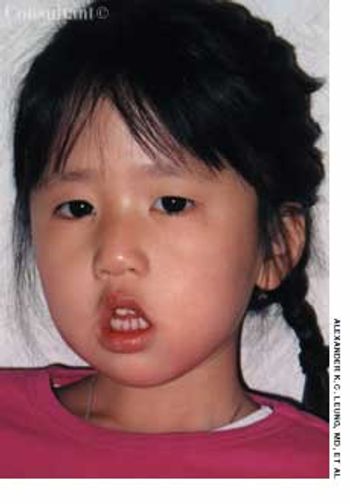
Concerned parents sought evaluation of their 3-year-old daughter, whose developmental milestones were somewhat delayed. The child sat without support at 10 months of age and walked at 17 months of age.

Concerned parents sought evaluation of their 3-year-old daughter, whose developmental milestones were somewhat delayed. The child sat without support at 10 months of age and walked at 17 months of age.
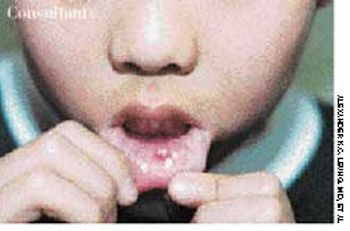
This 6-year-old child presented with a painless mass on his lower lip. The mass had increased in size slowly during the previous 2 months.
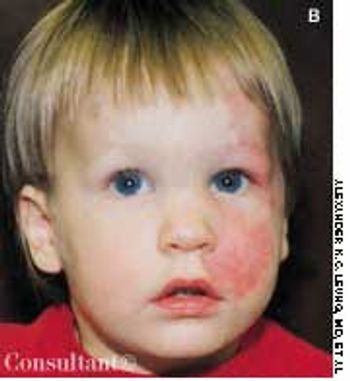
These lesions are always present at birth. They consist of mature dilated capillaries and represent a permanent developmental defect. They are red to purple, macular, and sharply circumscribed. They are usually unilateral and may occur anywhere on the body, although they tend to favor the face. Unlike salmon patches, port-wine stains do not fade; in fact, they tend to darken and become nodular with age.
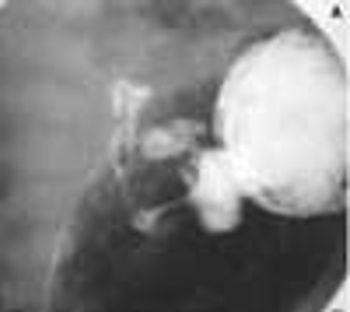
This obstruction results from hypertrophy of the circular and longitudinal muscularis of the pylorus and the distal antrum of the stomach. It occurs in approximately 3 of every 1000 live births and is 4 times more common in boys. Pyloric stenosis (PS) is relatively uncommon in African American and Asian infants. The observation that it occurs primarily in first-born infants has been disputed.

A 13-year-old girl was notably short and had short fourth metacarpals and metatarsals. She was very mildly mentally retarded.
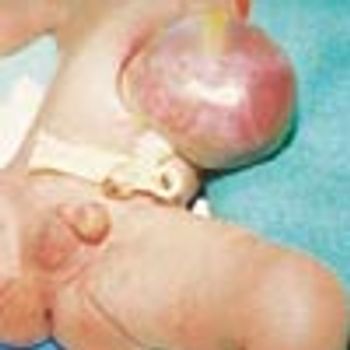
A mass covered by a translucent membrane was found in the umbilical area of an infant born by cesarean section at 38 weeks' gestation to a 26-year-old gravida 3 para 2 mother.
