
A new study found the probability of initiating psycholeptics and having a postpartum psychiatric emergency was lower in early and late discontinuer groups vs the continuer group.

Multisite Chronic Pain Increases Dementia Risk, Hippocampal Injury: UK Biobank Analysis

Online E-health Program Reduces Daily Opioid Use, Improves Pain Scores vs Usual Care

A new study found the probability of initiating psycholeptics and having a postpartum psychiatric emergency was lower in early and late discontinuer groups vs the continuer group.

About 60% of dual vapers experienced depression and 52% experienced anxiety, according to findings from a survey of over 2500 youth and young adults.

Nearly half of US adults aged 50 to 80 years report at least 1 symptom of addictive eating, a caution flag for primary care according to these experts.

Rebekah Bernard, MD, family physician and national speaker on physician wellness shares 3 pieces of advice on connecting with colleagues again.

An experimental program shows promise for better integration of screening for and treating alcohol use disorder into primary care practice.

Find key takeaways from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's latest Youth Risk Behavior Survey in our new slideshow.

Primary care is increasingly the setting for mental health discussions, diagnosis, and treatment, underscoring the need for both structural and process change.
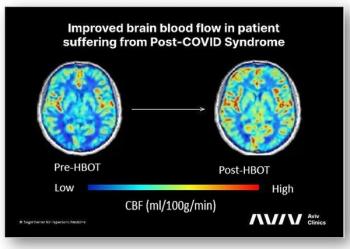
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy in a randomized placebo-controlled trial resulted in improved global cognitive function, energy, sleep, and pain interference in long COVID patients.

Mental health issues among health care professionals have always been normal; now that we can acknowledge them, we must, says a family physician and wellness advocate.

While 60% of US psychologists have no openings for new patients, demand for treatment continues to rise, especially among adolescents and health care workers.

A vaccine against fentanyl could stop the intense euphoria the drug creates and also block dangerous physiologic responses like respiratory depression, a new study suggests.

Not every physician has to be a mental health expert to assist their colleagues, staff, and patients in improving their mental well-being. Just start the conversation.

For the first time, the task force recommended screening children aged 8 and older for anxiety in primary care settings.

There was no change in physician burnout in the past year and it remains significantly higher than pre-pandemic times, according to a new nationwide survey.

Telehealth continues to support continuity of care and to increase access to and willingness to use the health care system, according to survey authors.

The numbers drive up concern but do not provide context for this very complex issue, according to the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention.

The percentage of adults who received any mental health treatment increased, women were more likely than men to receive treatment, and 3 more key findings.

Family physicians and psychiatrists were the specialties with the greatest number of visits, according to study authors.

Anxiety may affect cardiometabolic health earlier in life than previously thought, according to a new long-term study of US middle-aged men.

Dr Ahmad's book explores in depth the complex long-term consequences of COVID-19 for medicine, mental health, and social conventions.

The prevalence of mental disorders has been rising globally and the conditions today remain a leading cause of disease burden worldwide, found 30-year systemic analysis.

Americans with anxiety, depression, and PTSD would be willing to try ketamine, psilocybin, and MDMA if they worked better than traditional medications, a Harris Poll finds.

Suicidal thoughts and behaviors among US adults arise due to several factors, including geography, socioeconomic status, and race and ethnicity, according to new CDC report.

Older adults who report being "highly lonely" are up to 2.5 times more likely to use opioid analgesics, sedatives, and anxiolytics.

Compared to psychiatrists and subspecialists, the proportion of visits to primary care was higher for patients with depression or anxiety and any mental illness in a new cross-sectional study.