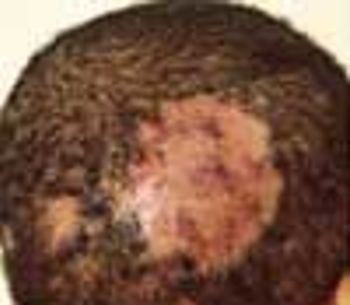
This is a common infectious problem, especially among school-age children. In many cases, there are well-defined areas of hair loss that can mimic alopecia areata.

This is a common infectious problem, especially among school-age children. In many cases, there are well-defined areas of hair loss that can mimic alopecia areata.
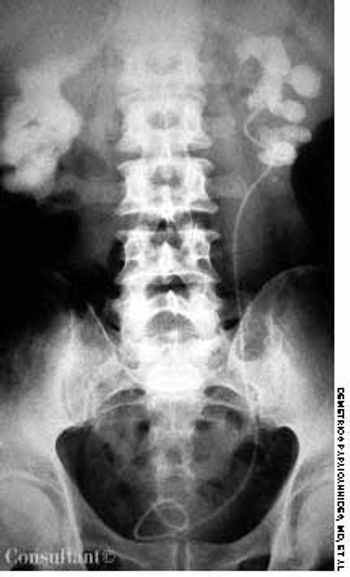
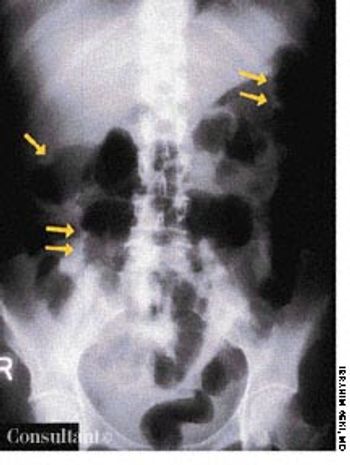
A roentgenogram of the kidneys, ureter, and bladder of a 58-year-old man shows bilateral stones in the renal pelvis and the renal calyces. The patient had a history of recurrent urinary tract infections caused by Proteus mirabilis. A ureteral catheter (pigtail) had been placed in the pelvis of the left kidney to facilitate drainage.
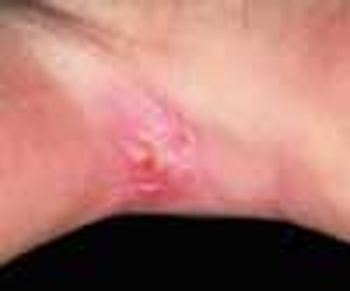
A scaling, red, fissured area between digits 4 and 5 on her right hand sent a 33-year-old woman to her physician. Diagnosis of interdigital Candida was confirmed by a potassium hydroxide evaluation of material from the site.

A week after the onset of headache, fever, chills, nausea, weakness, and malaise, a 23-year-old man presented to the emergency department of a hospital on Long Island in New York. He reported that analgesics had not eased his symptoms. The patient's only past hospitalization was a splenectomy secondary to an auto accident at age 16.
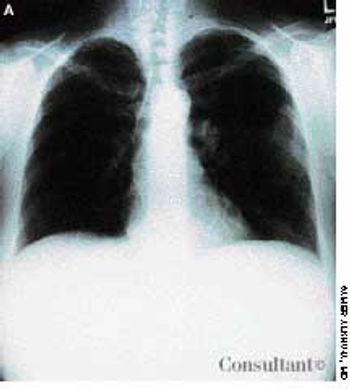
A 40-year-old woman with AIDS had been feverish for the past 24 hours and had a nonproductive cough. She had smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 20 years.
Four days after having been given cefuroxime for sinusitis, a 49-year-old woman experienced abdominal cramping, diarrhea, fever (temperature of 39.4°C [103°F]), and nausea. These problems persisted for 1 week, at which time the patient arrived at the emergency department. She had no recent history of travel, ingestion of undercooked food, or exposure to anyone with similar digestive problems.