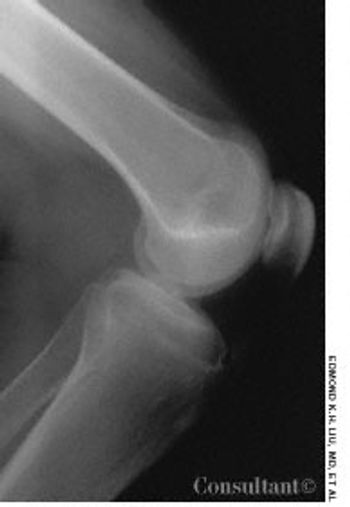
For the past 3 years, a 17-year-old boy had experienced intermittent pain in the right knee. The pain worsened when he went up and down stairs, ran, jumped, or knelt.
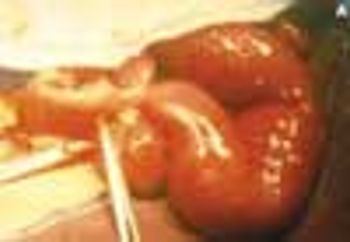
This condition is characterized by a localized narrowing of the jejunum without a disruption of continuity or defect in the mesentery. At the stenotic site, there is often a short, narrow segment with a minute lumen where the muscularis is irregular and the submucosa is thickened. The resultant intestinal obstruction is incomplete.
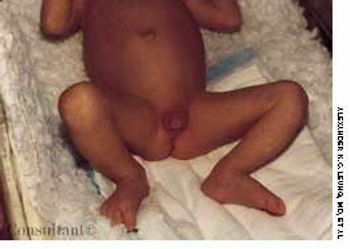
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is an autosomal recessive disorder. Deficiency of 21-hydroxylase accounts for 95% of all cases.
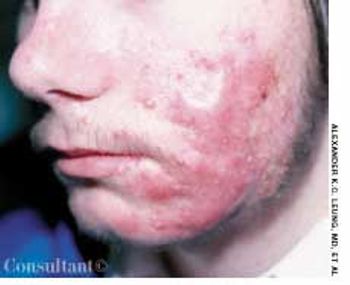
For the past 3 years, comedones, papules, pustules, and nodules had been erupting on the face of a 16-year-old boy. Acne vulgaris had been diagnosed. Topical tetracycline cream and oral tetracycline were used without success.
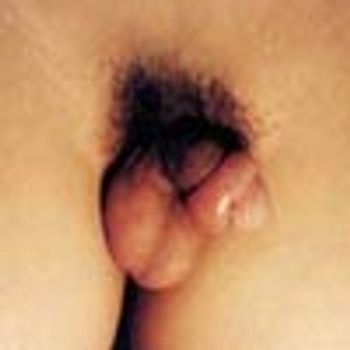
A painful, swollen penis was the presenting complaint of an 11-year-old boy. The swelling erupted 1 to 2 hours before the photograph was taken, when the child had attempted to retract the foreskin.
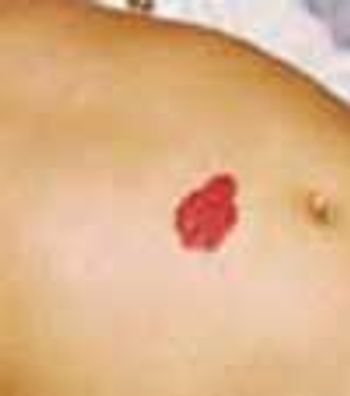
A 6-month-old girl presented with a reddish mass on the abdomen that was not apparent at birth and was first noted when the child was 1 month old. The lesion-which was asymptomatic-started to shrink and fade when the child was 3 years old. A year later, the color was very faint. When the child was 6 years old, the lesion was hardly visible.
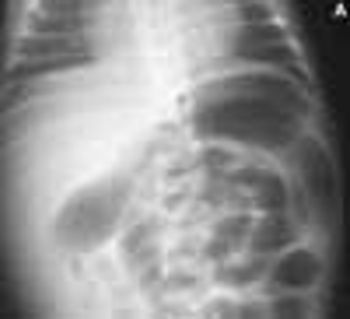
Affected infants present shortly after birth with a large bowel obstruction secondary to transient dysmotility in the descending colon. Although the cause is unknown, immaturity of the colonic myenteric plexuses has been demonstrated in some cases. More than 50% of affected infants are born to mothers with diabetes. Other predisposing factors include hypoglycemia and sepsis.
