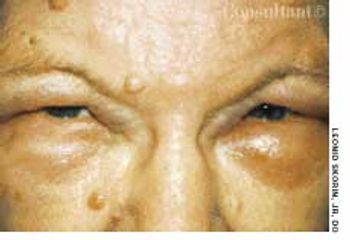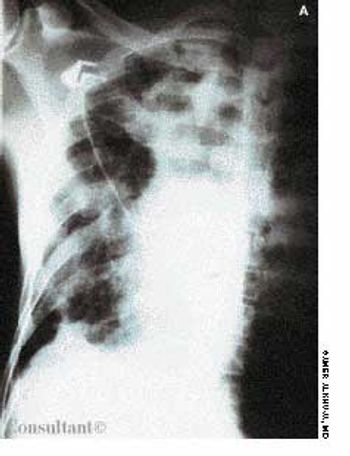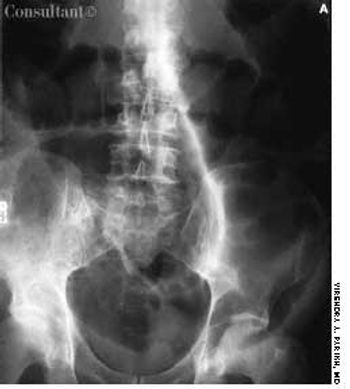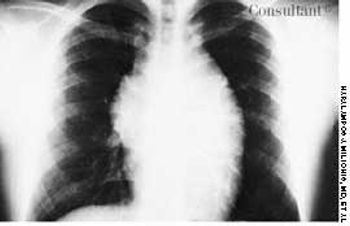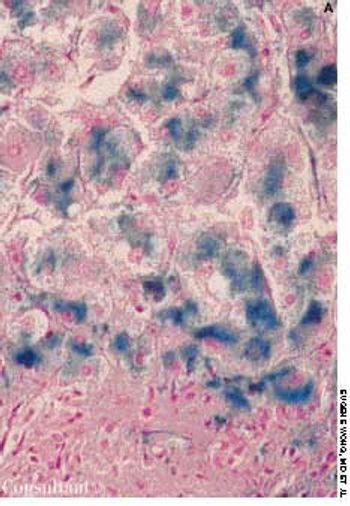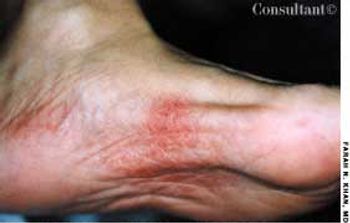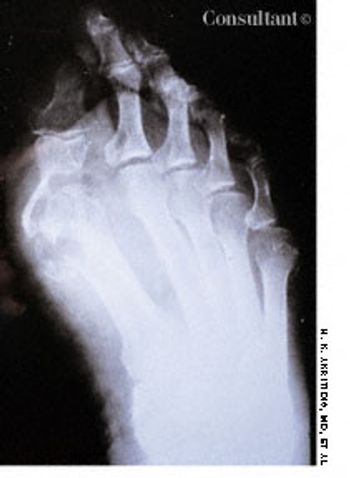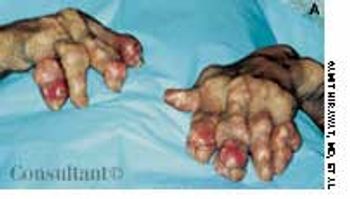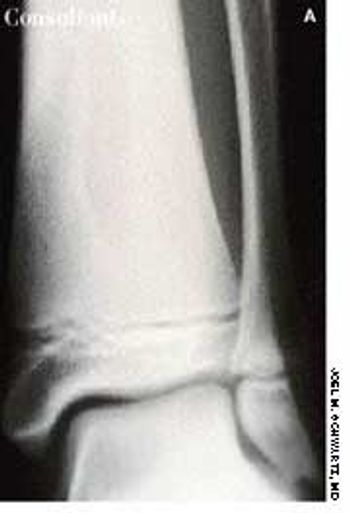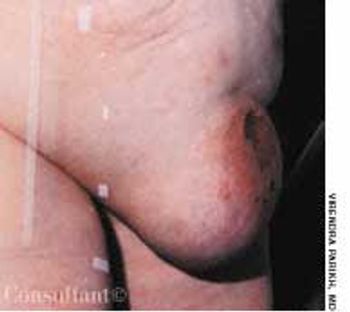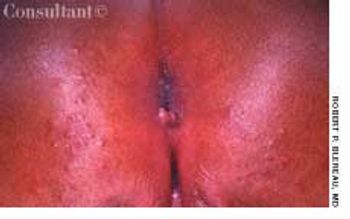
A 3-mm long, double-tipped, polypoid lesion appeared just anterior to the anus on an 8-month-old girl 2 days earlier. The lesion was excised in the office: a local anesthetic was administered, and the base was lightly electrodesiccated. Antibiotic ointment was applied until the area healed. Pathologic findings identified an infantile perianal pyramidal protrusion.