
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) affects 1% ofadults during their most productiveyears and can result in significant disability.The goals of therapy are to reducepain, limit joint destruction, andpreserve function.

Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) affects 1% ofadults during their most productiveyears and can result in significant disability.The goals of therapy are to reducepain, limit joint destruction, andpreserve function.

Excess weight increases the risk of having a heart attack, stroke, high blood pressure, arthritis, diabetes, depression, fatigue, and certain types of cancer. Losing weight and keeping it off are very difficult for most persons who are overweight. Here are some suggestions to help you lose pounds and keep your weight down.

In this article, we review the factors that contribute to obesity. We then describe effective approaches to weight control, including exercise, dietary modification, drug treatment, and bariatric surgery.

A number of studies have found an increased prevalence of anxiety and depression in patients with asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Although the relationship is not completely understood, it is clear that psychological disorders can adversely affect the course of both diseases.

Although widely regarded as a raredisorder, hereditary hemochromatosisis the most common genetic disease inCaucasians. In certain populations ofnorthern European descent, 1 of every200 persons is homozygous for thecausative mutation.1

As many as 300,000 sportsrelatedconcussions arediagnosed each year inthe United States.1 Thisfigure underestimatesthe true incidence, however, becausemany concussive injuries are notrecognized by the injured persons,trainers, or physicians. A recentstudy found that 4 of 5 professionalfootball players with concussionwere unaware that they had sufferedthis injury.2

Abnormal uterine bleeding can be defined as bleeding that deviates from the patient's normal pattern; it may be heavier, more frequent, or abnormal in timing. Bleeding of any kind in a postmenopausal patient should be considered abnormal unless she is receiving hormonal therapy that is associated with regular cyclic withdrawal bleeding.

An 83-year-old man presents to the emergency department after he fell down his basement stairs and was unable to walk.

Most pain in or around the oral cavity is attributable to tooth or mucosal pathology. However, tooth or mucosal pain may also be caused by a variety of other conditions, including brain pathology; vascular inflammatory and cardiac disease; jaw infection or neoplasm; neuropathic abnormality not associated with central pathology; pathology in the neck and thoracic region; myofascial and temporomandibular joint pathology; and disease of the ear, eye, or nose, or of the paranasal sinuses, lymph nodes, and salivary glands. Accurate diagnosis is facilitated when the features of pain presentation in this region are understood.

ABSTRACT: A number of nondental conditions may cause significant oral pain. Pain associated with temporal arteritis is localized to the maxillary posterior teeth, the maxilla, or the frontal-temple region. This pain is often associated with exquisite tenderness of the scalp and face. The pain of trigeminal neuralgia is typically felt in the anterior maxillary or mandibular anterior teeth; it radiates along the mandible toward or into the ear on the ipsilateral side of the trigger. Pain may remit for months or years but is often severe when it recurs. Burning mouth syndrome preferentially affects postmenopausal women older than 50 years; one half to two thirds of patients experience spontaneous remission within 6 to 7 years, with or without treatment. The pain of postherpetic neuralgia is unilateral and restricted to the affected dermatome; it may be aggravated by mechanical contact or chewing.

56-year-old man with a history of diabetes mellitus and hypertension presents with chest pain, emesis, pallor, and diaphoresis.

Abstract: Acute chest syndrome (ACS) is one of the most common causes of death and hospitalization among patients with a sickle hemoglobinopathy. The clinical presentation is characterized by the appearance of a new infiltrate on a chest radiograph, with 1 or more new symptoms, including fever, cough, chest pain, and dyspnea. Additional findings include leukocytosis, hypoxemia, and auscultatory signs of consolidation. The differential diagnosis includes pneumonia, pulmonary infarction, fat embolism syndrome, pulmonary edema, and bone infarction. Treatment of ACS involves supportive care, empiric antibiotic therapy, and red blood cell transfusion when indicated. The decision of whether to use simple or exchange transfusions depends on the severity of illness and the risk of acute respiratory failure. Currently, hydroxyurea is the only FDA-approved drug designated as a preventive therapy. (J Respir Dis. 2005;26(12):529-534)

Low back pain is a widespread and costly complaint that affects virtually all Americans at some point in their lives. After the common cold, it is the second most frequent cause of work absence in the United States.