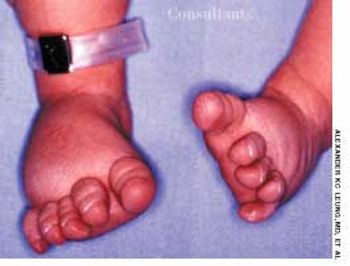
A male infant was delivered at term to a 24-year-old woman. The pregnancy had been uncomplicated; the vaginal delivery was normal. Apgar scores were 7 at 1 minute and 9 at 5 minutes. Birth weight was 3020 g (6 lb 11 oz); length, 51 cm (20 in); and head circumference, 36 cm (14 in).

This lesion consists of a dilated central feeding arteriole and smaller radiating branches that together suggest a spider's body and legs. The lesion blanches when pressure is applied. Pulsations visible in larger nevi are evidence of the arterial source of the lesion.
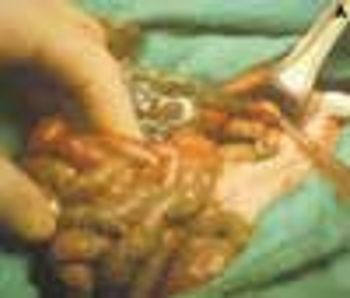
This condition, which accounts for about 30% of cases of intestinal obstruction among neonates, is characterized by the inspissation of thick, tenacious meconium in the bowel. The most common cause is cystic fibrosis; approximately 6% to 20% of infants with cystic fibrosis have meconium ileus. Hyperviscous mucus secreted by abnormal intestinal glands, an abnormal concentrating process in the proximal small intestine, and a deficiency of pancreatic enzymes have been implicated in the pathogenesis. The histologic hallmark is distention of the goblet cells in the intestinal mucosa.
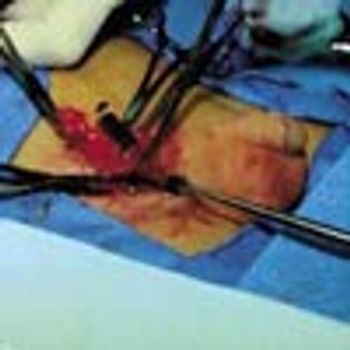
A 7-year-old boy presented with two testicles on the left side of the scrotum. The superior one was half the size of the inferior one, which measured 2 × 1 cm. The testicle on the right side measured 2 × 1 cm. Surgical exploration was done, and the atrophic left supernumerary testicle shown in the photo was removed. Biopsy specimens taken from the remaining testicle were normal.
Following an uncomplicated pregnancy, a 30-year-old gravida 2, para 1 mother delivered a term infant boy. The neonate's Apgar scores were 7 at 1 minute and 9 at 5 minutes. Birth weight was 3.2 kg (7.1 lb); length, 50 cm (19.7 in).
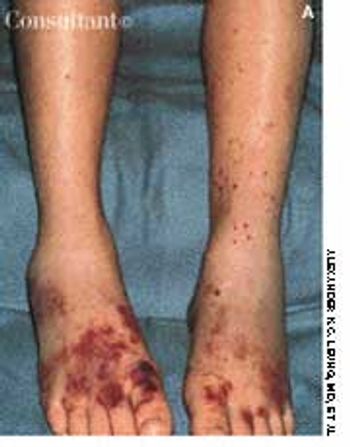
Two 7-year-olds show the purpuric rash of the lower body and legs that is typical of Henoch-Schönlein purpura. This disease is a vasculitis that chiefly affects small vessels of the skin, joints, gastrointestinal tract, and kidney.
