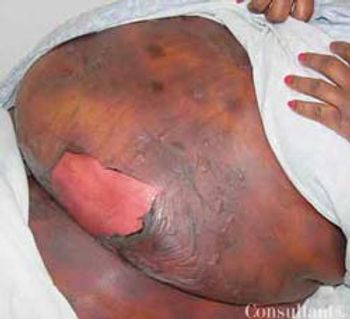
During his last routine pediatric visit, a 4-month-old boy with a large head circumference (98th percentile for his age) was referred for radiographic evaluation. The infant had been delivered by cesarean birth because of cephalopelvic disproportion; his head size had gradually increased since birth. There was a family history of this condition.