Atrial Fibrillation
Latest News
CME Content

An 86-year-old woman presented with a 1-week history of worsening dyspnea, wheezing, and orthopnea. She denied chest pain, cough, or fever. She did not smoke cigarettes. Her oxygen saturation was 86% on 2 L/min via nasal cannula.

Gout, once considered a disease of kings, is now a common and equal opportunity disease that affects as many as 3 million people in the US. Gouty arthritis has now become a serious problem in organ transplant recipients; in diuretic users; and in patients with CKD, hypertension, metabolic syndrome, heart failure, plus more.
The authors’ opening salvo seems to say it all (again). . . “A patient’s nocturnal BP profile, without the pressor effect of physical activity, emotional stress, and environmental factors that are usually present during the day, is more representative of the true BP status and a stronger predictor of cardiovascular outcomes.”
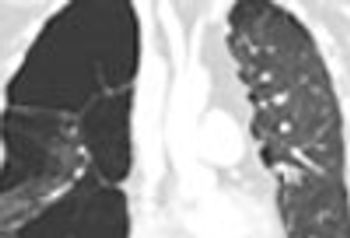
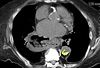
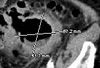
A 54-year-old man presented to the ED with palpitations identified as atrial flutter and RVR. Medical history included stage IV renal-cell carcinoma, end-stage COPD, NYHA class IV heart failure, and recent pulmonary embolism. A CT scan of the thorax was ordered.
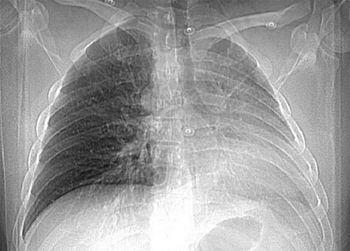
A 26-year-old man presented with sudden onset of palpitations and shortness of breath after incidentally taking tadalafil. He had no other symptoms and no history of illnesses during childhood. He drank socially but denied smoking and use of illicit drugs.
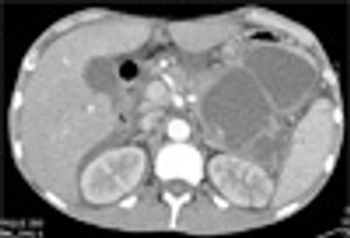
A 38-year-old man with a history of alcoholism, intravenous drug use, and cerebrovascular accident was referred for assessment of possible endocarditis, based on history, fever 39 °C (102.9 °F) and mildly elevated troponin level.

For years, GI toxicity and risk of bleeding were the issues of most concern when deciding to prescribe an NSAID. The cardiac effects associated with these drugs were considered a positive in that least some have been shown to provide prophylaxis against myocardial infarction.
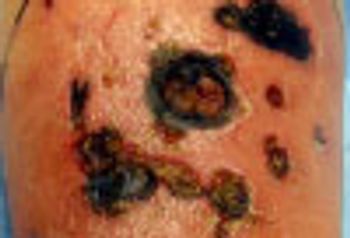
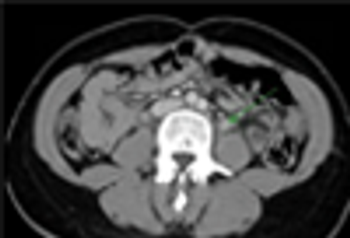
A 41-year-old woman came to the emergency department complaining of pain in the lower right portion of her abdomen that had become steadily worse over the past 2 days.
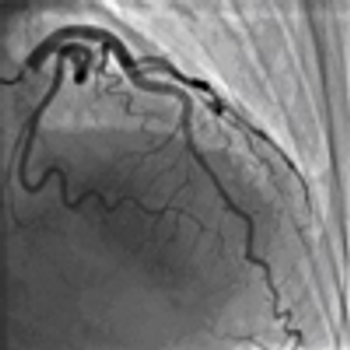
A 48-year-old African American man with no significant medical history sustained a gunshot wound to the face and shoulder.

