The physical exam – looking into the eyes and throat, taking the blood pressure, sounding the chest – is part of the process of medical diagnosis. It's one way a physician attempts to determine the cause of a patient's complaint.

The physical exam – looking into the eyes and throat, taking the blood pressure, sounding the chest – is part of the process of medical diagnosis. It's one way a physician attempts to determine the cause of a patient's complaint.
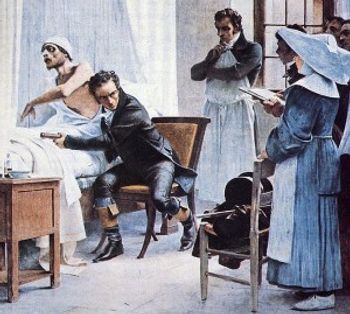
A 48-year-old man was admitted with a sore throat, subjective fever, and cough of 2 days’ duration. Two days before admission, he had dysphagia, began to drool, and felt like he was choking.
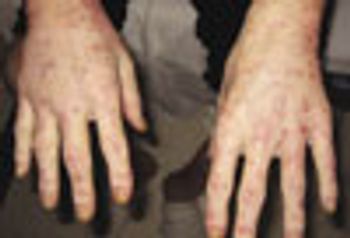
For 4 months, a 45-year-old man with a history of alcohol abuse had made multiple visits to the emergency department (ED) and a dermatology clinic for evaluation of a diffuse, scaly, and intensely pruritic rash. The rash, which was photosensitive, had started on his upper extremities and spread proximally to the trunk and lower extremities.

When counseling patients about why they should receive the influenza vaccine, I remind them that each year the disease kills 250,000 to 500,000 persons worldwide and more than 37,000 persons in the United States. This means that influenza kills more people per year than auto accidents.
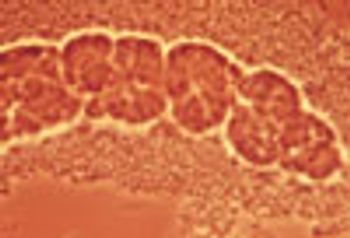
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) has become a burgeoning epidemic. Patients with various stages of CKD initially seek care from their primary care physician; some of these patients sustain acute, reversible renal injuries as well.
A 54-year-old woman presents for an initial consultation. She has multiple chronic disorders, including type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension, for which she takes various medications-none of which are new.
How best to manage ulcerative colitis? Here: highlights from guidelines from the American College of Gastroenterology on assessment, treatment, indications for surgery, and cancer surveillance.

Yes, ACE inhibitors should be used with caution in patients with acute renal injury and high-grade renal vascular lesions, but these drugs are designed to help, not hurt kidneys. Now fast forward to another caveat: avoid or discontinue statins in patients who have elevated liver enzyme levels. Get ready for a therapeutic paradigm shift.
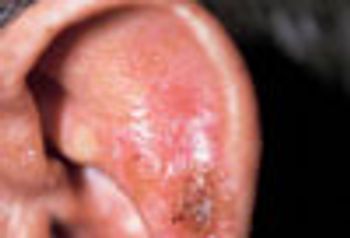
A tender, crusting eruption first arose on a 69-year-old man’s ear 10 days earlier; an antibiotic failed to clear the lesion.
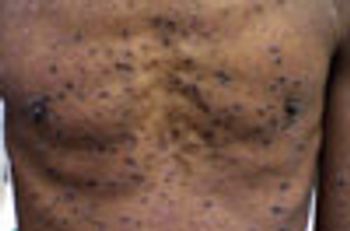
A 37-year-old man presented to the emergency department with painful, burning, blistering skin lesions. The lesions started 3 days earlier on the face and spread to the trunk and extremities. Ten days before presentation, the patient had received a diagnosis of AIDS.
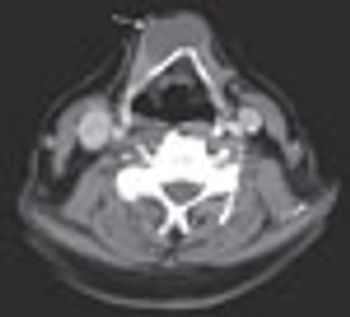
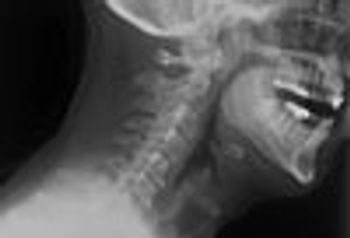
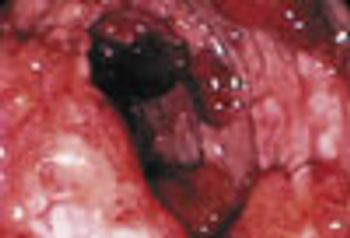
For several years, an asymptomatic mass had been growing on the neck of a 54-year-old-man. Physical examination revealed a firm, nontender mass located slightly left of midline at the level of the hyoid bone.
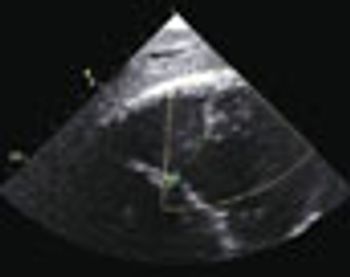
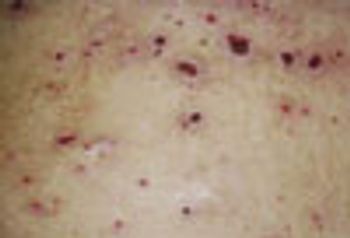
A previously healthy 55-year-old woman complained of fever, weakness, and generalized malaise for the past 3 to 4 weeks. She had been treated with ciprofloxacin, amoxicillin, and azithromycin for 21 days with no resolution of her symptoms. Five days before she was hospitalized, multiple nonspecific constitutional complaints developed.

