
A 30-year-old man has had painful genital lesions for the pastseveral days. He recently returned from a business trip during which hehad several unprotected sexual encounters.

A 30-year-old man has had painful genital lesions for the pastseveral days. He recently returned from a business trip during which hehad several unprotected sexual encounters.
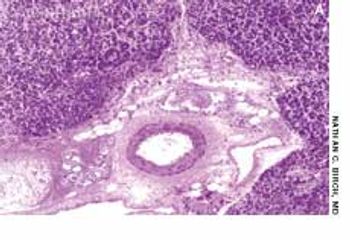
A 48-year-old man with jaundice, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain was hospitalized. The patient- a recovering alcoholic- was afebrile and reported abstinence from alcohol for 6 months.
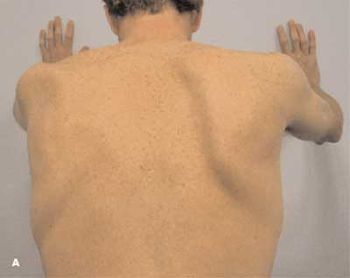
Several hours after he had installed ceramic tile, a 33- year-old man experienced muscle spasms and felt pressure in his right shoulder. He denied previous injury to the area.
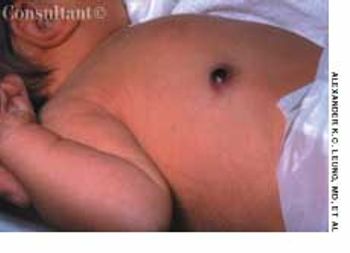
A male infant was born to a 29-year-old woman (gravida 3, para 2), following an uncomplicated pregnancy and normal vaginal delivery. At birth, a brownish 1-cm nodule was noted on the right side of the upper abdomen. The infant was otherwise healthy.

ABSTRACT: The cardinal feature of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is abdominal pain or discomfort associated with altered bowel habits. Because no serologic marker or structural abnormality exists, the diagnosis is based on clinical findings. A systematic symptom-based approach, including the Rome II criteria, ensures diagnostic accuracy. Determine whether a specific event-such as gastroenteritis, antibiotic use, or a food-borne illness-precipitated the IBS symptoms. Be alert for warning signs of cancer, infection, or inflammatory bowel disease, such as fever or unexplained weight loss. Only minimal laboratory testing is required; however, further evaluation may be warranted if a patient does not respond to treatment or loses weight, if the dominant symptom changes, or if other "red flags" are identified.

An 83-year-old woman is brought by her daughter for evaluation becauseof increasing confusion during the past few days. The patienthas early Alzheimer dementia, hypertension, and type 2 diabetes. She takes donepezil, 10 mg/d;lisinopril, 5 mg/d; and glipizide, 5 mg bid. She is unable to bathe and dress herself as well as previously,has been crying for no apparent reason, and has lost her appetite.
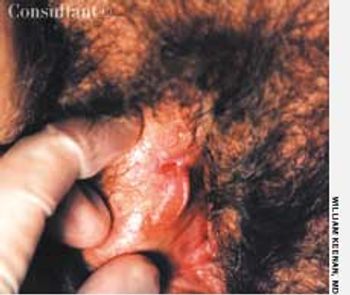
A 67-year-old woman presented with a painful genital ulcer. She denied new sex partners and previous genital lesions.

Ezetimibe/simvastatin (Vytorin)recently became available for thetreatment of high LDL cholesterollevels, as adjunctive therapy to dietarymodification, in patients withprimary hypercholesterolemia ormixed hyperlipidemia. This drug,from Merck/Schering-Plough Pharmaceuticals,inhibits the productionof cholesterol in the liver and blocksthe absorption of cholesterol in theGI tract, including cholesterol obtainedfrom food.

For 8 months, a 44-year-old man hashad a 2-mm superficial ulcer on histongue. The lesion is surrounded bya thin white rim and an area of whitediscoloration. The patient believesthat the ulcer resulted from thescratching of the rough edge of atooth against his tongue.

