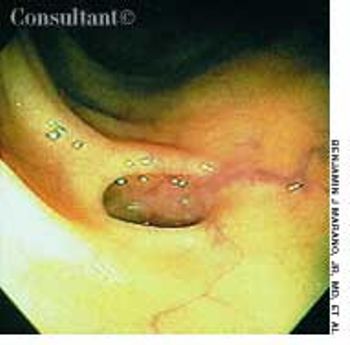
An 84-year old woman, who depends on a weekly dose of magnesium citrate to have a bowel movement, has extensive diverticulosis throughout the length of the colon.

An 84-year old woman, who depends on a weekly dose of magnesium citrate to have a bowel movement, has extensive diverticulosis throughout the length of the colon.
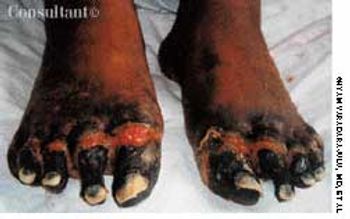
A 21-year-old man slept in a car in upstate New York for three winter nights. Discomfort and swelling of his toes developed, which progressed to marked discoloration of the digits.

A 13-year-old girl was notably short and had short fourth metacarpals and metatarsals. She was very mildly mentally retarded.

Bilateral skewfoot in a 7-year-old boy. The deformities were rigid in this child, and there was no improvement with growth.
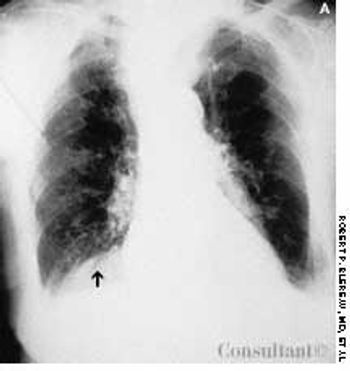
A 95-year-old woman was brought to the emergency department with hemoptysis. Erect posterior-anterior (A) and lateral (B) chest films showed a density at the base of the right lung posteriorly. A CT scan (C) revealed that the mass was the right kidney above the diaphragm and adjacent to the heart. The kidney had migrated through a foramen of Bochdalek.
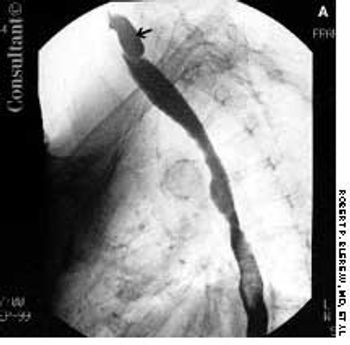
For 2 months, food particles had been regurgitating into a 72-year-old woman's throat after meals. Barium esophagography revealed a Zenker, or pharyngoesophageal, diverticulum.

A 68-year-old woman was admitted to the hospital with rapidly increasing, painful swelling of the left eye. She had moderately severe, corticosteroid-dependent chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
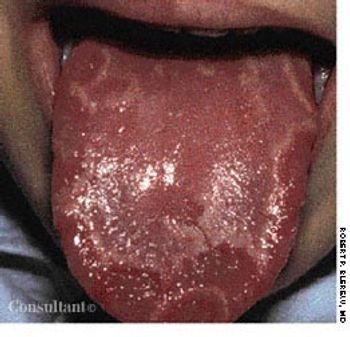
The smooth areas in the typical "mapping" of geographic tongue, shown here, represent flattened or denuded filiform papillae.

A mass covered by a translucent membrane was found in the umbilical area of an infant born by cesarean section at 38 weeks' gestation to a 26-year-old gravida 3 para 2 mother.
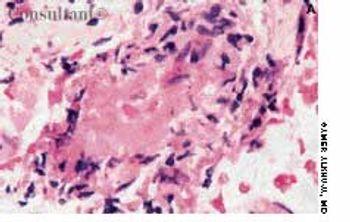
Following two witnessed tonic-clonic seizures, a 65-year-old woman with a history of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease was admitted to the hospital. Results of laboratory studies included serum creatinine level, 2 mg/dL; blood urea nitrogen level, 28 mg/dL; and erythrocyte sedimentation rate, 61 mm/h. The patient's antinuclear antibody (ANA) titer was 1:40 with a speckled pattern, and creatinine clearance was 17 mL/min. An ultrasonogram revealed bilateral small kidneys. CT and MRI of the head revealed no abnormalities.

A 49-year-old woman noticed a growing lesion near the inner corner of her left upper eyelid. The lesion had become conspicuous because of its size and color; the patient wanted it removed.
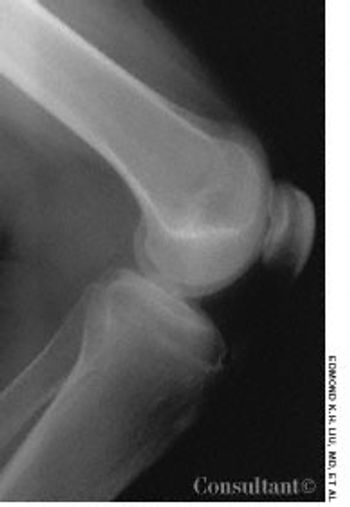
For the past 3 years, a 17-year-old boy had experienced intermittent pain in the right knee. The pain worsened when he went up and down stairs, ran, jumped, or knelt.

