
An 85-year-old man with a history of hypertension, coronary artery disease, and diabetes mellitus presented with syncope. He had fallen down a flight of stairs and now complained of left shoulder pain

An 85-year-old man with a history of hypertension, coronary artery disease, and diabetes mellitus presented with syncope. He had fallen down a flight of stairs and now complained of left shoulder pain

Abstract: Shortness of breath is a common complaint associated with a number of conditions. Although the results of the history and physical examination, chest radiography, and spirometry frequently identify the diagnosis, dyspnea that remains unexplained after the initial evaluation can be problematic. A stepwise approach that focuses further testing on the most likely diagnoses is most effective in younger patients. Early bronchoprovocation challenge testing is warranted in younger patients because of the high prevalence of asthma in this population. Older patients require more complete evaluation because of their increased risk of multiple cardiopulmonary abnormalities. For patients who have multiple contributing factors or no clear diagnosis, cardiopulmonary exercise testing can help prioritize treatment and focus further evaluation. (J Respir Dis. 2006;27(1):10-24)

16-month-old previously healthy child is hospitalized after 36 hours of worsening painful edema and erythema of the right lower leg and high fever with chills.

A 76-year-old man presents with a sudden severe, painless loss of vision in his left eye.

A 45-year-old man was referred to our pulmonary clinic for progressive dyspnea and worsening asthma. His shortness of breath had been worsening over the past 2 years. He denied fever, weight loss, and other systemic complaints.

Abstract: The manifestations of indoor mold-related disease (IMRD) include irritant effects, such as conjunctivitis and rhinitis; nonspecific respiratory complaints, such as cough and wheeze; hypersensitivity pneumonitis; allergic fungal sinusitis; and mycotoxicosis. The diagnosis of IMRD depends on eliciting an accurate history and excluding preexisting pathology that would account for the patient's symptoms. Laboratory tests, imaging studies, and spirometry can play an important role in ruling out other diagnoses, such as allergic or nonallergic rhinitis, asthma, and pneumonia. The diagnosis of IMRD also involves integrating the results of immunologic, physiologic, and imaging studies with the results of indoor air-quality studies. (J Respir Dis. 2005;26(12):520-525)

Under what circumstances is endoscopy advisable for a patient with dyspepsia?

A 49-year-old man has had dyspnea on exertion for 1 month; it has worsened during the past 2 days. He has also had 2 episodes of epistaxis and increasing abdominal distention, without pain, during the past 6 months.

Chronic diarrhea presents difficulties for clinicians as well as for patients. Because the differential diagnosis is enormous, management can be challenging. In this article, we present a strategy for quickly narrowing the differential based on a simple analysis of stool characteristics. We then describe an appropriate workup for each of the basic types of diarrhea.

Up to 10% of Americans older than 20 years have type 2 diabetes, and more than 20% have the metabolic syndrome. The prevalence of both diseases has risen by 33% over the past decade as a result of an increasingly sedentary lifestyle, the obesity epidemic, the growth of ethnic groups at risk for the disease, and the aging of the population.
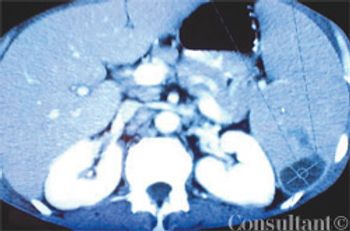
A 51-year-old man with a history of AIDS (CD4 count of 59 cells/µL), anemia, neutropenia, and AIDS-related dementia presented with persistent fever, abdominal pain, and diarrhea of 2 months' duration. He did not adhere to his regimen of HAART and prophylactic therapy with atovaquone and azithromycin.

Abstract: In addition to causing pulmonary disease, infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis can result in a wide range of extrapulmonary manifestations, including abdominal involvement. Patients with acute tuberculous peritonitis typically present with fever, weight loss, night sweats, and abdominal pain and swelling. Intestinal tuberculosis is characterized by weight loss, anorexia, and abdominal pain (usually in the right lower quadrant). A palpable abdominal mass may be present. Patients with primary hepatic tuberculosis may have a hard, nodular liver or recurrent jaundice. The workup may involve tuberculin skin testing, imaging studies, fine-needle aspiration, colonoscopy, and peritoneal biopsy. Percutaneous liver biopsy and laparoscopy are the main methods of diagnosing primary hepatic tuberculosis. Treatment includes antituberculosis drug therapy and, in some cases, surgery. (J Respir Dis. 2005;26(11):485-488)

During a laparotomy for perforated sigmoid colon diverticulitis, a 75-year-old woman was found to have extensive peritonitis. She underwent sigmoid colon resection and colostomy. Postoperatively, she recovered slowly. The peritoneal fluid grew Escherichia coli, and she was given broad-spectrum intravenous antibiotic therapy.

