For 3 years, a 53-year-old man had noted increasingly extensive changes in his skin, including facial thickening, a progressive reddish tinge, and annular lesions on his trunk. He also complained of itching on the periphery of his face.

For 3 years, a 53-year-old man had noted increasingly extensive changes in his skin, including facial thickening, a progressive reddish tinge, and annular lesions on his trunk. He also complained of itching on the periphery of his face.
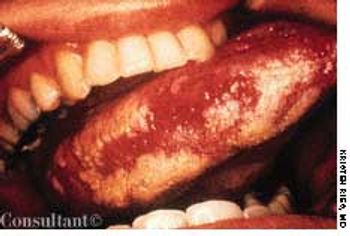
During the past 2 weeks, a 34-year-old man with HIV infection experienced worsening mouth pain while chewing.
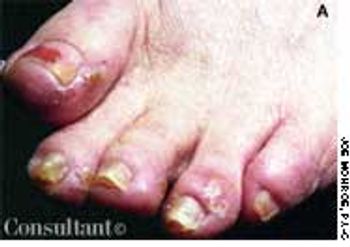
Exquisite pain of 3-days' duration in his right index finger sent a 19-year-old man for medical consultation. He recalled that a thorn had become embedded in the finger while gardening 1 week earlier.
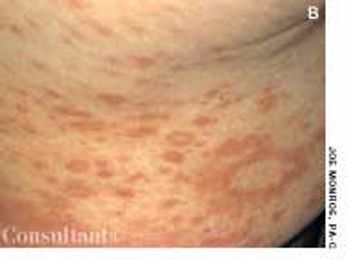
A 42-year-old woman had had athlete's foot for years, but the condition suddenly worsened when inflamed, pruritic vesicles appeared on both feet. A few days later, tiny, mildly itchy vesicles erupted on her palms; the rest of the hands were not involved. One week after the palmar eruptions, the patient noted 2 round, reddish brown, asymptomatic 3-cm macules on her trunk. These lesions had faint scaling on the trailing edge of the slowly advancing arciform borders.
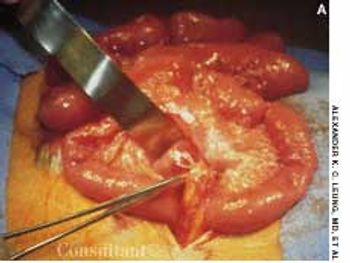
Adhesions can form within the peritoneal cavity after abdominal surgery, especially if there is an underlying inflammatory condition such as appendicitis or inflammatory bowel disease. The incidence of adhesive intestinal obstruction following a laparotomy is approximately 2%. Most adhesive obstructions occur within 3 months of the laparotomy, and 80% occur within 2 years. Adhesive obstructions tend to be more common in children than in adults.
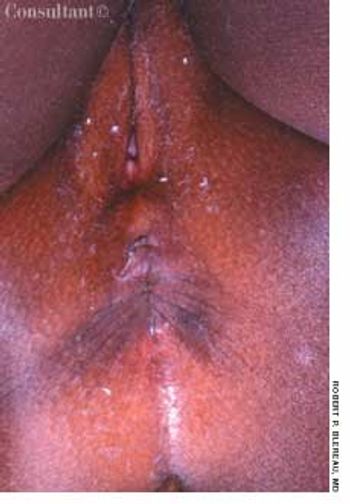
Enterobiasis-an infection by pinworms-is caused by the nematode Enterobius vermicularis. Treatment is a single dose of oral albendazole, mebendazole, or pyrantel pamoate.