Patients who have previously been treated for depression sometimes find it difficult to tell when their symptoms are returning.

A cardiovascular risk reference guide, Framingham global risk assessment scoring guide, cardiovascular checklist, and cardiovascular risk-reduction treatment plan.

Cardiovascular (CV) risk-reduction regimens require comprehensive assessment, patient education, and follow-up, which can be difficult and time-consuming in a busy primary care practice. Moreover, compliance among patients at high risk can be poor. The use of evidence- based risk assessment checklists and patient education materials can enhance care and improve compliance; in addition, thorough documentation can ensure full reimbursement for services.

A 24-year-old Korean woman, who was 20 weeks' pregnant, was referred to an allergist for an elimination diet and evaluation of the risk of allergies to her unborn child. She had a several-year history of perennial allergic rhinitis with seasonal exacerbations.

For patients with osteoarthritis, nonpharmacologic treatment can be an effective adjunct to drug therapy. Patient education is essential; both community-based and independent self-care programs are available. Weight loss can improve function and alleviate symptoms; however, it is more effective when dietary modification is accompanied by increased physical activity.

Recently, the National Guideline Clearinghouse compared smoking cessation recommendations from the Public Health Service, the University of Michigan Health System, the Singapore Ministry of Health, the New Zealand Guidelines Group, and the US Preventive Services Task Force. Highlights of guidelines from the US groups are presented here.

In patients with underlying disease, a preoperative evaluation and targeted perioperative management strategies can minimize surgical complications and maximize healing. This article focuses on how to identify surgery patients at risk for complications caused by diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and other medical conditions; I also describe strategies to minimize such risk.

Traumatic brain injury may occur without visible head injury; it manifests as confusion, focal neurologic abnormalities, an altered level of consciousness, or subtle changes on neuropsychological testing. The initial evaluation includes assessment of the patient's airway and respiratory, circulatory, and neurologic status.

Abstract: The coexistence of asthma and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) in a given patient presents a number of diagnostic and treatment challenges. Although the relationship between these 2 diseases is complex, it is clear that risk factors such as obesity, rhinosinusitis, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can complicate both asthma and OSA. In the evaluation of a patient with poorly controlled asthma, it is important to consider the possibility of OSA. The most obvious clues are daytime sleepiness and snoring, but the definitive diagnosis is made by polysomnography. Management of OSA may include weight loss and continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP). Surgical intervention, such as uvulopalatopharyngoplasty, may be an option for patients who cannot tolerate CPAP. Management may include specific therapies directed at GERD or upper airway disease as well as modification of the patient's asthma regimen. (J Respir Dis. 2005;26(10):423-435)

An 87-year-old woman who recently moved to an assisted living facility from her home is seen for evaluation of facial edema and erythema after a bee or wasp sting sustained 2 days earlier. Patient denies pain, pruritus, or visual changes. She took one dose of diphenhydramine shortly after the event and has noticed that the edema, which affected primarily the right side of the face, near the sting, has improved.

An 87-year-old woman who recently moved to an assisted living facility from her home is seen for evaluation of facial edema and erythema after a bee or wasp sting sustained 2 days earlier. Patient denies pain, pruritus, or visual changes.
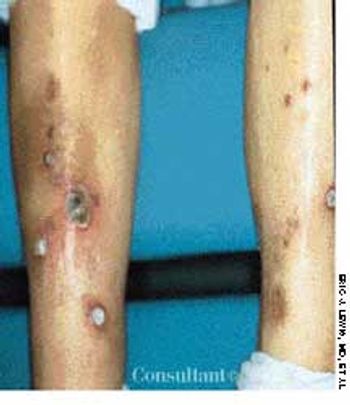
A 63-year-old woman who was on long-term hemodialysis because of diabetic end-stage renal disease had a 7-month history of waxing and waning papules and plaques on the front of both legs. The asymptomatic multiple, discrete, slightly erythematous, round to oval lesions ranged from 5 mm to 3 × 4 cm. Several had heaped-up borders and contained central crust and keratotic debris; others were superficial ulcers with central eschars. The lesions improved only slightly following twice-daily application of a superpotent topical corticosteroid preparation.