This newborn came into the world with a right lower canine tooth. Natal (predeciduous) teeth are present at birth, whereas neonatal teeth erupt within 30 days of birth. Both natal and neonatal teeth are generally primary teeth; they may erupt as a result of vertical displacement of tooth follicles.
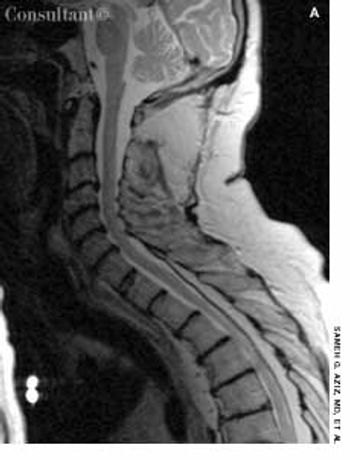
A 62-year-old man who was receiving long-term corticosteroid therapy for Wegener granulomatosis presented with progressive leg weakness over 1 week. He had the stigmata of Cushing syndrome: moon facies, truncal obesity, and a dorsocervical fat pad.
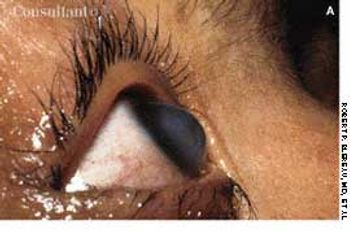
This 20-year-old woman with Down syndrome has bilateral keratoconus, a common, noninflammatory, paracentral corneal ectasia that is occasionally hereditary. Symptoms vary from none to severely blurred vision. Opacity of this patient's right cornea developed after her eye had teared excessively for 1 day, during which time she continually rubbed it.

This condition is characterized by a localized narrowing of the jejunum without a disruption of continuity or defect in the mesentery. At the stenotic site, there is often a short, narrow segment with a minute lumen where the muscularis is irregular and the submucosa is thickened. The resultant intestinal obstruction is incomplete.
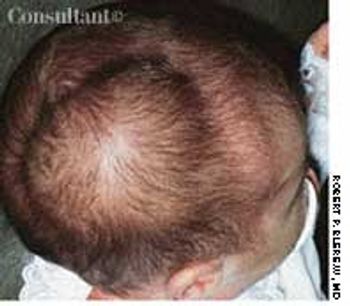
A right parietal cephalhematoma was first noted on this 2-week-old girl 2 days after her birth. Robert P. Blereau, MD of Morgan City, La, explains that a cephalhematoma is caused by bleeding under the outer periosteum of a newborn's skull bone, usually the parietal bone, and becomes evident as a swelling by day 2 or 3 after delivery. The swelling is confined to the involved bone and, therefore, does not go past the suture lines or the midline of the skull.
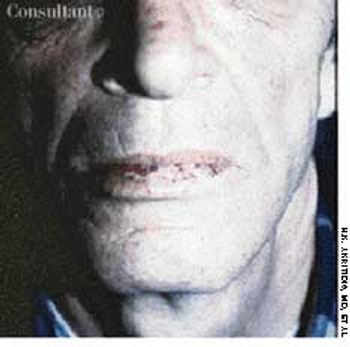
A 62-year-old man was admitted to the hospital with iron deficiency anemia, as demonstrated by low serum iron and ferritin levels and high total iron–binding capacity. He had had this condition for at least the last 5 years and had been treated with ferrous sulfate sporadically. The history coupled with the laboratory findings and the telangiectatic lesions on his lower lip led to a diagnosis of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia, or Rendu-Osler-Weber disease.
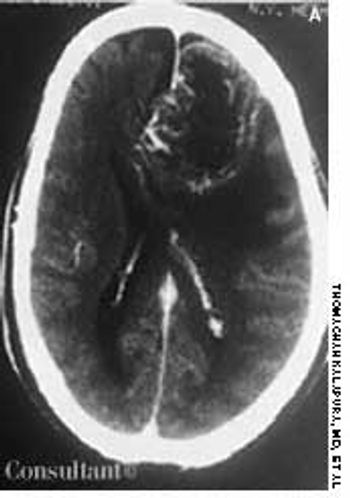
A 57-year-old man was brought to the emergency department with severe bifrontal headache, which he had had for 3 weeks. Family members reported that the patient exhibited episodes of confusion and loss of recent memory since the onset of the headache.
A 56-year-old man who had hematuria for 2 weeks underwent ultrasonography. This disclosed a well-circumscribed cyst in the lower pole of the left kidney and echogenic foci in the upper pole of the right kidney, without any evidence of posterior shadowing. A hyperechoic, well-circumscribed, circular focus was also seen in the right lobe of the liver. Abdominal CT confirmed the presence of a left renal cyst and revealed a 4.7-cm hypodense lesion in the right lobe of the liver, which suggested hemangioma.