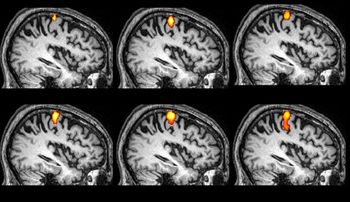
Results from the CRYSTAL-AF study find that nearly one-third of patients who experience cryptogenic stroke may have undetected atrial fibrillation.

Results from the CRYSTAL-AF study find that nearly one-third of patients who experience cryptogenic stroke may have undetected atrial fibrillation.

A recent white paper declares it time to abolish the ambiguous term. Given current knowledge of atrial fibrillation, the 60-year-old description serves only to confuse.

Men who engage in intensive workouts early in life may increase their risk for cardiac arrhythmias when they are older, a new study finds.

Aging baby boomers will more frequently appear in primary care offices with cardiovascular diseases that place them at high risk for both clotting and bleeding. Many will also have atrial fibrillation. Is there a sure-fire therapeutic formula for all?

In a clinical trial setting, performance of the new oral anticoagulant and the long-time gold standard was similar. In the real world, where adherence can be a problem, there is a risk/benefit ratio to consider.

Warfarin continued in the periprocedural period yielded lower rates of stroke, TIA, and minor bleeding than use of heparin to bridge catheter ablation surgery for AF.

A small study provides good evidence that radiofrequency ablation as first-line therapy has a lower failure rate vis a vis recurrence of AF when compared with antiarrhythmic therapy. But, there is more to this story.

According to a study published in the British Medical Journal, the risk of atrial fibrillation/atrial flutter is greater in NSAID-naive patients than in those with previous exposure.

Four updates to the guidelines are important for primary care physicians to review.

In clinical scenarios where warfarin is still the drug of choice for anticoagulation, it is still a challenge to achieve optimal time in therapeutic range. Is there promise in a new dosing paradigm?

Results of a new study suggest that number of LAA lobes may one day be useful as an element of the CHADS2 scoring system for embolic risk in patients with atrial fibrillation.

Comprising 15,400 patients from 46 countries, the RE-LY AF registry offers a notable opportunity to study variations in presentation of atrial fibrillation and its risk factors.

In dialysis patients, anticoagulation for AF may be cause for clinical equipoise, regardless of bleeding risk score. New research, reported here, may begin to shift the balance.

An observational study of patients with atrial fibrillation suggests that routine screening for depression at office visits may help augment treatment.

A new study provides more evidence of important bidirectional relationships between AF and other cardiovascular comorbidities.

Risk factor control is essential to reduce the symptom burden and severity of atrial fibrillation. A new study finds that weight loss is a highly effective tool in an overall mitigation strategy.

A new study finds a lower incidence of AF in non-White races even though these groups have a higher risk of comorbidites that predispose to AF.

Andexanet alfa is a recombinant factor Xa molecule that binds to and sequesters factor Xa inhibitors in the blood, making them unavailable to bind to native factor Xa.

In new-onset atrial fibrillation there is good evidence for obtaining a troponin T level. High levels are associated with highest rates of stroke, embolism, and cardiac mortality.

Dabigatran was shown in post-hoc analysis of the RE-LY trial to be associated with an increased risk of MI compared with warfarin.

Rivaroxaban when used to treat patients with atrial fibrillation who have had a previous MI is associated with higher risk for adverse events.

Whether to prescribe an antiplatelet or antithrombotic agent for a patient who has AF but is otherwise healthy can be a difficult decision.

Cardioversion for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation must include pre- and post-procedure anticoagulation to avoid thromboembolic risk.

Only one agent can be used for anticoagulation in individuals with mechanical valves.