A review of 140 trials and 26 observational studies supports metformin as the best first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes in adults, both stand-alone and in combination with other medications. But second-line treatments are still a judgment call.
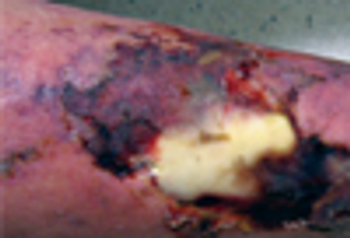
An 88-year-old man presents with a 2-month history of a non-healing ulcer on his right lower limb.
Cirrhosis and ascites developed in a 52-year-old man with a history of chronic hepatitis C and alcohol abuse. He was hospitalized because of bleeding esophageal varices, which were successfully treated with elastic band ligation.

Exercising at least 4 times a week can increase left ventricular mass and preserve elasticity, thereby reducing the risk of diastolic heart failure. Researchers from Texas presented their study results at the American College of Cardiology’s 60th Annual Scientific Session.
Here: a succinct review of the diagnosis and treatment of pemphigus vulgaris, dermatomyositis, cicatricial pemphigoid, linear IgA bullous disease, coma bullae, and stasis bullae.

A Danish study found no clinical benefit from using NT-proBNP (b-type natriuretic peptide) to identify and monitor high-risk patients with chronic heart failure, according to research from the NorthStar study presented at the American College of Cardiology’s 60th Annual Scientific Session in New Orleans.

Compared with medical therapy alone, coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) significantly reduced cardiovascular deaths and the composite end point of all-cause deaths and cardiovascular-related hospitalizations, reported investigators from the Surgical Treatment of Ischemic Heart Failure (STICH) trial. However, the effect of the two management strategies on overall survival in patients with ischemic heart failure was similar.

The panel presented three challenging cases of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFPEF) (see Update on Diastolic Heart Failure). In an innovative twist, the panel solicited feedback from a standing-room-only audience through SmartPhone technology-attendees voted for their favored diagnostic approach, therapy, or final diagnosis, with voting results instantly integrated into the presenter’s Powerpoint display.

Diastolic heart failure (or HFPEF-heart failure with preserved ejection fraction) is characterized by inadequate myocardial relaxation and diastolic filling ("stiff ventricle"), with heart failure signs and symptoms despite normal ejection fraction. The most common cause is long-standing hypertension.

Systemic inflammation has been identified as a risk factor for the development of heart failure in population studies. In the 5-year prospective MESA study, researchers from Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore recorded a baseline nonspecific marker of systemic inflammation, C-reactive protein (CRP).

Researchers from Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston presented results from the PROTECT (ProBNP Outpatient Tailored Chronic Heart Failure) study. NT-proBNP (b-type natriuretic peptide) is a biomarker released from myocardial tissue in response to high levels of wall stretch and has been studied as a marker for decompensated systolic heart failure.

A 44-year-old man presents for a preemployment physical examination. He is healthy, and he currently takes no long-term medications. A detailed review of systems reveals no ischemic chest pain, dyspnea with exertion, orthopnea, or any other symptoms of either coronary artery disease (CAD) or heart failure.
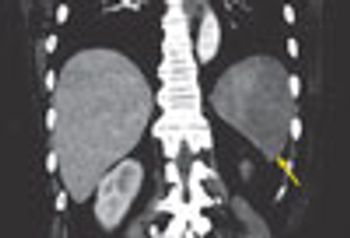
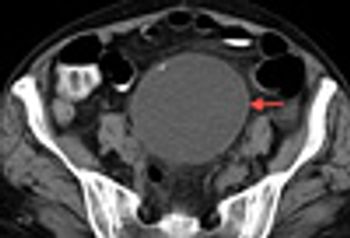
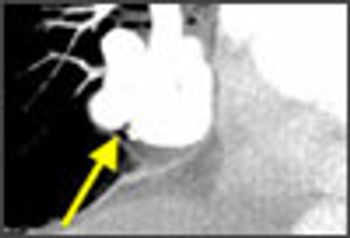
A 53-year-old woman presented with sudden onset of left upper quadrant abdominal pain. She had a history of atrial fibrillation, hypertension, and congestive heart failure.
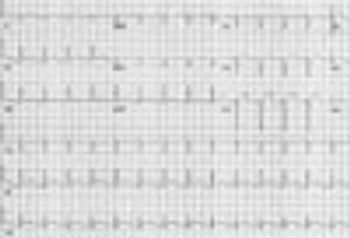
A 50-year-old man was brought to the emergency department (ED) after a witnessed syncopal event. He was awake but confused and unable to provide a history.