ABSTRACT: The early signs of diabetic neuropathy can be detected during a routine clinical examination. Inspect patients' feet for deformities and sensory loss, which indicate risk of ulceration. Prolonged poor glycemic control, alcohol abuse, and obesity increase the risk of amputation. Autonomic dysfunction, which can lead to sexual dysfunction and gastropathy, can be detected by measurement of heart rate and blood pressure. A resting heart rate of about 100 beats per minute and a decrease of about 30 mm Hg in systolic blood pressure within 2 minutes of standing are abnormal findings. Electromyography and nerve conduction studies confirm the diagnosis. Improved metabolic control is the main goal of treatment. Analgesics, neuromodulators, and tricyclic antidepressants are effective for managing pain. In patients with autonomic neuropathy, treat the associated symptoms.
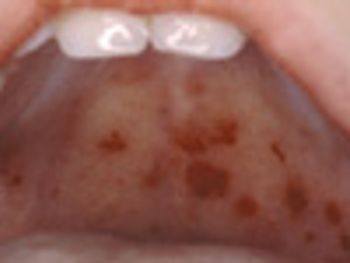
When palatal petechiae are present along with exudative tonsillitis and cervical adenitis, and test and culture are positive, a Strep diagnosis is more secure.
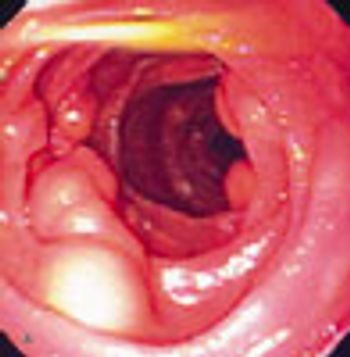
An 81-year-old woman presented with abdominal pain of 6 months’ duration, anorexia, and a 4.5-kg (10-lb) weight loss. Her history was otherwise unremarkable. She denied fever, chills, diarrhea, and vomiting. The pain was diffuse; no rebound or guarding was noted. The peripheral lymph nodes were not palpable.

A 20-year-old woman presents with a 3-week history of a pruritic, progressivelyenlarging erythematous lesion on one arm. She has a cat and recentlystarted horseback riding lessons. She is otherwise healthy and takes nomedication.

Despite the manydouble-blind,placebo-controlledtrials thathave demonstratedthe efficacy of statins inreducing the risk of cardiovascularevents, a largenumber of patients who aretreated with these drugsstill experience suchevents. This may be becausepatients who requireintensive lipid lowering arenot receiving adequatedosages of statins.
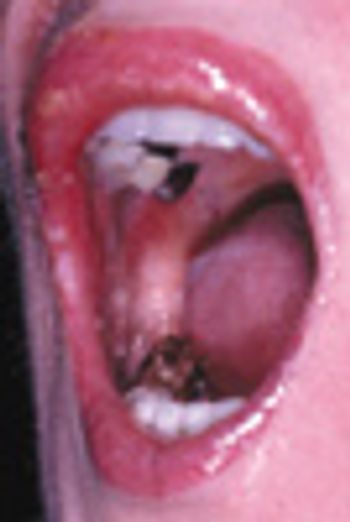
A 65-year-old woman sought evaluation of a unilateral, asymptomatic rash that involved the oral mucosa and lips. The rash consisted of ulcerations and vesicles. The suspected diagnosis of herpes zoster was confirmed 4 days later when the patient experienced lancinating pain throughout the affected area and into her scalp and neck.
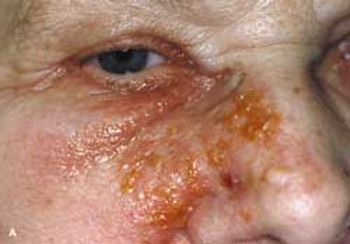
For a few days, this 73-year-old woman had had an itchy, painful rash on the right side of her face. Despite its proximity to her eye, she had no ocular involvement and no blurring of vision.
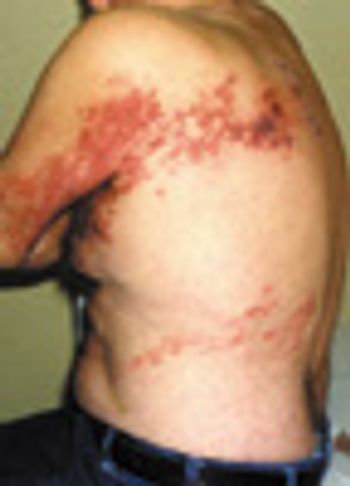
Two weeks earlier, this 66-year-old man had been hospitalized because of leftsided chest pain. However, cardiac evaluation revealed no abnormalities.
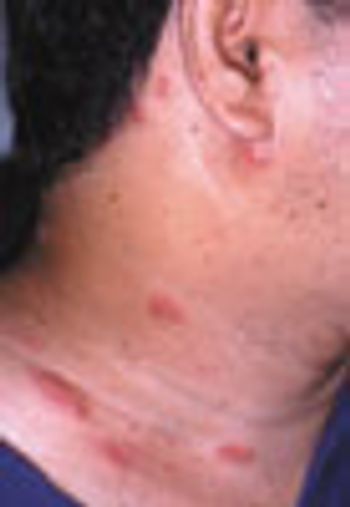
For 3 days, a 44-year-old man had several crops of tiny vesicles with raised erythematous bases on the right side of his neck and 2 elongated maculopapular lesions at the base of the neck. All of the lesions were within the C3 dermatome.