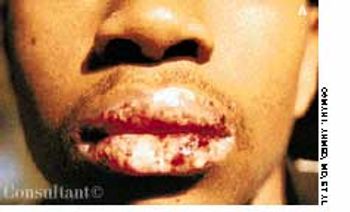
Erythromycin had been prescribed for a 15-year-old boy who complained of flulike symptoms. Twenty-four hours after starting the medication, he awakened with painful ulceration of his mouth and lips. The erythromycin was discontinued, and hydroxyzine (25 mg, three times daily) was started for possible macrolide sensitivity. His condition worsened over the next 3 days, however, and he was hospitalized when the severe oral pain made it impossible for him to tolerate food or drink. At no point had he any nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fever, or chills.
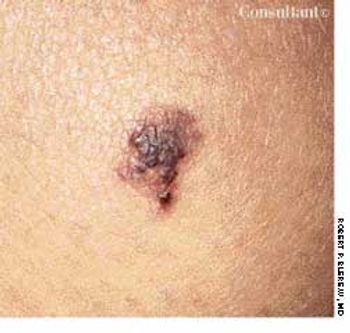
This lesion on her knee had been present for 5 years, reported a 22-year-old woman. It was not related to any trauma, and its size had not changed, but occasionally it became darker or lighter.

Gonococcal infection is the leading cause of bacterial arthritis in adults.
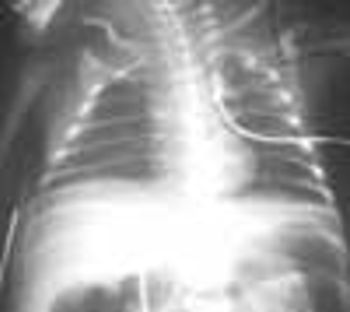
The extent of mucosal or transmural intestinal necrosis varies. Pneumatosis progresses from the submucosa through the muscular layer to the subserosa. The distal ileum and proximal colon are most frequently involved.
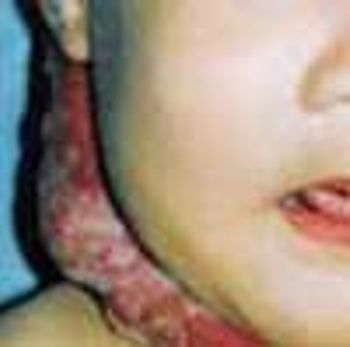
These collections of dilated vessels deep in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue are present at birth. They usually present as bluish or reddish lesions that are cystic, firm, and compressible. About 60% to 80% of cavernous hemangiomas undergo spontaneous involution, often with central clearing and fibrosis.
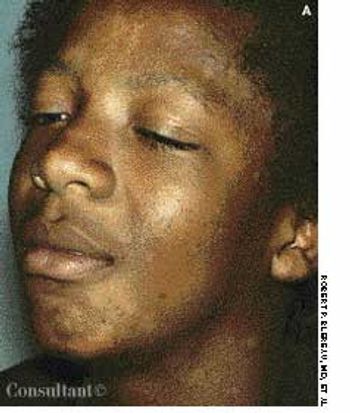
Although tinea versicolor is fairly common, its appearance on the face and neck is unusual, notes Robert P. Blereau, MD of Morgan City, La. His patient, a 30-year-old woman, exhibits the pale, rounded, fine-scaled lesions typically found on tanned or dark-skinned persons.
