
Among youth aged 10 to 17 years with uncontrolled hyperglycemia dapagliflozin led to a statistically significant reduction in A1c vs placebo in the T2NOW phase 3 clinical trial.


Among youth aged 10 to 17 years with uncontrolled hyperglycemia dapagliflozin led to a statistically significant reduction in A1c vs placebo in the T2NOW phase 3 clinical trial.
Find details on optimizing diabetes care in primary care settings, benefits of GLP-1RAs for patients with HF and diabetes, and tirzepatide use for obesity-related OSA.

Your daily dose of the clinical news you may have missed.
Global prevalence of adults 65 years and older with T1D increased 180% in the past 30 years, researchers reported.
More than 50% of patients with MASH receiving 1 of 3 doses of tirzepatide achieved MASH resolution without worsening of fibrosis vs placebo, according to data from phase 2 study.
The panel of experts from UCSD concludes the discussion on delaying the onset of stage 3 T1D by providing key takeaways and clinical advice on the treatment of patients with this condition.
Focusing on the utilization of teplizumab, the expert panel from UCSD shares insights in how to select patients for this treatment and provide practical tips for the infusion process, and infusion location options.
The panel reviews the TN-10 trial investigating teplizumab, focusing on patient inclusion criteria, patient outcomes, and adverse reactions.
Diabetes specialists from UCSD discuss teplizumab, the first FDA-approved drug for delaying onset of T1D, highlighting its benefits and mechanism of action.

Schafer Boeder, MD and Andrea Stallings, PA delve into the intricacies of autoantibody screening tests for T1D with detailed insights on their methodologies, interpretation nuances, and practical analysis considerations.

Following a couple of audience polling questions, Andrea Stallings, PA and her UCSD colleagues, comment on identifying suitable candidates for T1D screening, understanding autoantibodies involved in this condition, and determining when to rescreen those at risk for disease progression.

Addressing the significance of acting early in T1D care, a group of diabetes experts delve into the impact of delaying intervention during stage 2 of the condition.

Schafer Boeder, MD and his colleagues provide a comprehensive overview of the stages of T1D in patients with diabetes, highlighting the various signs and symptoms associated with each stage.

A panel of experts on diabetes management introduce themselves and provide an overview of the condition, highlighting risk factors, disease burden, and the benefits of collaborative care.

Your daily dose of the clinical news you may have missed.
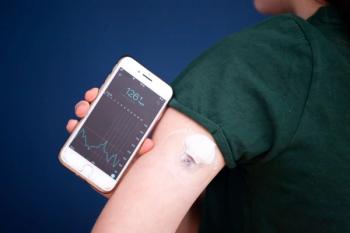
Abbott becomes the second company to receive FDA clearance for an over-the-counter continuous glucose monitoring system.

There are lots of products in development for weight loss and to treat other metabolic diseases which means more options for more people.

Your daily dose of the clinical news you may have missed.
ENDO 2024. New findings suggest GLP-1RAs and SGLT-2is may be more beneficial than other diabetes agents for patients with T2D and MASLD.
The pluripotent GLP-1 mimetic reduced risk for renal disease endpoints by 24% and MACE by 18% plus significantly retarded decline in eGFR vs placebo, study authors reported.

Your daily dose of the clinical news you may have missed.
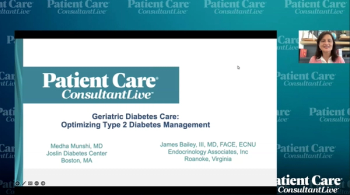
Medha Munshi, MD, and James Bailey, III, MD, FACE, ECNU, discuss older adult patient cases and review their respective treatment approaches, sharing final takeaways to provide practical insights for managing diabetes in this patient population.

Medical experts discuss the importance of optimizing medication regimens for older patients with diabetes, emphasizing the need to keep treatment plans simple and highlight the value of continuous glucose monitors in monitoring patients and adjusting therapies accordingly.

Key opinion leaders in the management of diabetes discuss the process of deprescribing, or the process of medication simplification to encourage adherence and ease of regimens in older adult populations with type 2 diabetes.

Drs Medha Munshi and James Bailey offer insights into navigating the type 2 diabetes treatment landscape. They emphasize the importance of prioritizing cardiovascular and renal outcomes when selecting treatments for older adult populations.