Men who have undergone localprocedures in the genital or analarea (eg, abscess drainage) find itdifficult to get a bandage to adhereto the skin because of the pubichair.

The diagnosis of many serious infectious diseases relies heavily on clinical suspicion, particularly in the early stages of the illness. In this 3-part series, we provide useful clues to the triage and diagnosis of these diseases. Here we discuss staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome (TSS) and streptococcal TSS.

Ulcerative colitis affects about 500,000 persons in the United States and accounts for more than 30,000 hospitalizations and 1 million workdays lost each year. The exacerbations and remissions that characterize the clinical course of the disease can make its management particularly challenging. What is the optimal approach to treatment? And which agents are most effective for maintenance therapy?

The gold standard for diagnosis is joint aspiration and synovial fluid analysis; however, compensated polarized light microscopy is not available in most primary care practices. In part 2 of his 3-part podcast, Dr Lieberman discusses the diagnosis of gout in real-world practice.

Will you recognize these potentially life-threatening infections when you see them? Inside: clues to early diagnosis.
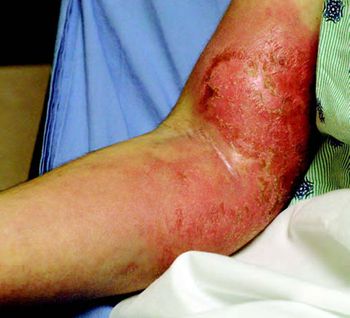
For 3 days, a 28-year-old woman with a history of polymyositis and possible dermatomyositis had fever, chills, and nonproductive cough. She complained of rash, joint pain, and progressive immobility because of severe muscle weakness. For the past 6 years, she had been taking prednisone (60 mg/d), hydroxychloroquine (200 mg bid), and tramadol (100 mg q6h prn for pain).
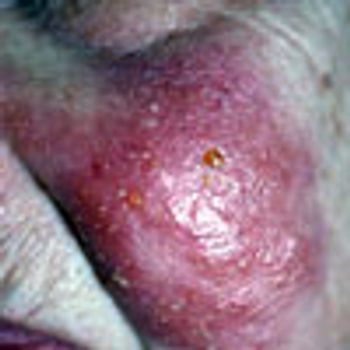
For 5 days, a 68-year-old woman has been bothered by a painful swelling on her left cheek. There is no history of trauma or bite. She takes a diuretic for mild hypertension. Amoxicillin/clavulanate was started 2 days earlier pending the results of a bacterial culture.What is the likely diagnosis?

Every year thousands of physicians must take-and pass-an examination to become board certified in internal or family medicine. Thousands more must pass a board recertification examination to maintain their license to practice medicine- and similar exams are required of physician assistants and nurse practitioners. To pass a certification or recertification examination requires up-to-date and in-depth knowledge in at least a dozen areas of clinical medicine.

Patients who followed a written action plan for exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) had shorter recovery times, reported Canadian researchers.

Turmeric, a spice used in curry, may help prevent Clostridium difficile infection. Rattan Patel, MD, of Cedars Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles, and his colleagues found that curcumin (the active ingredient in turmeric) inhibited the growth of various strains of C difficile in vitro.

In this engaging session, 5 patients with complex and difficult cases of ulcerative colitis were presented to an expert panel, which consisted of Maria Abreu, MD, Edward Loftus, MD, and David Rubin, MD. The panel moderator was Jean-Paul Achkar, MD.

In the very first episode of the TV series Marcus Welby, MD, our hero delivers an after dinner speech to a group of young interns. As he’s introduced, he hastily scribbles the title of his talk and hands it to the hospital director: "The future of the general practice of medicine, if any." The year was 1969.
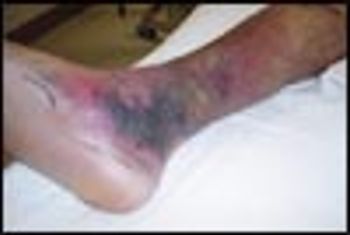
A 69-year-old man with stage II chronic kidney disease due to hypertension fell from his bicycle and presented to the emergency department (ED) with abrasions, ecchymoses, and a 3-cm laceration on his right leg. The patient was an avid cyclist. His wounds were cleaned and the laceration sutured. There were no fractures, and the patient was discharged home.