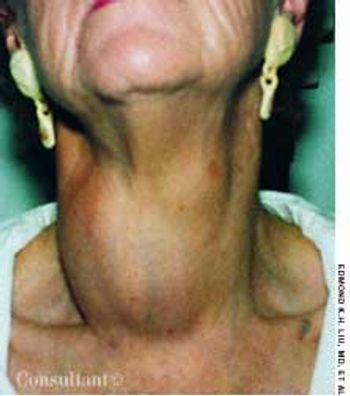
A mass in the neck of a 65-year-old woman had grown slowly and progressively during the last 5 years. The patient was otherwise asymptomatic; in particular, there was no heat or cold intolerance, irritability, weight loss, increased appetite, palpitations, lethargy, constipation, dysphagia, or dyspnea.
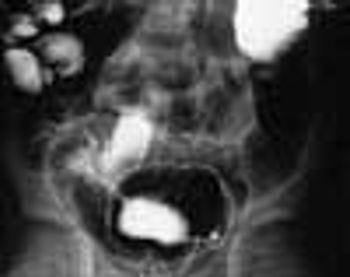
A 6-year-old boy presented with bloody diarrhea; fatigue; decreased appetite; weight loss; and occasional, mild abdominal pain for the past 2 months. The child had 6 to 8 bowel movements daily, 1 or 2 of which occurred at night.
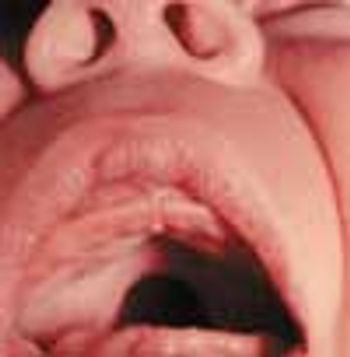
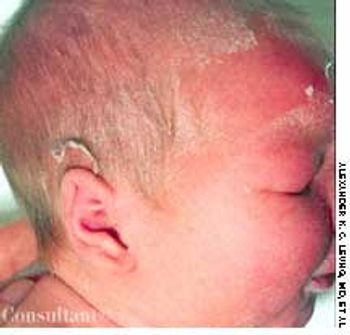
This neonate was born with a high arched and cleft palate and a small jaw-the result of Pierre Robin syndrome, an autosomal recessive disorder also characterized by micrognathia and pseudomacroglossia.
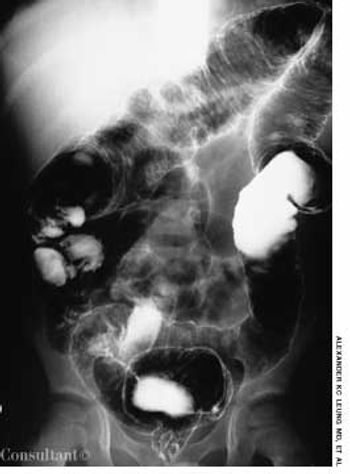
A 6-year-old boy is brought for evaluation of bloody diarrhea, fatigue, decreased appetite, weight loss, and occasional, mild abdominal pain of 2 months' duration. The child had 6 to 8 bowel movements daily, 1 or 2 of which occurred at night.
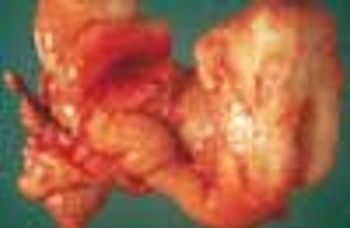
Alimentary tract duplications are uncommon. Gastric duplication accounts for only 3.8% of these duplications. The cause is not known, but faulty separation of the endoderm and notochord early in embryonal development is thought to be responsible. The anomaly occurs in twice as many female as male infants.
