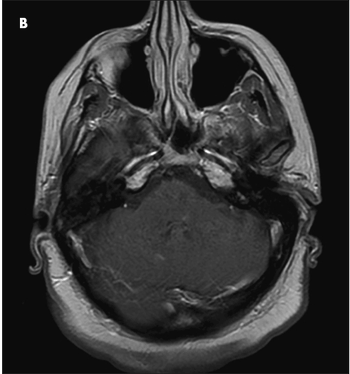
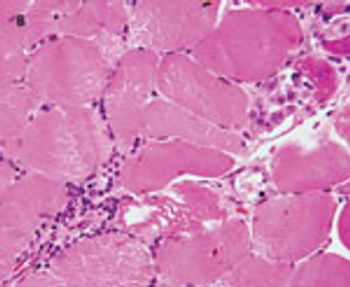
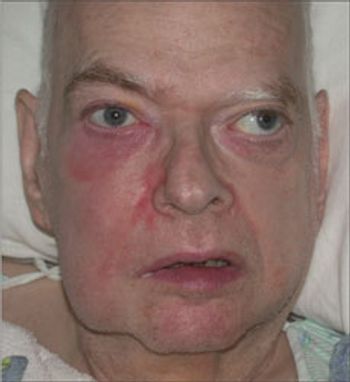
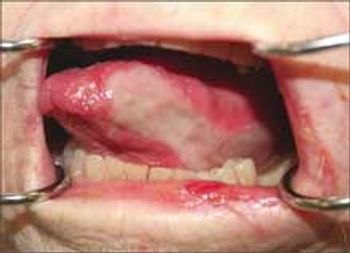
No matter what primary care demographic your practice represents, it would be most unusual not to encounter patients infected with hepatitis C virus (HCV). Since HCV infection is chronic and can lead to cirrhosis (occurring in 20% of patients over a period of 10 to 20 years), decisions regarding its management, referral, and follow-up are of the utmost importance.