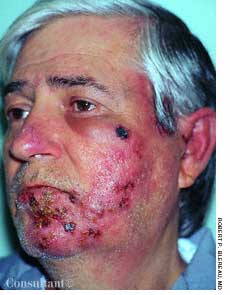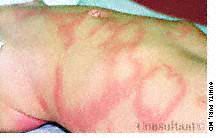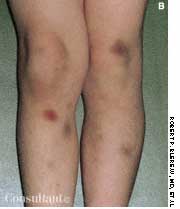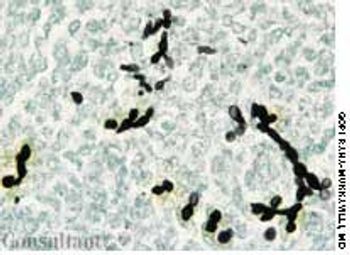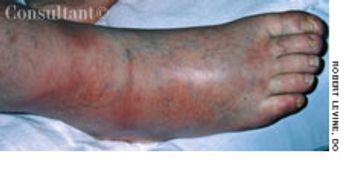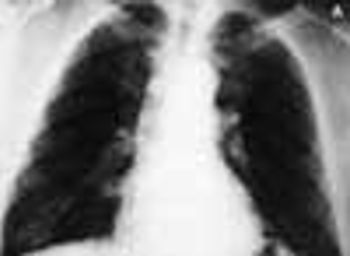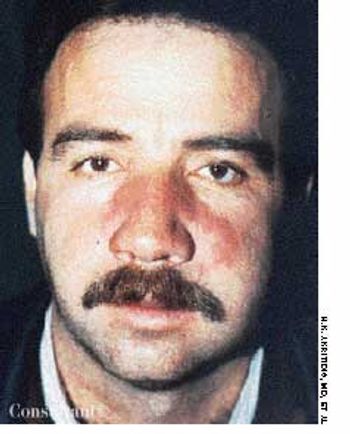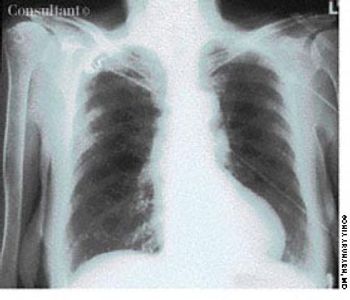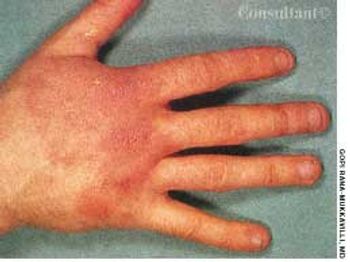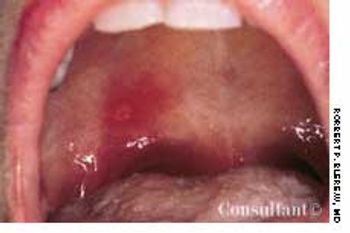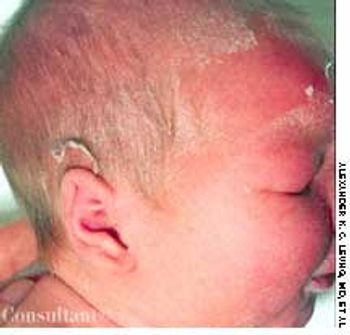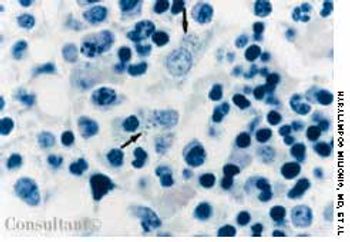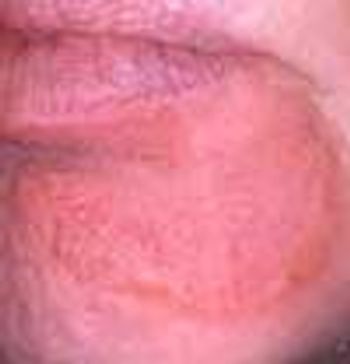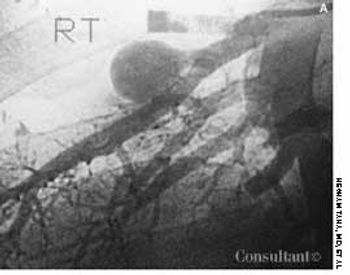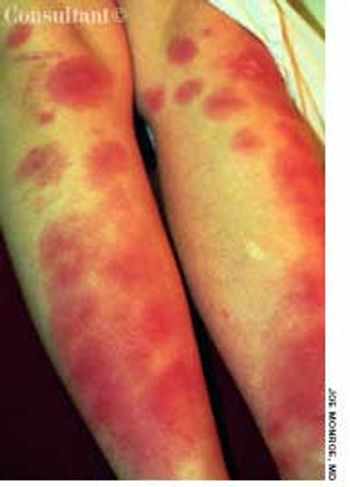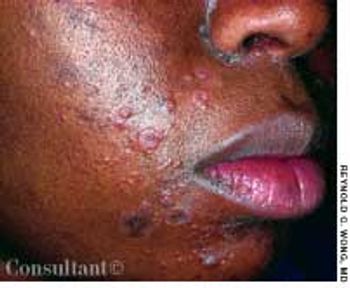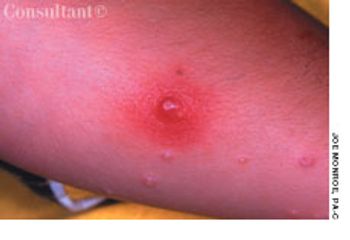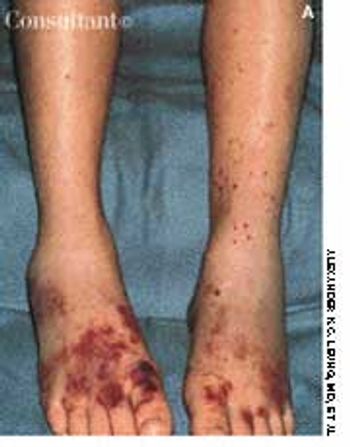