
Should acute infection with hepatitis C virus (HCV) be treated? If yes, what is the recommended treatment?

Should acute infection with hepatitis C virus (HCV) be treated? If yes, what is the recommended treatment?

The prevalence of anal human papillomavirus (HPV) infection was 24.8% among a study population of 222 heterosexual men who confirmed that they had never engaged in male-male sexual intercourse. 1

The CDC's Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommends that all persons older than 60 years be immunized against herpes zoster with a single dose of the live, attenuated virus vaccine. Furthermore, it urges clinicians to offer the vaccine at the first available clinical encounter.

I work for the Child Protection Team at a local university. Recently, I saw a 9-year-old girl who had been taken to the local emergency department (ED) with sudden left-sided abdominal pain.

Several recent studies from Europe and the United States confirm that tailoring the dosage and duration of pegylated interferon alfa 2b and ribavirin therapy can optimize treatment of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection.

Specialty medications constitute the fastest-growing segment of drug spending under the pharmacy benefit. This study evaluated the impact of a specialty pharmacy prior authorization (PA) program on prescription drug costs for biologic response modifiers (BRMs) used in the treatment of persons with rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn disease, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, psoriasis, and other spondyloarthropathies. A retrospective, case-control, one-to-one matching approach based on patient age, sex, and client characteristics was used. Case clients were enrolled in the specialty pharmacy PA program from January 1 through December 31, 2005. The control group consisted of clients who were not enrolled in the program during this time. The average costs per eligible member per month (PMPM), for the total, plan, and member were $1.32, $1.29, and $0.03, respectively, in the case group, and $1.44, $1.41, and $0.03, respectively, in the control group. Clients who implemented the specialty pharmacy PA program for BRMs saved an estimated total cost of $0.12 PMPM. Implementing a specialty pharmacy PA program reduced BRM costs. (Drug Benefit Trends. 2008;20:26-31)

Identifying the cause of a persistent, asymptomatic aminotransferase elevation can be challenging. The possible diagnoses are many and varied. To narrow the differential, begin with a detailed history.

Fear of bioterrorism persists because of new reports of biological warfare, including the most recent attack that involved a Russian spy who was poisoned with polonium-210. However, vaccination against potential biological weapons, such as anthrax and smallpox, is controversial because of associated adverse effects.
Six months after testing positive for HIV in 10 bands, a 24-year-old homosexual man presented with a macular rash on his palms and soles. He first noticed the lesions 2 weeks earlier; they were not pruritic or painful. He also had a brighter, more inflamed rash in the groin and antecubital fossae that was presumed to be a yeast infection and was treated with fluconazole. He had no other symptoms.

NAPLES, Italy -- Long-term antiviral treatment may partly reverse liver cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C, researchers here said.

Within the past 7 years, the incidence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Clostridium difficile infections has significantly increased. Risk factors for MRSA infection include previous antibiotic therapy and living arrangements such as prisons or military barracks that involve close, frequent contact with infected persons. Treat stable patients with MRSA skin infections with oral antibiotics in addition to incision and drainage; hospitalization and intravenous antibiotics are recommended for patients whose condition is unstable or who are unlikely to adhere to an oral regimen. A new strain of C difficile, BI/NAP1, has been associated with recurrent infection; more severe disease that mandates urgent colectomy; and dramatically higher mortality in vulnerable populations, such as older adults. Although oral metronidazole has been the mainstay of treatment of C difficile infection, oral vancomycin may be slightly more effective in patients with severe disease.

HOUSTON -- Human papillomavirus (HPV) infections are likely buoying up oropharyngeal cancer rates while other head and neck cancers decline, researchers said.

BALTIMORE -- When treating hepatitis B and HIV co-infection, physicians should use caution with the antiviral drug entecavir (Baraclude), researchers here said.

The incidence offluoroquinoloneresistantgonorrheacontinues torise in the UnitedStates, and the CDC isnow urging physicians toprescribe cephalosporinsfor patients with gonococcalinfections.

HOUSTON -- Patients with hepatitis C virus infection may have a 20% to 30% increased risk of developing non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, researchers here reported.

I read with interest the case of lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV) featured in Dr Henry Schneiderman's recent "What's Your Diagnosis?" column (CONSULTANT, February 2007, page 187). As one who has had a career-long interest in sexually transmitted disease, I feel compelled to make a few remarks regarding this case.

Yesterday, my laboratory reported to me that a pharyngeal swab tested positive for chlamydial infection (detected by DNA testing). This was not the first time I diagnosed sexually transmitted pharyngeal chlamydial infection in a patient. Readers beware: it does happen.

ATLANTA -- After a decade of decline, syphilis rates rose by 19% from 2000 through 2003, largely because of cases among men who have sex with men, according to a CDC study.

ATLANTA -- The rate of fluoroquinolone-resistant gonorrhea has become so high in the U.S. that physicians have been urged to switch to the last line of defense, the cephalosporins.

BOSTON -- Co-infection with HIV and either hepatitis B or C remains a clinical challenge, but new therapies appear to have increased the opportunities for effective treatment.

The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommendsthe zoster vaccine for persons aged 60 years and older, whether ornot they have had a previous episode of herpes zoster.

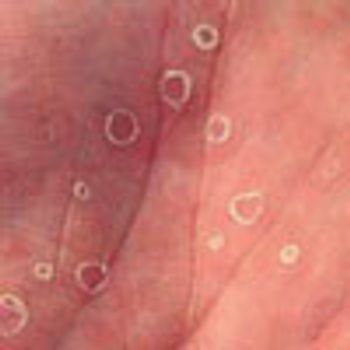
It is sometimes difficult for women with genital warts to visualize their lesions. Offer patients a hand-held mirror so that they can see what the lesions look like, and recommend that they use a similar mirror at home to monitor the lesions' size and number.

This infection is caused by reactivationof varicella-zoster virus (VZV),which may remain latent in thedorsal root and cranial nerve gangliafor decades. Reactivation oftenoccurs for no apparent reason, althoughstress and immunosuppressionmay increase the risk.

This infection is caused by reactivationof varicella-zoster virus (VZV),which may remain latent in thedorsal root and cranial nerve gangliafor decades. Reactivation oftenoccurs for no apparent reason, althoughstress and immunosuppressionmay increase the risk.

LONDON -- Treating herpes simplex with valacylovir (Valtrex) reduces the levels of HIV in women who are infected with both viruses, according to researchers here.