Atrial Fibrillation
Latest News
CME Content


What does the patient with atrial fibrillation who would benefit from oral anticoagulation look like today? Q & A, here.

Results of the LEGACY study show long-term weight loss decreases AF burden and supports sustained sinus rhythm. A short slide show summarizes the 2015 ACC late-breaking abstract.
A small study highlights a big point: manage risk factors that affect the atrial fibrillation substrate and ablation therapy success rates improve (ARREST-AF Cohort Study).
What is your command of the components of this risk prediction tool for patients with atrial fibrillation? Find out with our 4-question quiz.
The absence of an antidote may soon disappear as a reason to avoid prescribing a novel oral anticoagulant to patients with atrial fibrillation, based on promising phase III trial results.

When is a rhythm control strategy appropriate? Which patients are candidates for amiodarone? When is AF ablation the answer? Here, a top-line review of rhythm control for atrial fibrillation.
The risk for major bleeding and GI hemorrhage in patients taking dabigatran was greater than in those taking warfarin; warfarin, however, was associated with a greater risk of intracranial hemorrhage.
In analysis of this randomized controlled trial of apixaban vs warfarin for nonvalvular atrial fibrillation, there was an increased risk of stroke and systemic embolism among patients taking amiodarone and warfarin.

New drugs that treat stubborn illness seen often in primary care lead this group of Top 5 Papers for 2014. Type 2 diabetes, cryptogenic stroke, and hep-C are key targets.

A nurse describes his own bout with atrial fibrillation-the symptoms and his attempts to cardiovert to normal rhythm-from his hospital bed.
Overall it looks as though pharmacologic rate control is still the preferred therapy for new onset AF, but a new study identifies some interesting trends in the use of drugs for both rhythm and rate.

Atrial fibrillation and dementia have long been linked, partly because both tend to affect the elderly. But there may be a causal link as well related to management of anticoagulation.

The recent AFFORD trial suggests no clinical role for omega-3 fatty acids in preventing atrial fibrillation or in modulating disease markers.

A new study finds that iPhone-based technology deployed in local pharmacies can detect asymptomatic atrial fibrillation. iECG anyone?

Results of a recent study suggest the presence or absence of CMBs may help refine risk prognostication in patients with AF.

The cost vs the benefit of community screening for disease is often hotly debated. A new study suggests that detection and treatment of asymptomatic AF may be worth that effort.
Lone atrial fibrillation describes isolated episodes of AF that have been previously considered benign. A revised picture is emerging, according to a new study.

A very large observational study heightens concern around use of digoxin in the treatment of newly diagnosed atrial fibrillation, despite guideline recommendations.

A new study identifies obesity and inactivity as independent risk factors for atrial fibrillation in postmenopausal women. Exercise attenuated the risk in the study cohort.
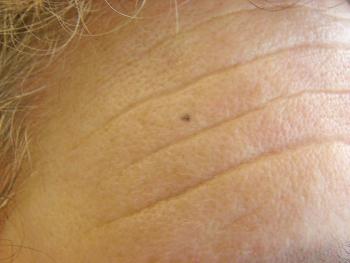
A new dark spot on the forehead; overprescribing of benzodiazepines; alcohol and atrial fibrillation . . . can you answer the quiz questions on these topics?

A very large Swedish study and meta-analysis found a dose-response relationship between incident atrial fibrillation and alcohol, with an approximate 8% increase in risk for the arrhythmia per daily drink consumed.

High-sensitivity troponin T and N-terminal-pro-BNP were shown in 2 important studies to help predict risk of stroke and embolic events in patients with atrial fibrillation.

In a proof-of-principle study, German researchers evaluated an affordable, accessible, and cost-effective way to help diagnose atrial fibrillation after ischemic stroke, with promising results.
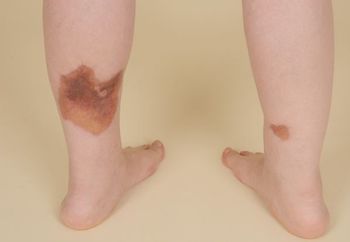
Put yourself to the test: This week’s quiz questions you about skin disease, diabetes, sarcoidosis, atrial flutter, and pain medications.