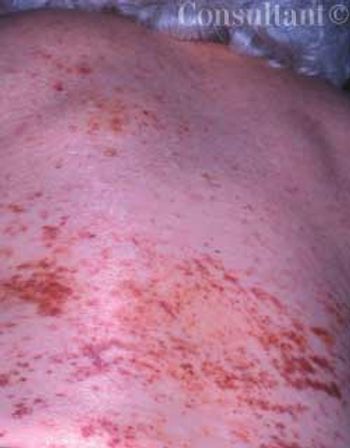
Diffuse petechiae suddenly arose on the back and abdomen of a 79-year-old woman. Within several days, the asymptomatic lesions covered her arms and face as well.

Diffuse petechiae suddenly arose on the back and abdomen of a 79-year-old woman. Within several days, the asymptomatic lesions covered her arms and face as well.

ABSTRACT: A cough is considered chronic when it persists for 3 or more weeks. Typically, chronic cough is a lingering manifestation of a viral upper respiratory tract infection; other, more serious causes-such as asthma, sinusitis, or gastro- esophageal reflux-must also be considered. Look to the history for diagnostic clues and order a chest film, which may point to pneumonia, hyperinflation, atelectasis, or cardiac or pulmonary abnormality. Diagnostic test methods will depend, in part, on the child's age; for example, the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends against imaging of the sinuses in children 6 years or younger. Pulmonary function tests can be useful in diagnosing asthma if the child is able to cooperate. Consider ordering a barium swallow for a very young child whose cough may be the result of a vascular anomaly. A pH probe study can help you determine whether cough is secondary to gastroesophageal reflux. Treatment is directed at the underlying cause.

In November 2002, cases of an atypical pneumonia were reported in the Guangdong province of southern China. By the following June, outbreaks of the illness-known as severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)-had occurred in Germany, Ireland, the United States, Canada,Hong Kong,Singapore, and Vietnam.

For 3 months, a 50-year-old man had been bothered by a worsening and spreading rash on his feet and lower legs. The multiple, nodular, fungating lesions were nonpruritic. The heterosexual, unmarried patient did not use intravenous drugs and did not know his HIV status; he denied any significant medical history.

For 2 years, a slightly pruritic, light brown, scaly rash had been present on a 20-year-old man’s neck. During the past 8 months, the eruption spread to the upper chest and upper arms. The patient reported that the rash changes color with the seasons. Multiple round to oval, hypopigmented, slightly scaly macules were noted on the neck, chest, and upper arms. Tinea versicolor was strongly suspected.
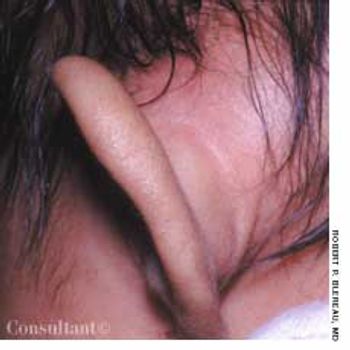
Concerned that her 7-week-old daughter's left ear was far more prominent than the right one, the mother took the infant to the emergency department (ED) for evaluation. The swelling had begun 3 or 4 days earlier; the patient was otherwise asymptomatic.

A 34-year-old woman presented with a3-day history of painful blisters of theupper lip and nose. Five days earlier,a rapid antigen test had confirmedstreptococcal pharyngitis; amoxicillinwas prescribed. The patient had nohistory of herpes and was immunocompetent.She had several youngchildren and did not work outsidethe home.

A 62-year-old woman sought medicalevaluation for persistent swellingof her lower lip and right cheek. Thecondition had been present for 8 to9 months. A 6-month course of oralprednisone prescribed by anotherpractitioner had no effect. The patienthad no history of chronic diseaseand no pain, paralysis, ulcerations,scaling, or dental or tongue problems.
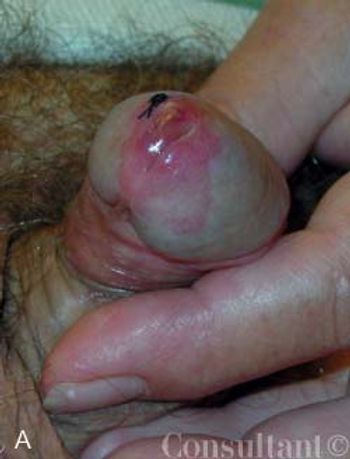
An uncircumcised 58-yearold man presented with a persistent “rash” on his penis of 5 years’ duration. He complained of localized irritation with coitus. Over-the-counter ointments and corticosteroid preparations had failed to clear the eruption. The patient had hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and coronary artery disease. He had been monogamous for the last decade and denied any risk factors for sexually transmitted diseases.

A 34-year-old woman (gravida 3, para 2) presented at 28 weeks’ gestation with a 3-week history of a pruritic rash that had progressively worsened. Multiple vesicles and bullae were noted; erosions and crusts on older lesions were also present. The patient had had no prodromal symptoms; she denied fever, chills, nausea, and vomiting. The purplish hue on her body resulted from application of the topical antibacterial agent, gentian violet, which the patient had obtained in Mexico.

A 38-year-old man was concerned that the small lesions on his lips were flatwarts. A biopsy identified Fordyce, or sebaceous, glands of the lips.