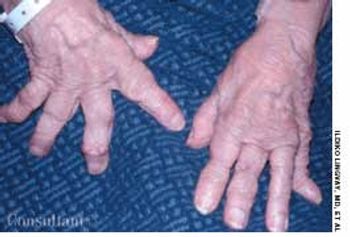
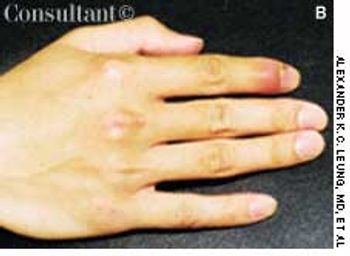
A 76-year-old woman had a 40-year history of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). She had repeatedly refused treatment with disease-modifying drugs, including methotrexate. Nodules began to develop 15 years after the initial diagnosis; they recurred after surgical removal.
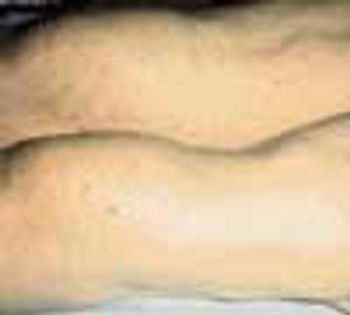
A variety of rheumatic diseases-systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and the vasculitides among them-manifest as “lumps, bumps, and holes” involving the extremities. Each of these diseases works through specific mechanisms on different structures of the skin to produce a distinctive pathology. In doing so, each provides clues to the cause, which the history and physical examination can help confirm.
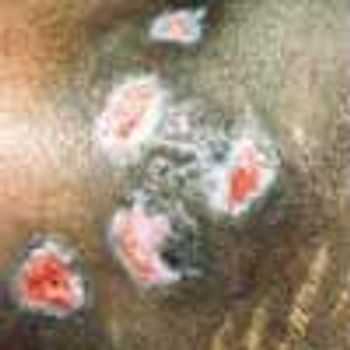
Pyoderma gangrenosum (PG) is a chronic, recurrent condition characterized by cutaneous ulceration. In half of patients, PG is associated with an underlying illness, such as inflammatory bowel disease, RA, SLE, or a lymphoproliferative disorder.

Persistent, purulent drainage from the perirectal region for 3 months prompted a 60-year-old man to seek medical evaluation. He also complained of minimal bleeding from the anus and perianal itching. The patient reported that he recently obtained some relief after a boil in the same area spontaneously burst.
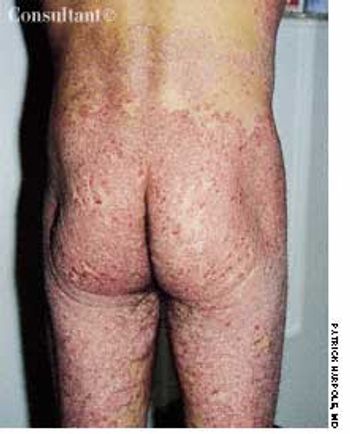
A 29-year-old man presented with a complaint of venereal warts and a long history of mild psoriasis, which he had treated with fluocinolone. He returned 3 months later complaining of chest congestion of 10 days' duration; it had been treated with ciprofloxacin at an urgent care facility.
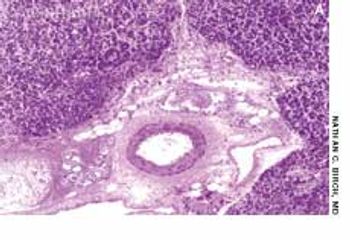
A 48-year-old man with jaundice, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain was hospitalized. The patient-a recovering alcoholic-was afebrile and reported abstinence from alcohol for 6 months.
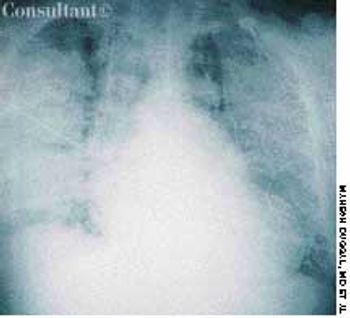
A 65-year-old man was hospitalized with dyspnea and fever of a few days' duration. He complained of excessive malaise, fatigue, and weight loss but denied any hemoptysis. The patient had a history of alcohol abuse.