Read the cases of 4 patients whose chief complaint is a 2-week history of neck pain, try your hand at making a quick diagnosis, then go to the next page to read the outcome.

A cardiovascular risk reference guide, Framingham global risk assessment scoring guide, cardiovascular checklist, and cardiovascular risk-reduction treatment plan.

The growing epidemic of type 2 diabetes makes it imperative to identify persons at risk, screen for impaired glucose tolerance (IGT), and treat to prevent progression. Calculation of body mass index (BMI) is an appropriate starting point for identification of patients with possible IGT.

Cardiovascular (CV) risk-reduction regimens require comprehensive assessment, patient education, and follow-up, which can be difficult and time-consuming in a busy primary care practice. Moreover, compliance among patients at high risk can be poor. The use of evidence- based risk assessment checklists and patient education materials can enhance care and improve compliance; in addition, thorough documentation can ensure full reimbursement for services.

As many as half of patients who are evaluated for abdominal pain do not receive a precise diagnosis. And for about half of those who are given a diagnosis, the diagnosis is wrong. In this article, I will use actual cases (not "textbook" examples) to illustrate an approach to abdominal pain that begins with a careful differential diagnosis. I also offer some general guidelines for evaluating patients.
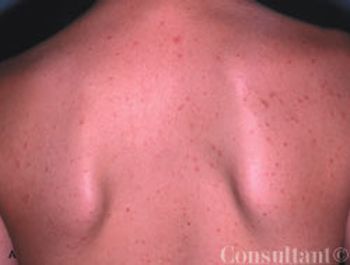
These pinpoint pustules, some with excoriations, and surrounding erythema appeared on the posterior trunk and outer arms of a 15-year-old boy after he had wrapped his upper body in a wool blanket. These lesions were occasionally pruritic, especially on the arms, where most of the excoriations were noted.

Abstract: Many patients with sarcoidosis are asymptomatic at presentation and have bilateral hilar adenopathy on a chest radiograph obtained for other reasons. Symptomatic patients usually present with chronic cough, dyspnea, or noncardiac chest pain. Extrapulmonary organ involvement is not uncommon. Lung biopsy shows well-formed noncaseating granulomas in a bronchovascular distribution. Interstitial lung disease also may result from collagen vascular disease, such as systemic lupus erythematosus and Sjögren syndrome. In patients with acute hypersensitivity pneumonitis, cough, dyspnea, and flu-like symptoms occur within 12 hours of exposure to the inciting antigen, such as pigeon stool or moldy hay. Some patients have a subacute or chronic course, probably as a result of continued exposure to the offending antigen. In acute hypersensitivity pneumonitis, the chest radiograph may show diffuse small nodules, whereas in chronic disease, reticular lines or fibrosis may be seen. (J Respir Dis. 2005;26(10):443-448)

For patients with osteoarthritis, nonpharmacologic treatment can be an effective adjunct to drug therapy. Patient education is essential; both community-based and independent self-care programs are available. Weight loss can improve function and alleviate symptoms; however, it is more effective when dietary modification is accompanied by increased physical activity.

A 4-year-old boy is admitted with a 2-week history of high fever with rigors; profuse night sweats; progressive dull, aching, nonradiating right upper quadrant pain; and watery, foul-smelling diarrhea that contains no blood or mucus.

A 24-year-old woman complains of a severe, throbbing headache that is present when she is upright and is relieved when she lies down. When she is upright, she also experiences dizziness, blurred vision, light sensitivity, nausea, and occasional diplopia.

In patients with underlying disease, a preoperative evaluation and targeted perioperative management strategies can minimize surgical complications and maximize healing. This article focuses on how to identify surgery patients at risk for complications caused by diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and other medical conditions; I also describe strategies to minimize such risk.

Skin signs of systemic disease: sarcoidosis, rheumatoid nodules, Muir-Torre syndrome, diabetic vasculopathy, hyperlipidemic nodules, zinc deficiency, and Sister Mary Joseph nodule.