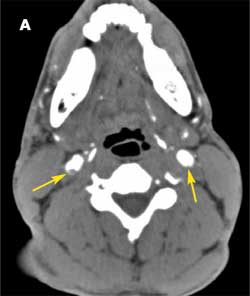
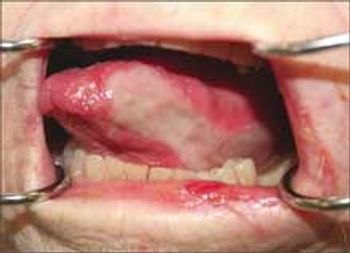
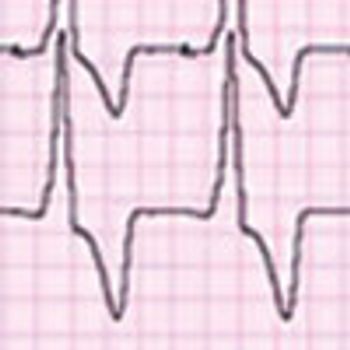
Here is a common clinical scenario. Your patient was admitted to the hospital with an acute myocardial infarction (MI). Intervention has been successful, and the patient's condition is now stable. The cardiologist is concerned about the patient's hemoglobin value of 9 g/dL. Active bleeding, hemolysis, and other potential causes of anemia (iron or vitamin B12 deficiency, for example) have been excluded. The decision is made to transfuse to raise the hemoglobin level above 10 g/dL.