
The reduction in dementia is not simply the result of the drugs reducing their blood pressure.

The reduction in dementia is not simply the result of the drugs reducing their blood pressure.

This condition is a more important risk factor than previously thought and should not be taken lightly.
Does this look like melanoma? Which is not true of Löfgren syndrome? Yoga and Afib; what cause of mental confusion? Skin lesions and HIV.. . . See if you can answer this week's quiz questions.

Löfgren syndrome is a form of acute sarcoidosis characterized by a triad of symptoms: hilar adenopathy, erythema nodosum, and arthralgias.
Stroke survival and thoughts of suicide; PCP shortage; pediatric headache treatments; antidepressants and prolonged QT interval; calcium supplements, men, and CVD.

Topiramate and trazadone showed only limited efficacy in pediatric headache. For flunarizine, pizotifen, propranolol, and valproate, no evidence was found to support their use.

Suicidal ideation among stroke survivors (7.8%) was higher than among those with a history of MI (6.2%), diabetes (5.2%), and cancer (4.1%).
Nervous system disorders are common, but the symptoms often resemble those of other medical conditions, complicating the diagnosis.
Neurologic complications associated with Down syndrome include dystonia, epilepsy, psychiatric problems, cardiac defects, and auditory and visual defects.

Stigma correlated most strongly with inability to work and was greater for chronic migraine than for epilepsy or episodic migraine.
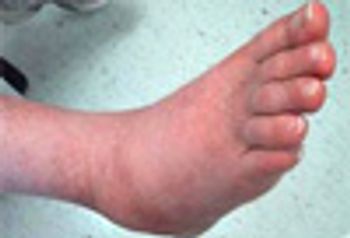
The primary goal of treatment is to minimize the progression of foot deformity by achieving and maintaining structural stability of the foot and ankle.

The worldwide sex ratio of MS has been substantially changing over the last century. Environmental factor/s appear to be at work in a sex-specific manner.

A series of studies unequivocally show a true absence of autoimmune disease aggregation in MS patients and their families.
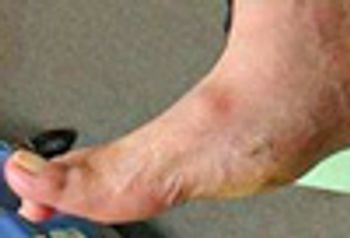
This enigmatic, destructive, and deforming condition most often affects persons who have diabetes.

Primary care physicians can take the lead in helping address these additional comorbidities in their patients with asthma.

Medication is seldom necessary. Education is the key element of therapy. An explanation of the process and a discussion of possible triggers-lack of sleep, stress, missed meals etc-is the most key intervention.

Primary care physicians need to be aware of the relationship, especially because the incidence in older women is high.
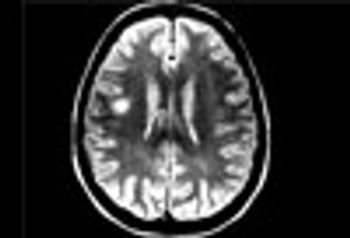
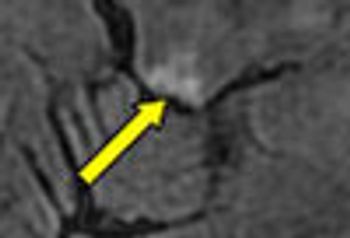
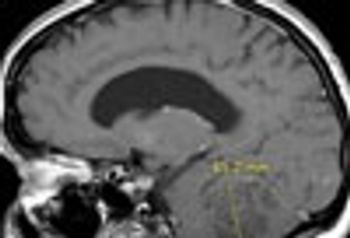
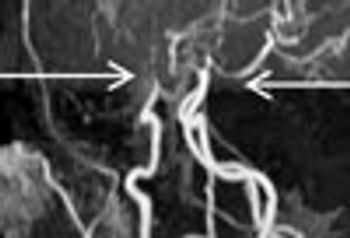
MRI is now central to the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Because of the modality’s high sensitivity to inflammation and demyelinating plaques, roughly 90% of all MS diagnoses are now based on MRI findings.

Sodium levels are known to be elevated inside the brain stem, cerebellum, and temporal poles early in the course of MS. This study showed total sodium concentrations to be significantly increased in advanced disease-particularly in normal-appearing brain tissues, concomitant with disability.

After a cardiac event, many patients experience psychiatric symptoms, including depression, but more recent studies have paid attention to anxiety.

Patients who are experiencing pseudoexacerbations or confirmed exacerbations of disease should be assessed and monitored for depressive and anxiety symptoms.
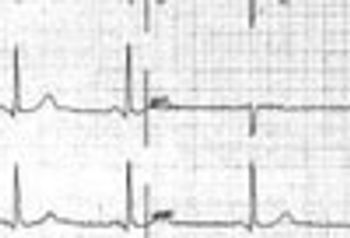
Signs and symptoms of organophosphate poisoning occur through an exaggerated cholinergic or nicotinic response at the neuronal synapse.

The excessive number of deaths in placebo-treated patients largely was the result of MS-related causes, especially MS-related pulmonary infections.

Epstein Barr virus activates potentially immunopathogenic and neuropathogenic proteins in cells deriving from peripheral blood mononuclear cells and astrocytes.

The monoclonal antibody alemtuzumab reduced disease progression and accumulation of disability versus interferon in phase 3 clinical trials.