
DALLAS - The American Heart Association in a set of recommendations on "healthy living" has taken new aim at consumption of saturated fats and trans fats.

DALLAS - The American Heart Association in a set of recommendations on "healthy living" has taken new aim at consumption of saturated fats and trans fats.

BOSTON ? High levels of retinol binding protein 4 (RBP4), which transports vitamin A as its main job, may be an early warning sign for insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes, according to researchers here.

WASHINGTON - Lorcaserin, an investigational drug for the treatment of obesity, was successful at producing weight loss ranging between four and 7.9 pounds (1.8 to 3.6 kg) in a 12-week study, reported investigators here.

WASHINGTON ? Among patients who live more than 50 years with type 1 diabetes, a significant proportion show evidence of a residual population of insulin-secreting beta islet cells, according to research presented here.

Plumbing analogies can help asymptomaticpatients comprehend the seriousnessof elevated lipid and bloodpressure levels.

My patient is taking a statin for hypercholesterolemia, and his liver enzyme levelsare markedly elevated. How should I proceed?

The treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is based on the patient's presenting symptoms and any significant abnormal findings. Symptoms can be managed with combined oral contraceptives (OCs), insulin-sensitizing agents, antiandrogens, and medications used to induce ovulation.

A long list of foodstuffs have been blamed for the nation's increasingly widespread weight and health problems. Now the spotlight has been turned not on what Americans eat--but on what they drink.

OAKLAND, Calif. - Capping prescription drug benefits at ,000 by Medicare+ Choice plans was a pennywise and pound foolish approach to cost containment, said researchers here.

PAWTUCKET, R.I. - Patients may not be getting the message about the heart risks associated with dyslipidemia when the message is delivered by-the-numbers, according to researchers here.

Which test--antistreptolysin O titers, coronary angiography, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), Western blot testing for Borrelia burgdorferi, or genetic testing for long QT syndrome--would help you diagnose a young man with worsening chest pain, frontal headache, and diffuse muscle and joint pain?

A 59-year-old man has had chest discomfort for several months. He firstnoticed the symptoms when he was doing heavy lifting and moving at work.The discomfort starts in the midsternal region and radiates to the left shoulderand arm. It is often accompanied by diaphoresis, but there is no dizziness ordyspnea. The discomfort always subsides a few minutes after the patientstops the activity that brought it on. More recently, he has experienced similarsymptoms while walking up steep hills on the golf course and dancing at awedding.

The authors of the Women’s HealthInitiative (WHI) study involving50,000 postmenopausal women concluded thata low-fat diet (goal: 20% of total calories) had no significant effect on the incidence of breast cancer, coloncancer, or heart disease. What should we be telling our patients?

In this article, I review several interventions that have been shown or are postulated to reduce breast cancer risk in women with no history of the disease; these include chemoprevention, physical activity, weight control, diet, alcohol use, and avoidance of specific carcinogens.

Q:What is the best and most efficient method ofevaluating pulmonary function in primary careoffice practice?

Excess weight increases the risk of having a heart attack, stroke, high blood pressure, arthritis, diabetes, depression, fatigue, and certain types of cancer. Losing weight and keeping it off are very difficult for most persons who are overweight. Here are some suggestions to help you lose pounds and keep your weight down.

In this article, we review the factors that contribute to obesity. We then describe effective approaches to weight control, including exercise, dietary modification, drug treatment, and bariatric surgery.

A 36-year-old man who had collapsedand sustained a bruised right shoulderwas brought to the emergency departmentwith acute emesis, cephalgia,blurred vision, aphasia, and righthemiparesis. He was confused but ableto follow simple commands.

Every day, patients are bombarded with conflicting information about what constitutes a healthful diet. By focusing on patients' needs, risk factors, lifestyle, and eating habits, you can help them make the right choices.

ABSTRACT: To provide effective dietary counseling, offer practical strategies that mesh with patients' lifestyles. Emphasize what to add to or include in the diet rather than what to avoid or cut back on, and aim for progress and small changes rather than a complete makeover. Recommend that patients "colorize" their diet (ie, include more colorful fruits and vegetables). Those who need to lose weight should keep a food log of all they eat and drink and use the "plate method" to control portion sizes.
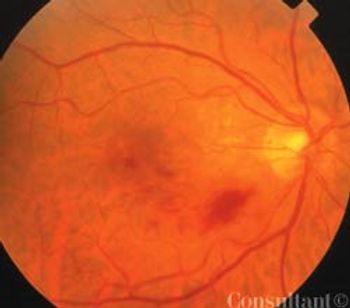
A 74-year-old woman had difficulty with reading for long periods. Recently, her vision seemed "milky." The patient was taking no medications; she had no significant medical history other than allergies to penicillin, codeine, and erythromycin.
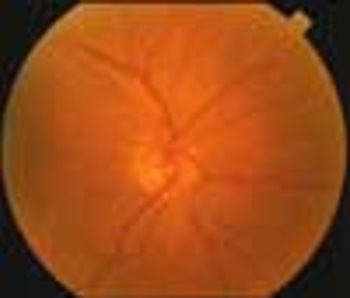
A 71-year-old man presented with a 6-week history of decreased vision in his right eye. The patient, who had hypertension and migraine headaches, had successfully recovered from a stroke that occurred 1 year earlier. His medications included aspirin, 81 mg/d, clopidogrel, atenolol, and furosemide. He also took gabapentin, 300 mg hs, for his migraine headaches. He had a remote history of cigarette smoking.

During the past decade or so, a multitude of weapons have emerged in the battle against the complications of diabetes mellitus.

A 56-year-old woman presents for a routine examination. She has been healthy, and results of previous examinations have been normal.

Although lipoprotein levels are known to be reduced in critically ill patients, the prognostic significance of this in patients with sepsis has not been established. However, a study recently conducted in Taiwan is worth noting; it found that low levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol on day 1 of severe sepsis were associated with increased risk of death.