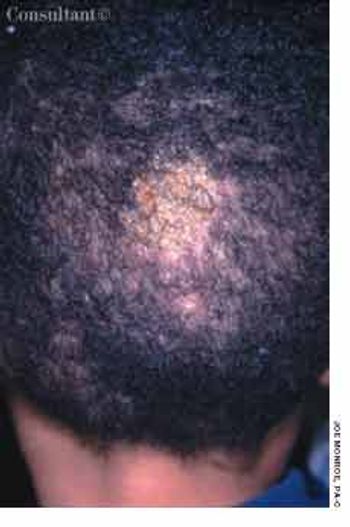
A 6-year-old African American boy is referred for evaluation of “cellulitis,” which had persisted for several weeks. The condition had failed to respond to oral antibiotics prescribed by another practitioner.
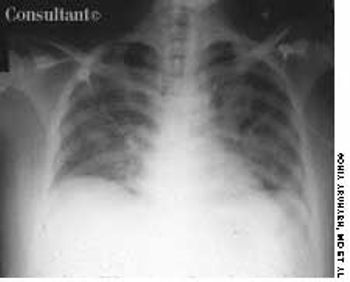
A 25-year-old man, who was an injection drug user, presented with a several-day history of dyspnea and fever. He complained of excessive malaise, fatigue, and weight loss but denied any hemoptysis. The examination of the lung revealed bilateral crackles in both lower zones.
Some cutaneous conditions are unique to pregnancy and the postpartum period. Others may affect both pregnant and nonpregnant women. Familiarity with these conditions is important in the evaluation of a pregnant patient with a rash or cutaneous lesion.
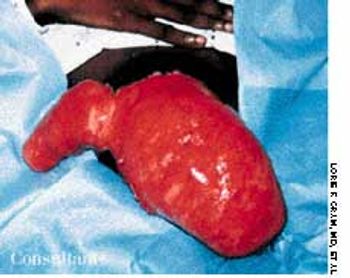
A 43-year-old woman was hospitalized with a 3-day history of fever and back pain. She was malnourished and seropositive for HIV infection. Results of blood and sputum cultures were negative. A community-acquired pneumonia was diagnosed. Chest film findings and the clinical presentation were inconsistent with Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia.
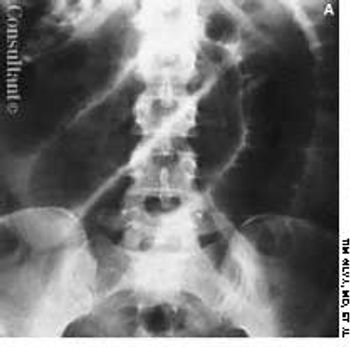
Cough, fever, diarrhea, and weight loss had disturbed a 52-year-old woman for 1 month. AIDS had been diagnosed 5 years earlier, but she had declined medical treatment. The patient's vital signs were stable when she was admitted to the hospital. Physical examination results were unremarkable except for thrush and mild, diffuse abdominal tenderness.
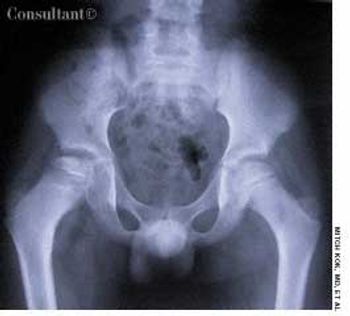
A 10-year-old boy presented with right hip pain and a limp. The patient was taking no medications and had no personal or family history of disease. He denied a history of trauma.

The collapse of the medial longitudinal arch, increased hindfoot valgus (eversion), and forefoot abduction in the foot of this 12-year-old girl (when weight bearing) are all typical features of a flexible flatfoot deformity.
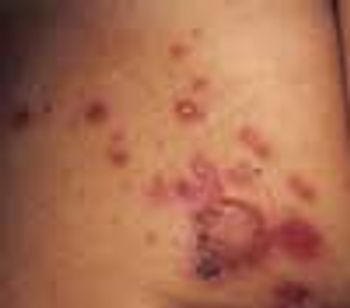
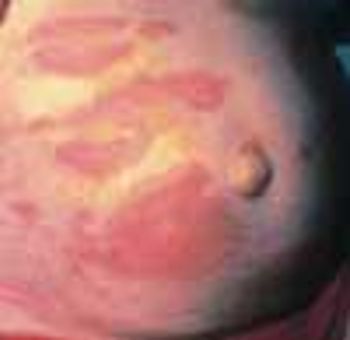
The numerous superficial, rounded, red-based ulcerations on the left buttock of a 3-year-old girl are characteristic of bullous impetigo. The varnish-like crust on the largest lesion is also typical of this skin infection.
