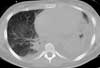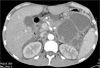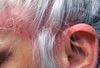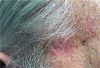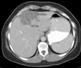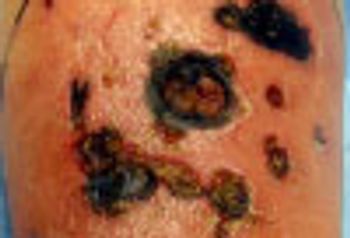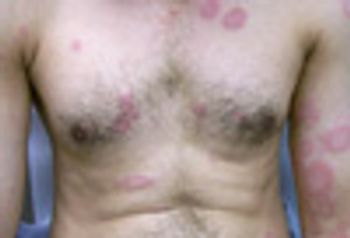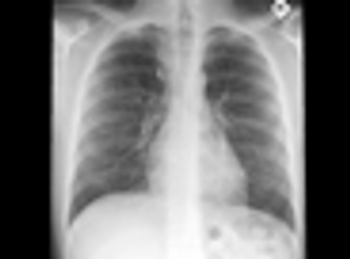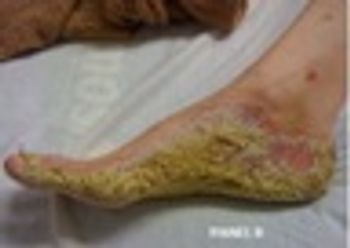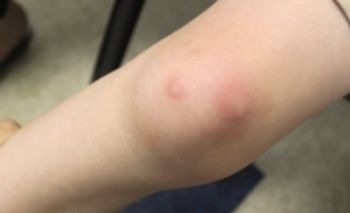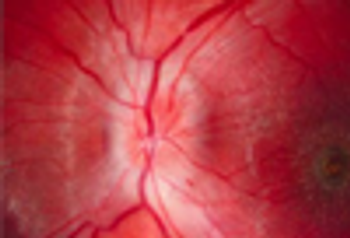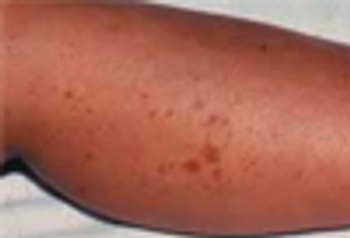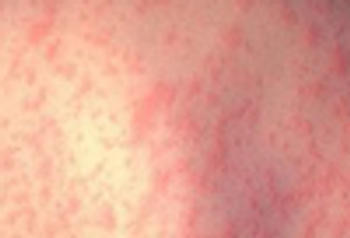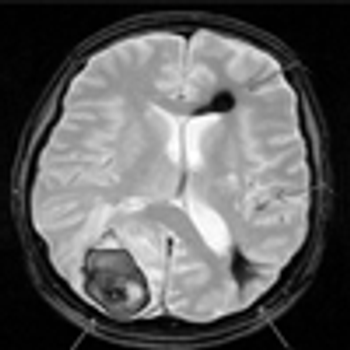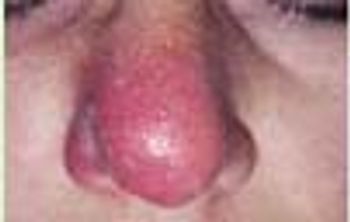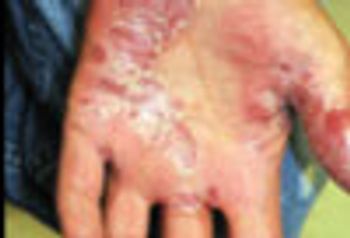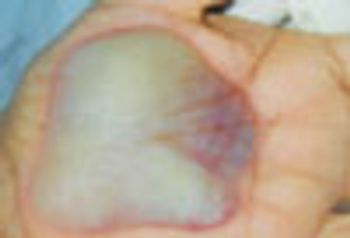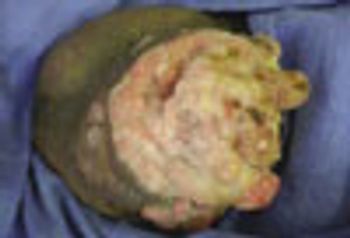
A 27 year-old woman was petting her cat, when the animal suddenly bit her on the arm. She rinsed copiously with isopropyl alcohol and applied an over-the-counter antibiotic ointment. But, 12 hours later, a large, red, swollen and exquisitely tender plaque had developed around the bite site.