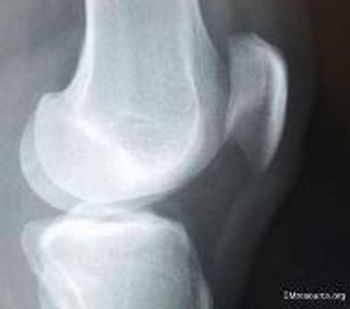
While demonstrating his retro dance moves, a 31-year-old injures his knee doing “the Twist.” Now he can barely walk. Would you order an x-ray?

While demonstrating his retro dance moves, a 31-year-old injures his knee doing “the Twist.” Now he can barely walk. Would you order an x-ray?

An occult fracture in the knee is most often a nondisplaced lateral tibial plateau fracture.
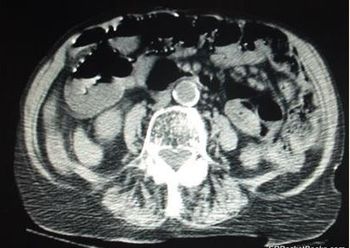
Symptoms have been present for 2 days. Lab studies are notable for BUN (43 mg/dL) and CO2 (21 mmol/L). The real problem is visible on CT of the abdomen and pelvis. Your diagnosis?
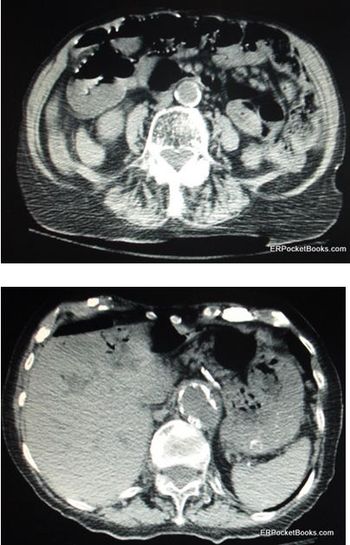
At risk for mesenteric ischemia-an uncommon but feared cause of abdominal pain-are the elderly and chronically ill.
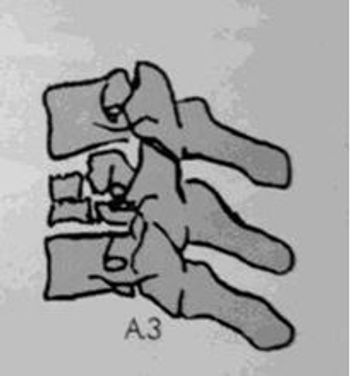
Rushing down a flight of hardwood stairs wearing socks lands a 38-year-old man on his back and then in the ED for evaluation of back pain that prohibits walking. Can you spot the problem on the x-ray?

Spinal fractures are most often the result of falls, motor vehicle accidents, or sports injuries. Lateral process fractures may occasionally be associated with renal injury.
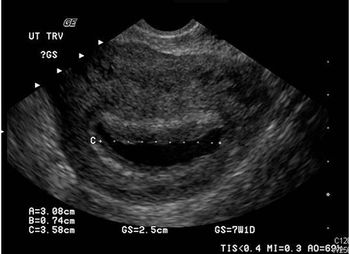
The pain and bleeding have persisted for 2 days. She last menstruated 5 weeks ago but doubts she is pregnant. Take a close look at the ultrasound image. Your Dx?

Results of a pelvic sonogram reveal the etiology of lower abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding in a 26-year-old woman.
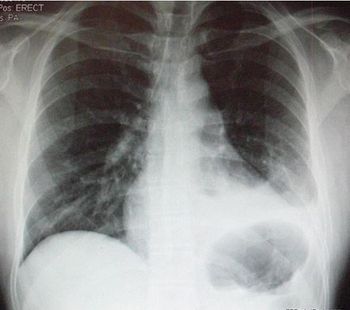
Recovery from a hemopneumothorax had progressed well for this 29-year-old man until today when he presents to the ED with dyspnea and pleuritic chest pain. What do you see on the chest x-ray?