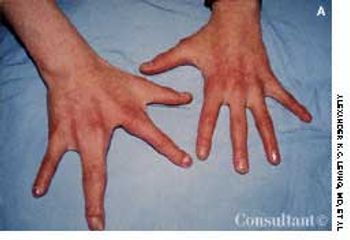
An 11-year-old girl presented with central clefting and syndactyly of the third and fourth digits of the right hand; sparse, fine blond scalp hair; sparse eyebrows; and numerous dental caries. Past health was unremarkable except that she had stenosis of the nasolacrimal ducts, which required probing when she was 1 year old. Her mother also had somewhat sparse and fine scalp hair and similar hand malformations with ridged and slow-growing nails, as well as mild conductive hearing loss.
A female infant was born vaginally to a gravida 4, para 1, 24-year-old woman at term. The child's birth weight was 2,800 g; her length was 51 cm. The mother had a history of three spontaneous abortions. The present pregnancy was complicated by threatened abortion at 15 weeks. The mother was given hydroxyprogesterone hexanoate, 500 mg IM weekly for 6 weeks.
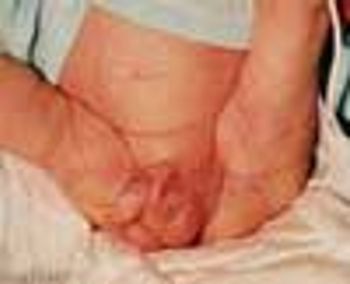
A 3120-g male infant was born to a 31-year-old gravida II para I mother at 37 weeks' gestation following an uncomplicated pregnancy. There was no history of oligohydramnios, but diminished fetal movements were noted. The infant was born vaginally with complete breech presentation and Apgar scores of 7 and 8 at 1 and 5 minutes, respectively.
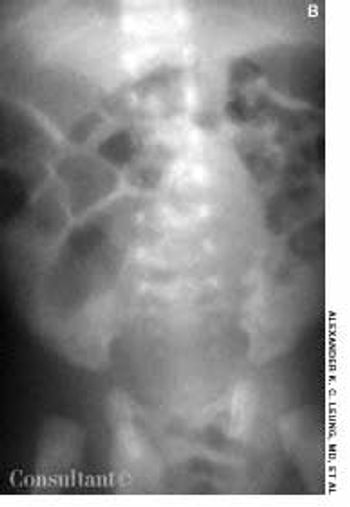
During the last few weeks of gestation or shortly after birth, the layers of the processus vaginalis normally fuse together and obliterate the entrance to the inguinal canal in the vicinity of the internal inguinal ring. An indirect hernia results from a failure of fusion of the processus vaginalis; the bowel subsequently descends through the inguinal canal.
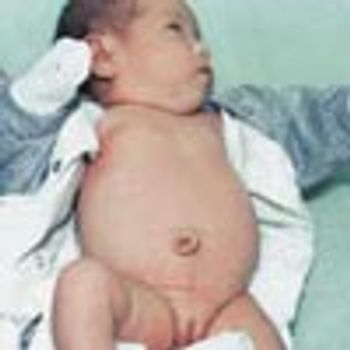
The mother of a 1-month-old infant was concerned because her child's umbilicus looked abnormal. The condition was diagnosed as umbilicus cutis.
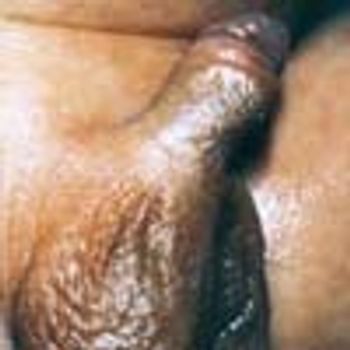
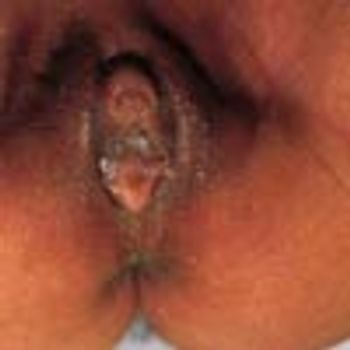
A 12-year-old boy presented with a 6-month history of a papule on the corona of the glans penis. The lesion was asymptomatic.