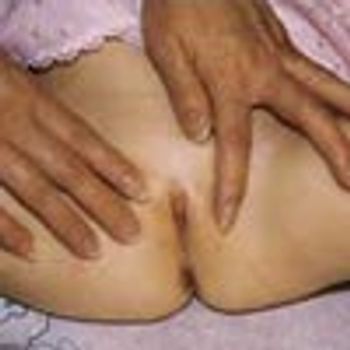
A 2-year-old girl presented with a 2-day history of urinary frequency and dysuria. Physical examination revealed complete fusion of the labia minora. Urine culture showed Escherichia coli with a colony count of 108/L. The child was treated with a 10-day course of amoxicillin that resulted in complete clearance of the urinary tract infection.

Two years ago, Dr Alexander K. C. Leung reported on a case of pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism. The patient was a 13-year-old girl with short stature, short fourth metacarpals and metatarsals, mild mental retardation, and no identifiable biochemical abnormalities.
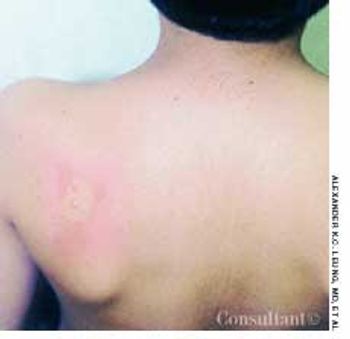
A 6-year-old boy had a nonpruritic rash on his back for 10 days. There was no associated fever. The child's mother had placed a bandage over the lesions to prevent transmission to her other children.
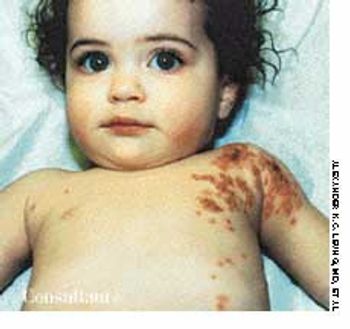
Five days before this 1-year-old girl was brought to her doctor's office, a rash had developed on her left shoulder and the left side of her chest. The abrupt onset of a high fever (temperature, 41°C [105.8°F]) and irritability accompanied the outbreak of the rash. The child had a history of asthma and eczema.
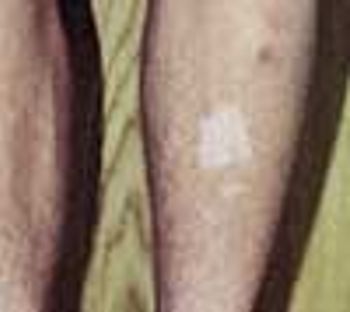
This 14-year-old boy presented with slowly progressive hypopigmented lesions that had been present on the lower extremities for the previous 2 years.
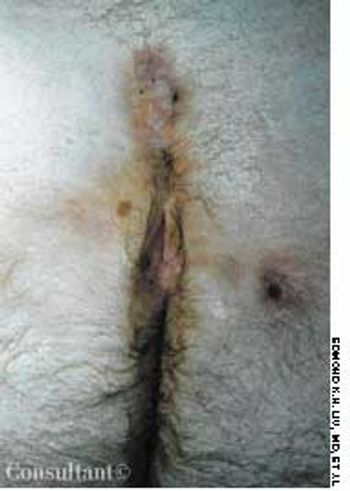
A 45-year-old man sought medical advice after suffering for 6 months with recurrent pain and a purulent discharge at the sacrococcygeal region. Two weeks before this consultation, an abscess on the patient's right buttock had been drained by another physician. The patient had insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus for 5 years; his medical history was otherwise unremarkable.

This disorder occurs in fetal development, when the midgut supplied by the superior mesenteric artery grows too rapidly to be accommodated in the abdominal cavity. Prolapse into the umbilical cord occurs around the sixth week of gestation. Between the tenth and eleventh weeks, the midgut retracts from its location at the exocelomic umbilical stalk back into the abdominal cavity. During this return, the midgut undergoes a 270-degree counterclockwise rotation about the axis of the superior mesenteric artery, followed by fixation to the posterior abdominal wall. Malrotation results from failure of the midgut to properly rotate and affix itself to this wall. This disorder occurs approximately once in 500 live births.
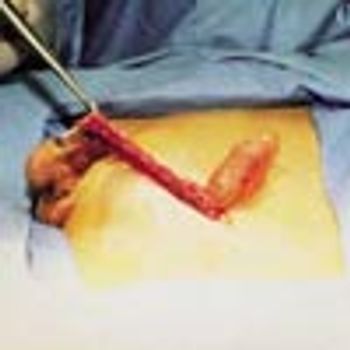
A 12-year-old boy was brought to his physician because of a tensely cystic mass in the right side of the scrotum. The spermatic cord could be felt above and below the lump. It had no cough impulse.

After 3 months of seeing this painless mass at the angle of the 3-year-old's left jaw, his parents sought medical advice for their son. The youngster had no constitutional symptoms. A Mantoux test was performed, and an erythematous, indurated area measuring 15 mm in diameter was found at the test site 48 hours later.

Published: March 1st 2005 | Updated:
Published: September 14th 2005 | Updated:
Published: September 14th 2005 | Updated:
Published: September 14th 2005 | Updated:
Published: September 14th 2005 | Updated:
Published: September 14th 2005 | Updated: