
My patient reports that erythemanodosum occurred when she took anoral contraceptive (OC) in the1990s.

My patient reports that erythemanodosum occurred when she took anoral contraceptive (OC) in the1990s.

The most appropriate choice is B. The history andphysical findings suggest that the patient may have afracture or contusion of the foot from trauma. There areno systemic signs that suggest an underlying infectious,chronic inflammatory, or oncologic process. A plain x-rayfilm of the foot is necessary to seewhether a fracture is present andwhether immobilization will be necessary.In the absence of fever and localerythema, infection appears unlikely,and a CBC count is unwarranted.

Children often resist examinations forotitis externa because of pain and tenderness.

ABSTRACT: A focused history taking and physical examination directed toward uncovering signs that suggest a serious underlying cause of low back pain are crucial. "Red flags" include pain that lasts more than 6 weeks; pain in persons younger than 18 years or older than 50 years; pain that radiates below the knee; a history of major trauma; poor rectal tone; constitutional symptoms; atypical pain (eg, that which occurs at night or that is unrelenting); the presence of a severe or rapidly progressive neurologic deficit; and a history of malignancy. These markers provide a cost-effective means of guiding your selection of laboratory and diagnostic imaging studies.

Foot ulcerations and infections are the leading cause of hospitalizationamong patients with diabetes; they occur in about15% of these patients. Given the rapidly increasing incidenceof diabetes, physicians can expect to see a growing numberof diabetic foot problems. Here, a group of experts, many ofwhom practice at the renowned Joslin-Beth Israel DeaconessFoot Center in Boston, offer guidance on all aspects of diabeticfoot care. The topics covered range from proven preventivestrategies to cutting-edge wound care techniques that drawon such new developments as growth factors and living skinequivalents. A detailed review of the pathophysiology of thediabetic foot is also included. The emphasis throughout is ona multidisciplinary approach that incorporates the servicesof diabetologists, podiatrists, orthopedic surgeons, orthotists,diabetic nurse educators, and others. Numerous black-and-whiteand color photographs, drawings, algorithms, and charts illustratethe text.

Although many patients with primary HSV-1 infection have no clinicalrecurrences, the failure to seroconvert occurs very seldom-inno more than 1% of patients.

Match each picture with the phrase below that best describes it. The organisms in these pictures might be microscopicor macroscopic, and they can be recovered from skin lesions or clothing by the patient and/or clinician.

Frequent hand washing is extremely important to help prevent nosocomial infections; however, compliance can be a problem. Encourage all staff members who have contact with patients to carry a bottle of quick-drying gel hand disinfectant with them.

A 72-year-old man slipped and fell backward in the bathroom, hitting hishead on the toilet seat; he suffered only minimal discomfort. The followingday, he presented with mild back pain and extensive bruising.

The parents of a 3-year-old boy bring him to your office after hecomplains of genital pain. The child is otherwise healthy; there is no knownhistory of trauma or difficult urination. The child has a low-grade fever and isin mild discomfort.

A 28-year-old man presents tothe emergency departmentwith high fever; progressive, severe,generalized, throbbing headache;blurred vision; and increasingconfusion. These symptoms started3 days earlier.

Which treatment approaches are effective in a woman who has persistent or refractory vaginal trichomoniasis? Should the male sex partner of a patient who has recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis be treated? Answers to these and other questions can be found in the recently updated CDC guidelines on managing sexually transmitted diseases

The differential diagnosis of intrascrotal pathology includes a myriad of benign and malignant entities. Timely detection is imperative to reduce the morbidity associated with many of these disease processes.

ABSTRACT: When a solitary lung nodule is detected, the key question is whether the lesion is malignant. The initial evaluation includes a careful history taking focused on risk factors for malignancy, a thorough physical examination, comparison of current chest films with previous ones, and CT scanning. Radiologic signs that suggest malignancy include lesion size greater than 2 cm in diameter, spiculated margins, lack of calcification, and change in size. Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery or thoracotomy is the next step for patients with a suspected malignant lesion. If the results of the initial evaluation are equivocal, positron emission tomography (PET) scanning is the preferred follow-up.

