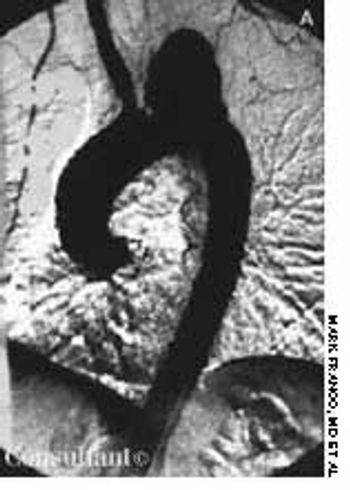
Here are two cases that demonstrate the discovery of aortic aneurysms through careful and complete physical examination and via radiographic studies obtained to evaluate other conditions.
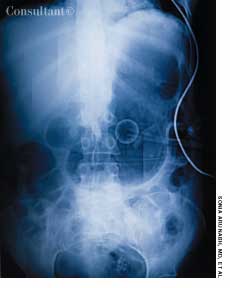

Here are two cases that demonstrate the discovery of aortic aneurysms through careful and complete physical examination and via radiographic studies obtained to evaluate other conditions.
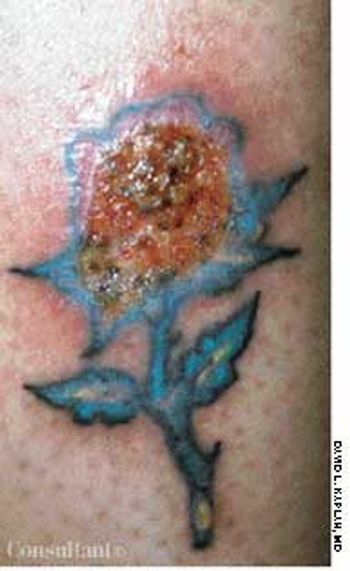
A 32-year-old woman with insulin-dependent diabetes noted a painful erosion at the site of "the rose tattoo," which she had gotten 5 days before.
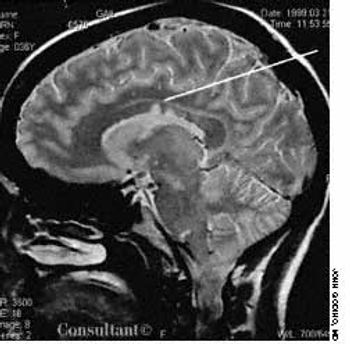
One week after an upper respiratory tract viral infection, a 36-year-old woman began to have progressive paresthesias of the lower extremities and right thorax. She sought medical evaluation 2 weeks later.

A 9-year-old girl was bitten around the right eye by a neighbor's dog. She sustained multiple punctures and lacerations of the right upper and lower eyelids

The wounds on the back of this boy's head resulted from an encounter with his neighbor's dog. The youngster's anxious parents brought him in for evaluation 1 hour after he was bitten.
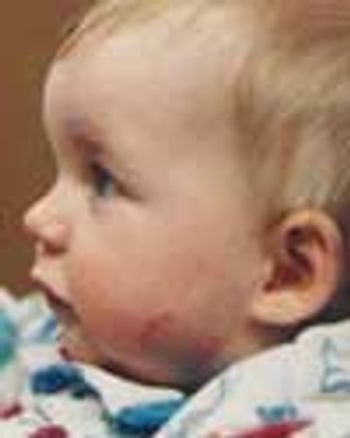
A 1-year-old girl was noted to have abrasions on the left cheek when she was picked up by her mother from a day-care center. The day-care provider reported that the girl had been bitten on the cheek by a 3-year-old boy during rough play. Her immunization status for tetanus was up-to-date.

How do you assess the likelihood of antibiotic resistance in patients presenting with suspected pneumococcal infection? Vanderkooi and associates addressed this in a study of 3339 patients with invasive pneumococcal disease. They found that antibiotic use in the 3 months before the onset of infection was the most important risk factor for antibiotic resistance. The single most important risk factor for resistance to a particular antibiotic was previous use of antibiotics from the same class.

Vitamin E has been evaluated for the treatment and prevention of several different chronic diseases in numerous clinical trials over the past 2 decades. However, only a limited number of studies have investigated the potential therapeutic or prophylactic effect of vitamin E on allergic rhinitis and respiratory infections. In contrast to trials on cardiovascular disease, which have failed to demonstrate a benefit from vitamin E supplementation,1,2 there is mounting evidence that this essential vitamin may be useful for prevention of the common cold and treatment of allergic rhinitis.