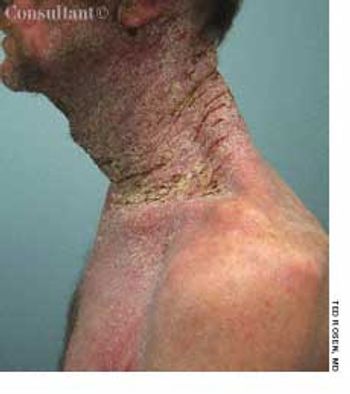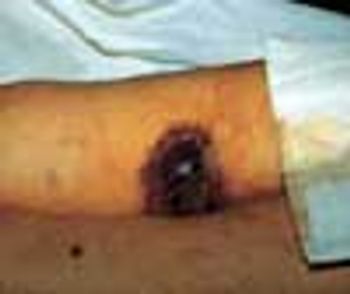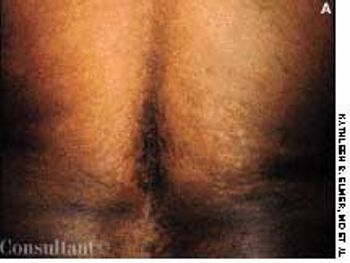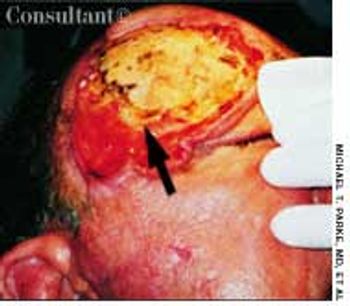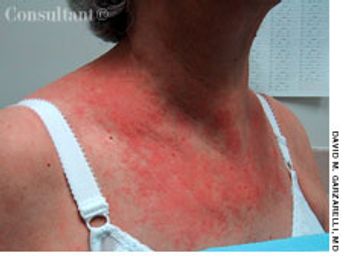
For several weeks, a 78-year-old woman had an intensely pruritic, diffuse, raised, slightly scaly, erythematous rash that persisted despite the use of several over-the-counter topical medications (such as hydrocortisone and clotrimazole cream). Since her last visit about 3 months earlier for a blood pressure reading, she had been well except for 2 episodes of night sweats. For several years, she had been taking levothyroxine and reserpine/hydrochlorothiazide; about 6 months ago, valsartan/hydrochlorothiazide had been prescribed.