ABSTRACT: In patients with renal colic, the location of the urinary tract obstruction largely determines the nature of the symptoms (eg, an obstruction in the distal ureter typically produces boring pain that radiates to ipsilateral groin, testicle, or labium). The initial evaluation includes urinalysis, a complete blood cell count, and a renal function panel. A full metabolic evaluation is warranted if the patient has risk factors for or a family history of stone disease, a history of bilateral stone disease, or chronic recurrent urinary tract infection, or if nephrocalcinosis is found on radiographic studies. Noncontrast CT is the imaging study of choice; it is nearly 100% accurate for detecting stone disease. Analgesia and volume expansion are the mainstays of management.

A middle-aged woman reports that for several days she has hada facial rash, some mild facial discomfort, and a low-grade fever. She deniesprevious illness, recent contacts with infected persons, or history of a similarrash.

For 3 days, a 36-year-old woman has had a painful rash on the dominant lefthand. She had noticed a tingling sensation before the lesions erupted. Thepatient is otherwise healthy and takes no medications. She is a teacher.

Match each picture with the phrase below that best describes it. The organisms in these pictures might be microscopicor macroscopic, and they can be recovered from skin lesions or clothing by the patient and/or clinician.Answers and discussion appear on the following page

A 39-year-old man sought evaluation ofnewly erupted skin lesions on his arms.Ten days earlier he had fallen on hisforearms, but no bruises appeared atthat time.

Is there a meaningful percentage of patients who contract Lyme disease but havenone of the early symptoms-neither the rash nor the flu-like symptoms (eg, fever,myalgia, headache, and stiff neck)-and in whom the disease only becomes clinicallyevident in a later stage when it is much harder to treat?
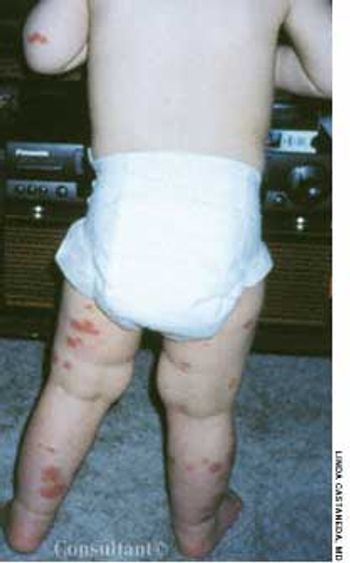
An otherwise healthy 18-month-old boy presented with palpable purpura over the legs, arms, and buttocks; his face, neck, and trunk were spared. The patient was otherwise asymptomatic, alert, and playful. His mother reported that the child had a “stuffy nose and cough” 1 month earlier.

Recently the CDC updated its guidelines for treating sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). This article focuses on genital herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection and human papillomavirus (HPV) infection.

For 1 week, a 2-year-old boy has hadasymmetric erythematous patcheson the anterior trunk. There is nofamily or personal history of eczema.His mother has not used new soapsor detergents recently; there are nopets in the household.
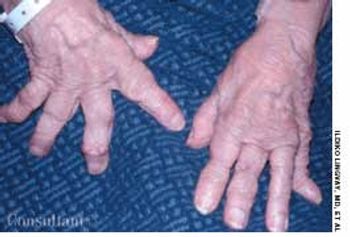
A 76-year-old woman had a 40-year history of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). She had repeatedly refused treatment with disease-modifying drugs, including methotrexate. Nodules began to develop 15 years after the initial diagnosis; they recurred after surgical removal.
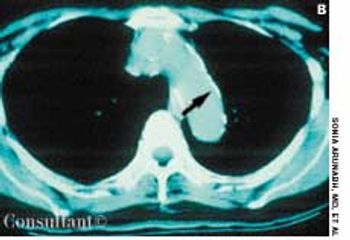
A 72-year-old woman presented for her annual physical examination. She had been treated for tuberculosis 20 years earlier. The patient did not smoke cigarettes; she denied fever, chills, and rigors.