Abstract: Tuberculous meningitis has several different clinical presentations, including an acute meningitic syndrome simulating pyogenic meningitis, status epilepticus, stroke syndrome, and movement disorders. Cranial nerve palsies and seizures occur in about one third of patients, and vision loss is reported by almost 50%. The cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) typically shows moderately elevated levels of lymphocytes and protein and low levels of glucose. The demonstration of acid-fast bacilli in the CSF smear or Mycobacterium tuberculosis in culture confirms the diagnosis. CNS tuberculosis may also manifest as intracranial tuberculomas. The characteristic CT and MRI finding is a nodular enhancing lesion with a central hypointensity. Antituberculosis treatment should be initiated promptly when either tuberculous meningitis or tuberculoma is suspected. (J Respir Dis. 2005;26(9):392-400)

This painless, bleeding lesion had developed insidiously on the penis of a 47-year-old HIV-positive man. The patient was inconsistently compliant with antiretroviral therapy. He had a history of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia and widespread cutaneous Kaposi sarcoma. The 2.5-cm, friable but firm, exophytic nodule was on the distal shaft of the penis.

A 51-year-old man presents with a painful inguinal rash that has persisted for 3 months despite application of a combination corticosteroid and antifungal cream. The rash is associated with a strong odor.

Each year almost 5 million Americans sustain an animal or human bite. Dog bites alone represent 0.4% to 1% of all emergency department (ED) visits and can range from trivial to life-threatening.

For years, cardiologists and primary care physicians have engaged in a spirited debate about the appropriate target for low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) lowering in patients with coronary artery disease.

This 11-year-old boy presented with pain and swelling of the right hand. The boy had been bitten by a German shepherd while trying to feed the animal a day earlier. He had cleaned the wound with water. The boy's tetanus immunization status was up-to-date, as was the rabies immunization status of the dog.

Urinary incontinence is common--especially among older adults--but underdiagnosed. Many persons with this disorder are reluctant to discuss it with their physicians; often, only direct questioning can uncover the problem.

57-year-old woman is hospitalized because of a 3-week history of persistent left-sided dull flank pain that worsens with movement and is associated with intermittent high fever.

Although proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are highly effective, clinical failure in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is seen regularly--not only in GI clinics but also in primary care offices. In fact, the prevalence of failure with PPIs has increased in proportion to the expanding indications for their use.

Is chronic fatigue syndrome related to infection? If so, how does this affect the approach to therapy? Because patients with chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) frequently report an infection-like event at the onset of their condition, the possible role of viral or other infections has been extensively investigated.

Advances in the understanding of multiple sclerosis (MS) have translated into aggressive treatment regimens that enhance patients' quality of life. In this article, we discuss the therapeutic options, especially treatments that are directed toward the underlying immunologic mechanisms of the disease. Because of its direct effect on quality of life, aggressive management of symptoms is emphasized.

A 43-year-old man presents to the emergency department with worsening substernal chest pain that has developed over several hours. He describes the pain as dull and oppressive; it radiates to the left shoulder and jaw and worsens on inspiration and with recumbency. It is not associated with nausea, dizziness, or diaphoresis. He is given nitroglycerin, morphine, hydromorphone, and meperidine parenterally, but none of these relieve the pain.

Scaling patches that resist antifungals; an outbreak of red papules; a velvety,hyperpigmented rash--can you identify the disorders pictured here?

MRSA is the second most common pathogen isolated in the ICU setting, associated with 52.9% of nosocomial infections.1 Colonization of patients with S aureus (methicillin-sensitive and methicillin-resistant) has been found to be important for the development of subsequent infections, including bacteremia.2-4 The primary reservoir of S aureus in humans is the anterior nares and, to a lesser extent, the perineum and skin.5,6 As a result, topical antibiotics and antiseptics have been used to eradicate colonization in a variety of patient populations in an effort to prevent infection and to control transmission of MRSA.

Coccidioides immitis is a di-morphic fungus that causes pulmonary disease with a variety of clinical and radiographic presentations. Miliary pulmonary disease is very uncommon and is found almost exclusively in immunocompromised patients. The authors describe the case of an immunocompetent patient who had disseminated coccidioidomycosis with a miliary pulmonary disease pattern. Obtaining a careful travel history and considering regional fungal infections was integral to making a prompt diagnosis.

Abstract: The standard therapies for acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease include short-acting bronchodilators, supplemental oxygen, and systemic corticosteroids. For most patients, an oxygen saturation goal of 90% or greater is appropriate. Bilevel positive airway pressure (BiPAP) is usually beneficial in patients with progressive respiratory acidosis, impending respiratory failure, or markedly increased work of breathing. However, BiPAP should not be used in patients with respiratory failure associated with severe pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome, or sepsis. Systemic corticosteroids are appropriate for moderate to severe acute exacerbations; many experts recommend relatively low doses of prednisone (30 to 40 mg) for 7 to 14 days. Antibiotic therapy is controversial, but evidence supports the use of antibiotics in patients who have at least 2 of the following symptoms: increased dyspnea, increased sputum production, and sputum purulence. (J Respir Dis. 2005;26(8):335-341)

The authors describe a case of acute eosinophilic pneumonia (AEP) that occurred in a previously healthy young man. The presentation was similar to that of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and the diagnosis was established by bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL). The authors note that it is important to recognize the subset of patients with AEP who present with an ARDS-like picture, especially since corticosteroids are very effective in this setting.