A 37-year-old man presents for evaluationof 3 reddish, tender, 2-cm, elevatedlesions on his right ankle that havefailed to respond to oral amoxicillin/clavulanate prescribed by anotherphysician. The lesions have beenpresent for 8 weeks. Each lesion has acentral opening and watery yellow drainage (Figure 1). The patient recentlyreturned from a trip to CentralAmerica, where he had sustained multiplemosquito bites.
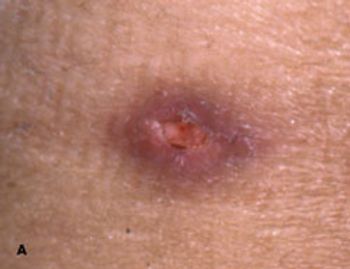
35-year-old Hispanic man presented with nonproductive cough; dyspnea; fever; and a painful, ulcerated, 1.5-cm, red-brown plaque on the left flank. He had had the lesion for 3 months and the symptoms for 1 week. The patient had grown up in Arizona, and he traveled there 4 months before the lesion arose.

ABSTRACT: Prompt treatment of herpes zoster with an antiviral such as acyclovir does not prevent post-herpetic neuralgia, but it can reduce the pain and duration of the disorder, particularly in older patients. Agents used to treat post-herpetic neuralgia include gabapentin, tricyclic antidepressants, lidocaine patches, capsaicin, and opioids. Effective treatment often requires the use of multiple medications. When you select a regimen, consider whether your patient is at heightened risk for adverse drug effects and whether he or she has comorbid disorders, such as depression, that might be amenable to treatment with the same medication used for post-herpetic neuralgia. Patients with intense pain and dysfunction are more likely to have a protracted disease course; early, aggressive intervention is warranted in this setting. For patients who continue to have disabling pain despite treatment, consider intrathecal corticosteroid or lidocaine injections or referral to a pain management center or specialist.

One fact of life for pediatricians is that our patients grow up. One of our last contacts with our young adult patients who continue on to college may be their pre-college physical examination or their request for a college pre-matriculation immunization form. A pre-college visit provides a good opportunity to review the young adult's immunization status to be certain that he or she is up-to-date. That visit is also a good time to verify that the student has received a booster dose of tetanus toxoid within the past 10 years, a complete series of hepatitis B vaccine, and any other vaccine (such as varicella) that may be indicated.

A54-year-old white woman presentswith extremely tender,firm lesions on the right hip and legsthat have been increasing in size andnumber over the past few months.

This 10-year-old boy presented forevaluation of a rash that developedduring a spring vacation on Florida’sAtlantic coast. After he had beenswimming in the ocean, a pruritic,erythematous, papular rash developedon his trunk, axillae, and groin. Approximately24 hours after the onsetof the rash, he experienced malaise,chills, and a sore throat. His past medicalhistory was unremarkable. Hehad been fully immunized and hadhad varicella infection.

A 30-year-old man presentedwith severe left flankpain radiating to his abdomenand gross hematuriaof 5 to 10 days’ duration.He also reported a 4- to 6-monthhistory of nausea with intermittentvomiting, anorexia, and progressiveweight loss. He took no medicationsand had no allergies.