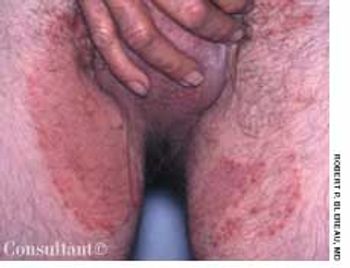
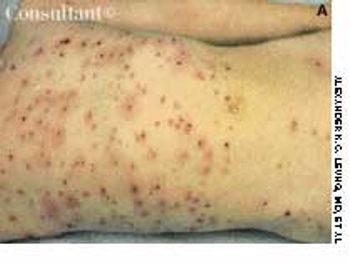
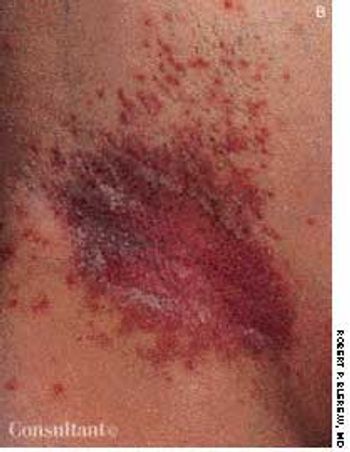
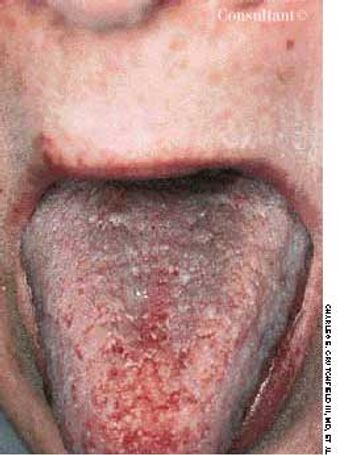
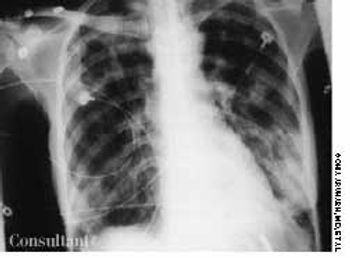
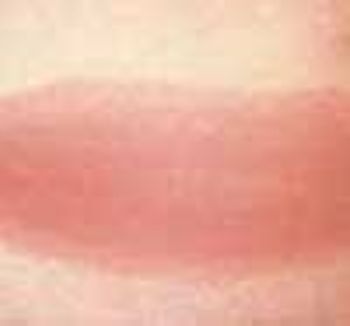
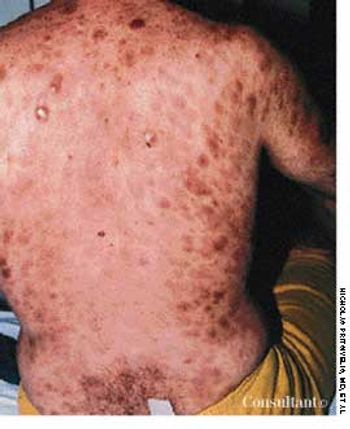
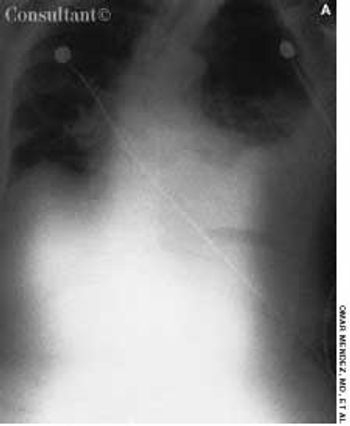
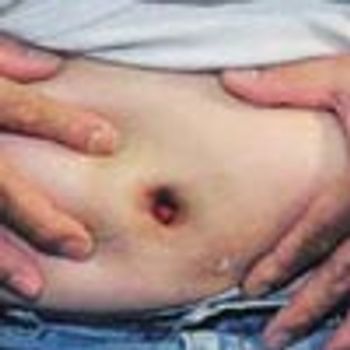
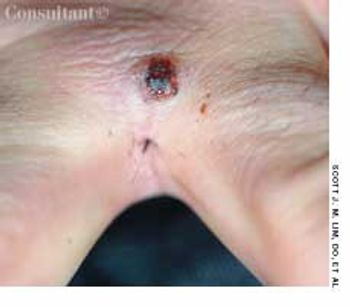
A 76-year-old man reported a 3-month history of an asymptomatic, raised, reddened lesion on his penis. The patient had type 2 diabetes mellitus. In 1994, a basal cell carcinoma had been excised from his chest and, 3 years later, a squamous cell carcinoma was excised from his left temple.