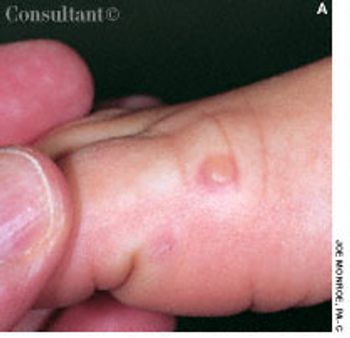
A 10-year-old girl complained of slight fatigue and malaise. A 6-mm tense blister had developed on the dorsum of her right foot, lesions had arisen on the palms, and a pinpoint, whitish ulcer had erupted anterior to the frenular attachment.
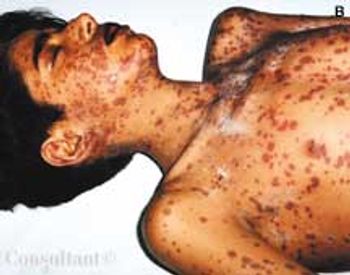
An 11-year-old boy presented to the hospital with a 3-day history of maculopapular rash over the face, trunk, and extremities. He had completed a 5-day course of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for otitis media 1 week before presentation. His medical history was otherwise unremarkable. Over the past 3 days, the rash had become pruritic and the lesions progressively larger. Some lesions were vesicular and bullous. There was diffuse involvement of the oral mucosa, conjunctivae, and genitalia.
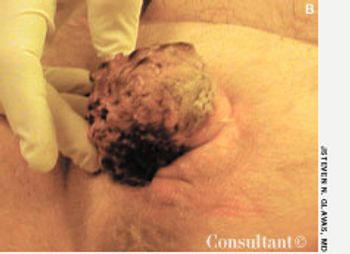
A 38-year-old man presented with a fleshy lesion beneath the tip of his penis. He had discovered it about 18 months before the initial evaluation. A second similar lesion resembling a “cauliflower” had appeared several weeks after the first. Both lesions had grown and had begun to bleed during intercourse.
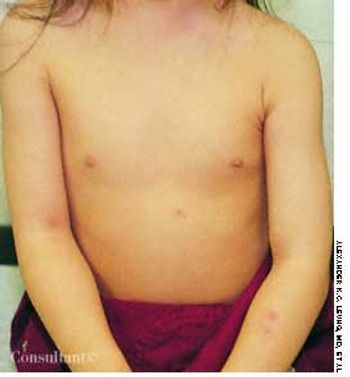
Two weeks after the subcutaneous injection of 0.5 mL of varicella vaccine in a 2-year-old girl's left arm, a nonpruritic rash developed on the child's upper abdomen and left forearm. She had no fever. The lesions subsided after 5 days.
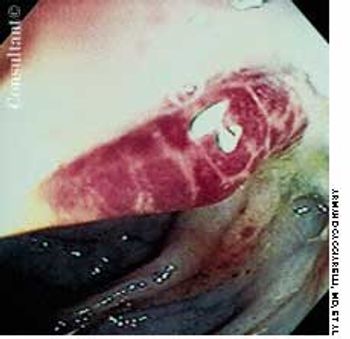
A 2-week history of diarrhea mixed with bright red blood was the presenting complaint of a 40-year-old man who was seropositive for HIV. Stool studies and culture results were negative for microorganisms. Colonoscopy demonstrated only the raised vascular lesion seen here in the sigmoid colon, which may have been responsible for the bleeding.