ABSTRACT: When influenza is present in the community, clinical symptoms are as accurate as rapid point-of-care tests for making the diagnosis; in this setting, the combination of cough and fever (temperature, 37.7°C [100°F] or higher) of acute onset has a positive predictive value of 77% to 79%. Accurate diagnosis ensures timely administration of antiviral agents and prevents unnecessary antibiotic use. In elderly persons, vaccination reduces illness severity, incidence of complications, and mortality. An intranasal vaccine is a new option for persons aged 5 to 49 years who are at risk for complications and refuse injection. Chemoprophylaxis with amantadine, rimantadine, or a neuraminidase inhibitor is a useful adjunct to vaccination in certain groups, such as nursing-home residents. Antiviral therapy started within 24 to 48 hours of symptom onset can reduce the duration of illness by 1 to 1.5 days and ameliorate symptoms in patients with uncomplicated influenza. However, treatment is expensive and does not prevent complications.
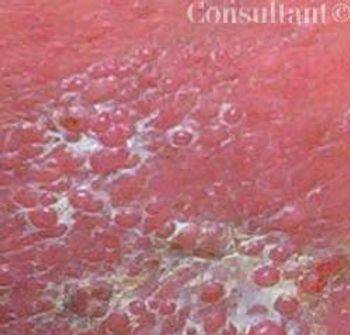
A 62-year-old obese woman with adult-onset type 1 diabetes mellitus had a 6-year history of bilateral leg edema. During the last year, the edema worsened and the skin on her legs thickened. She also had multiple, bilateral, painful, superficial ulcers that drained copiously.

A 12-year-old African American girl comes to youroffice for a well-child checkup. She is tall for herage (height above the 95th percentile) and obese(body mass index [BMI] above the 95th percentile).Physical examination reveals acanthosisnigricans on her neck, axilla, and upper abdominalregion (Figure) and a vaginal yeast infection.Routine urinalysis reveals a glucose level ofgreater than 1000 mg/dL, with negative proteinand ketones. A random blood glucose test, obtainedbecause of the glucosuria, is 249 mg/dL.

A 31-year-old man presents with a2-week history of a constant, dull acheand hearing loss in the right ear. Healso complains of intermittent sharppains that are usually followed bydrainage through the external auditorycanal. Another practitioner diagnosedacute otitis media with tympanic membraneperforation, for which he prescribeda 10-day course of amoxicillin.The patient completed the regimen buthas obtained no relief.

Because of recent threats of bioterrorism, smallpox vaccination was reinstated in the United States earlier this year. Since January 2003, more than 35,000 civilian and public health care workers in 54 jurisdictions have been vaccinated.

Foot ulcerations and infections are the leading cause of hospitalization amongpatients with diabetes; they occur in about 15% of these patients.

A slightly pruritic, red, scaly rash on an 8-year-old boy’shands has been progressively worsening since it appeared4 months earlier. Nail pitting also was noted. There are noother rashes on his body. The patient is active in sports;denies any new exposure to soaps, clothing, or other contactants;and spends time in the homes of his recently divorcedparents.

This condition features acutely tender nodules, marked erythema, and contusions that appear as a consequence of inflammation of subcutaneous fat.
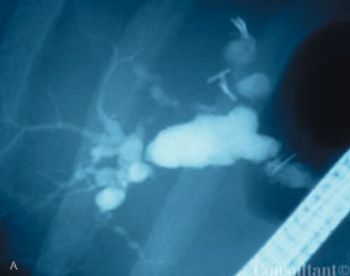
A 41-year-old man complained of upper abdominal pain and malaise of several months duration. He had emigrated to the United States from Korea 5 years earlier.

An obese 55-year-old woman had intermittent dysuria and frequent urination for 4 days and fever, abdominal pain, and vomiting for 3 days. Her history included type 1 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and angina; her medications included insulin, nifedipine, and nitroglycerin.

Many of my patients are confused. So aremany of my colleagues. Official bodies ofexperts barrage the media with pronouncementson what constitutes goodpreventive medicine: screening tests, eatingor abjuring certain foods, avoidance of exposures tosun or environmental hazards, "correct" behaviors. Althoughthey acknowledge that the data are, and alwayswill be, imperfect, these experts try their best to directpeople in the way that the evidence points-for now.

Reiter Syndrome (also called reactive arthritis) manifests as peripheral arthritis that is sometimes accompanied by such extra-articular findings as urethritis, conjunctivitis, and uveitis

n the United States, the number of cases and geographic range of West Nile virus infection have increased since 1999, when the virus first surfaced in the Western Hemisphere. This year, the virus is expected to spread to all states except Alaska and Hawaii.

ABSTRACT: Many patients with presumed mild intermittent asthma have unrecognized persistent symptoms; these can be elicited with specific questioning about coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, nighttime awakenings, and exercise intolerance. Asthma severity may vary with the season. For asthmatic patients with predictable seasonal allergies, prescribe inhaled corticosteroids for a few weeks or months beginning 2 to 3 weeks before usual symptom onset. Successful long-term management requires identification and control of asthma triggers, such as cigarette smoke, house dust mites, cockroaches, molds, and animal dander. Removing triggers or minimizing the patient's exposure to them may allow improved asthma control with lower dosages of corticosteroids.