Persistent symptoms of hemothorax or pneumothorax, in the absence of new x-ray findings require further inquiry, including chest CT, to rule out PE.
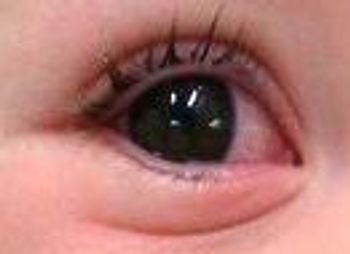
A diagnosis of adenovirus had been made at an urgent care center and zinc-oxide diaper cream was recommended. The rash did not respond and the child grew more irritable. There's more to the case, here.

Kawasaki disease is an uncommon febrile vasculitis of unknown etiology. It typically affects young children and can lead to significant morbidity and mortality if not diagnosed and treated.
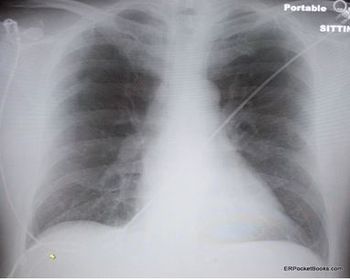
The symptoms have worsened over a 2-month period. Past medical history is unremarkable. Here, review the ED chest x-ray film and ECG. Do you see any clues to a diagnosis?


Progressive numbness in 3 fingers on both hands led this computer programmer to diagnose himself as having carpal tunnel syndrome. But, there's more to this story.

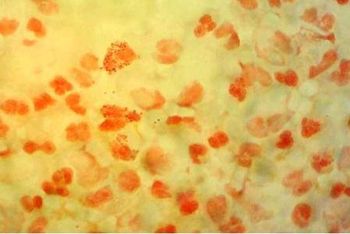
A 35-year-old woman, in the ED for the second time in the same day, is described by ambulance medics as "bizarre." ECG and labs are normal except for elevated urinary and peripheral WBC counts. More, here.

Bacterial meningitis presents with the triad of headache, fever, altered mental status. Stiff neck, vomiting, and photophobia may also be present.
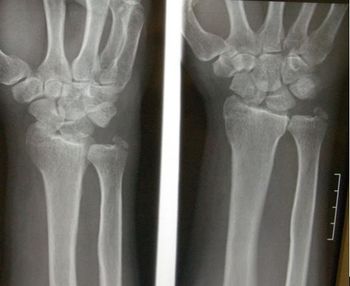
Test your radiographic skills with this emergency medicine case. Can you spot the injury? Is there more here than initially meets the eye?


Headaches have been awakening a man in his mid-40s at about 3 in the morning for a period of 2 weeks. On this, his second visit to the ED for the symptom, he claims numbness in one arm and reports vomiting earlier that evening. More details of the case, here.

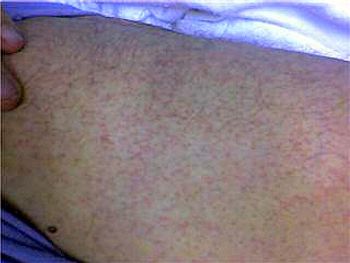
Recent travel to the Caribbean is the key clue that led to the diagnosis of dengue fever, which caused maculopapular rash, fever, headaches, and body aches.


Discitis, a bacterial infection within the vertebral disc, typically results from seeding during an episode of bacteremia.

A 46-year-old man with a history of HIV infection presents to the emergency department for left flank pain. A lateral x-ray film of the patient’s lumbar spine is shown. What is the diagnosis?

Attention to detail and a systematic approach combined with the knowledge and use of specific diagnostic exam tests will help minimize missing common orthopedic soft tissue injuries. Tips here.

Awareness of medical conditions and drugs that can suppress the immune system or cause other complications is key to providing safe and appropriate care for immunosuppressed patients. Details here.

Keeping your patients satisfied can help keep you sane-and possibly even happy. Here: strategies for enhancing clinician/patient communications.

Here: a fruitful approach to the evaluation of dizziness that focuses on timing, triggers, and associated symptoms, followed by a complaint-directed physical exam with special attention to specific germane aspects of the neurologic exam and (when indicated) selective testing.