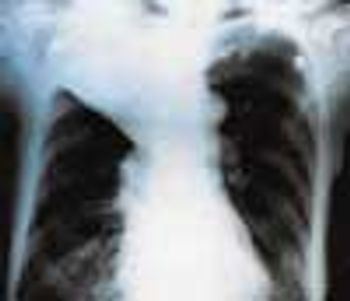
For the past 3 months, a 66-year-old man has suffered fatigue and loss of appetite and weight. He was not coughing, nor had he experienced fever, chest pain, or hemoptysis. He had no history of notable respiratory disease, and he was not aware of having had tuberculosis (TB).
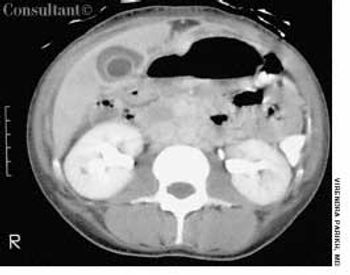
After 1 day of upper abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting, a 32-year-old man sought medical care. He had no significant medical history. The patient had tenderness and guarding in the right upper quadrant; no mass was detected. The remainder of the physical examination was normal.
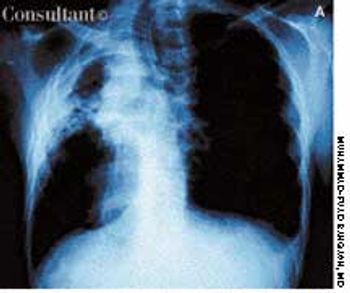
A 41-year-old man with a past history of tuberculosis presented to the emergency department with massive hemoptysis. The patient denied fever or chills but reported a 20-lb weight loss and intermittent hemoptysis during the last 6 months. Six years ago, he had been treated for tuberculosis.
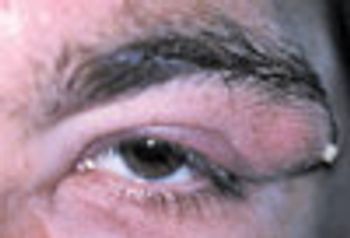
A swollen, painful eyelid prompted a 39-year-old man to seek medical attention. The patient had noticed swelling, redness, and irritation in his left lateral eyebrow area 2 days earlier. Upon awakening on the morning of his appointment, the left upper eyelid also felt full and tender and was drooping. A pointed draining area of purulent material had formed in the lateral brow region (not visible here). The patient was afebrile and denied any recent periorbital trauma. He was otherwise healthy; his only medication was a daily multivitamin.
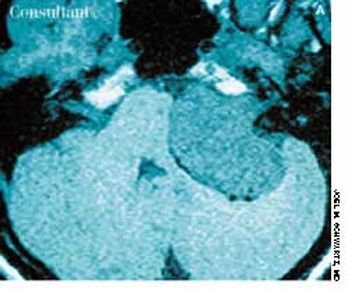
A 29-year-old woman complained of 6 months of tinnitus, hearing loss in the left ear, and leff-sided facial numbness. There was no history of trauma or recognized antecedent infection. Physical examination of the external and middle ears was unremarkable. Vestibular test results and tympanometry results were normal. An audiogram demonstrated nearly total sensorineural hearing loss in the left ear.
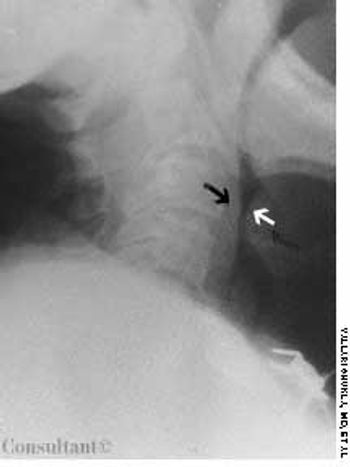
A 74-year-old nursing home resident was admitted to the hospital with shortness of breath and stridor. Radiographic examination of the neck revealed the “thumb sign” of a swollen epiglottis (Figure, white arrow); the black arrow indicates the normal posterior wall of the pharynx. Acute epiglottitis was diagnosed.
