
All News




The site offers guidance on key topics encountered in clinical practice, as well as short, quick-reading features that emphasize diagnostic quizzes, fast solutions, and color photography. Among the most popular features are "Dermclinic," "What's Your Diagnosis?" "Photoclinic," "What's the 'Take Home'?" and "Photo Quiz."


• Introduction • Limitations of Current Therapies • Safety and Effectiveness of Modern Insulin Therapy: The Value of Insulin Analogs • Addressing Barriers to Timely Intensification of Diabetes Care: The Relationship Between Clinical Inertia and Patient Behavior • Insulin Intensification: A Patient-Centered Approach
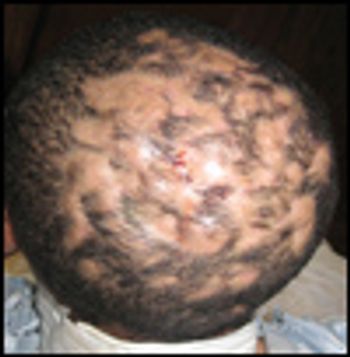
For the past 7 years, a 32-year-old African-American man had multiple nonpruritic scalp abscesses. He also reported intermittent fever and joint pain. The abscesses had been drained on many occasions, and he had received several antibiotics, although no organisms had been isolated. Collagen vascular disease, SAPHO syndrome (synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, osteitis), discoid lupus, and cutaneous sarcoid had been ruled out. During the past 7 years, he had been treated with prednisone, methotrexate, and hydroxychloroquine without any response.

Many elderly patients have fragile, atrophic skin.

Poor adherence is a problem we all confront regularly.

For my patients who use nasal spray, I advise them to use the right hand to spray into the left nostril and the left hand to spray into the right nostril.

Advise runners to write the date they start wearing a pair of running shoes on the underside of the tongue, with a permanent marker.

For more than a week, a 74-year-old man has had diminished vision in his left eye. He reports that the problem started acutely with a sensation of flashing lights in the affected eye, followed by the presence of dark floaters for several days.

American medicine is undergoing the greatest financial scrutiny in its history. The hue and cry for reform stems primarily from the soaring costs of health care. However, placing the blame for these costs solely on increased utilization of technology, cutting-edge pharmaceuticals, cost-shifting hospitals, and physicians misses a bigger mark.
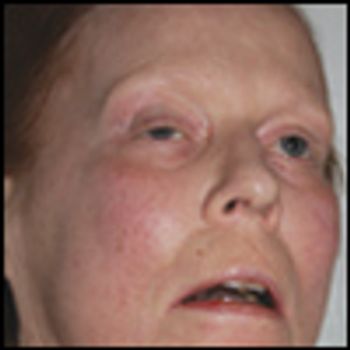
A 56-year-old woman seen during physician’s hospice visit. Stormy course from lupus nephritis, dialysisdependency, repeated episodes of dialysis-catheter–related peritonitis, each treated and followed by Clostridium difficile–associated disease.

What underlying disorders should primary care clinicians be alert for in patients with migraine?

Text files can be sent as e-mail attachments formatted for Macintosh or Windows. E-mail your submission to myra.partridge@ubm.com. The publisher supports Microsoft Word for Macintosh and Windows. When preparing the manuscript, please keep the format simple (ie, no hidden codes that indent text). Also, please do not use codes that place references at the bottom of each page.

Pay for performance (P4P) is causing physicians to examine how they provide care individually and collectively within local health systems. It is the most recent attempt by Medicare and commercial payers to reduce the cost and improve the outcomes of health care. Understanding P4P and deciding how to manage the multiple programs being implemented by payers will challenge physicians' ethics and practice resources. Improving health care for musculoskeletal diseases will require cooperation among the specialties that share responsibility for this care and improved methods for coordinating and documenting it.

Some women 75 and older who are in good health and have excellent functional status may benefit from mammography screening, while others who are in poor health and have short life expectancies probably do not.

Dr Mara Schonberg does an excellent job of presenting the pros and cons of continued breast cancer screening in elderly women and of explaining why the current guidelines are vague. My purpose here is not to take issue with anything that she presented, but to make some additional points in favor of continuing breast cancer screening into a woman's "golden" years.