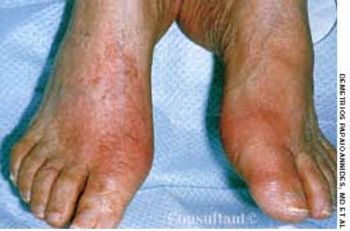
A 56-year-old man who consumed moderate amounts of alcohol was awakened by an intense burning pain in the right great toe; local erythema and edema were also present. Within hours, the pain became excruciating, and the same symptoms developed in the left great toe. Acetaminophen provided no relief. The patient's serum uric acid level was 8.8 mg/dL.
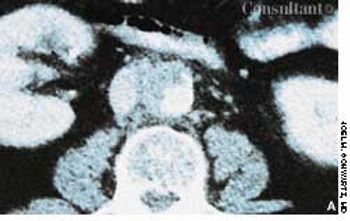
An obese 61-year-old man who had chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and sleep apnea heard a “pop” in his stomach while lifting a heavy weight; severe abdominal pain followed. He was short of breath the next morning, and his physician empirically prescribed cephalexin.
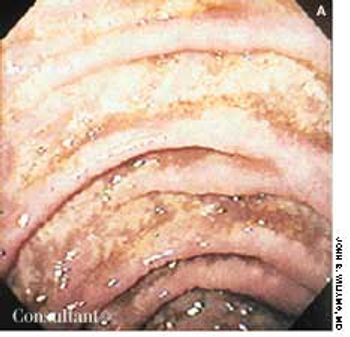
A 42-year-old man with a 2-year history of AIDS sought medical advice for intractable diarrhea, which he had had for several months. Standard AIDS medications were prescribed, but his compliance with the drug regimen was poor.
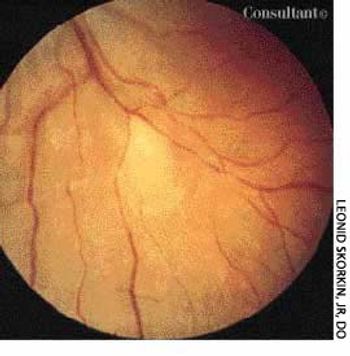
An 18-year-old woman presented with diminished vision and recent onset of floaters in the right eye. Her medical and ocular histories were noncontributory.
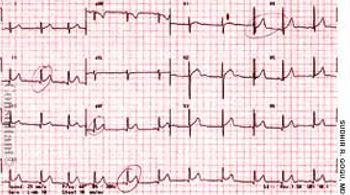
The mother of an 8-year-old girl sought medical care for her daughter who had complained of intermittent chest pain for 3 days. The patient denied nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. There was no shortness of breath, chills, fever, or diaphoresis. Her travel history included 2 trips to Mexico within the past year; the most recent trip ended 3 months before the pain started.
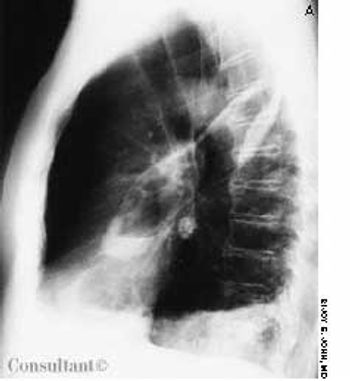
A 70-year-old man-nursing home resident-had had a cough, fever, and copious foul-smelling sputum for 1 week. Hemoptysis was noted off and on during the previous 3 days. The patient had no recent weight loss. A chest x-ray film and a CT scan showed an air-fluid level in the left oblique fissure of the lung as well as pleural thickening and infiltrates in the left lower zone.