
NOTTINGHAM, England -- Second-hand cigarette smoke leaves a suspicious trail of cardiovascular-disease biomarkers in non-smokers, found a large cross-sectional study here.

NOTTINGHAM, England -- Second-hand cigarette smoke leaves a suspicious trail of cardiovascular-disease biomarkers in non-smokers, found a large cross-sectional study here.

BOSTON -- Two new risk factors added to the traditional risk model enhanced prediction of a woman's 10-year risk of cardiovascular disease or stroke, researchers reported.

EVANSTON, Ill. -- Children who get less sleep than recommended are significantly more likely to be overweight or obese than their peers who get the right amount of sleep.

ROCKVILLE, Md. -- The FDA today approved over-the-counter sale of a low-dose version of Xenical (orlistat), a prescription diet drug that works by blocking the absorption of fat in the intestine. The OTC version will be called Alli.

HERSHEY, Pa. -- For women with polycystic ovary syndrome the fertility drug clomiphene proved superior to metformin, a diabetes drug. in achieving a live birth, researchers found in a head-to-head study.

WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. -- If patients are overweight or obese when they reach age 70, matters will probably get worse over the next decade, when aging bodies gain fat and lose lean mass in these vulnerable years, researchers reported.

Furunculosis is a deeper infection of the hair follicle generally attributable to S aureus.

Declining cardiovascular function, poor circulation, diabetes, obesity, cancer, immunodeficiency, renal disease, and thinned, xerotic skin provide the setting for a host of bacterial infections in elderly persons that can involve any level or structure of the skin.

A 49-year-old white man, in whom HIV infection had been newly diagnosed (CD4+ cell count, 25/µL; HIV-1 RNA level, 274,000 copies/mL), was transferred to our hospital for further workup and treatment of multiple neurologic deficits. He had presented to another hospital with a 4-day history of left-sided weakness and numbness, left-sided facial droop, dysphonia, and dysphagia that led to the initial diagnosis of an acute stroke.

Blastoschizomyces capitatus is an emerging pathogen that causes infection primarily in patients who have immune system dysfunction. The author reports a case of pulmonary blastoschizomycosis in an immunocompetent man who was successfully treated with voriconazole.

A 75-year-old woman had undergone a total thyroidectomy, with histologic evidence of poorly differentiated follicular thyroid cancer. She subsequently received an ablative dose of iodine-131. After a disease-free interval of about 2 years, she presented with evidence of recurrence in the thyroid bed. She had enlarged cervical lymph nodes and complained of dyspnea on exertion.

A 69-year-old man with a history of atrial fibrillation, pulmonary embolism, asthma, and obstructive sleep apnea presented to the emergency department for evaluation of dyspnea and light-headedness. He had been treated for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation over the past 5 years; fairly good control had been achieved with metoprolol and amiodarone. However, over the past several months, he had been experiencing intermittent episodes of atrial fibrillation.

ABSTRACT: Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor therapy is recommended for all patients with heart failure (HF) and a reduced ejection fraction. It is generally initiated in the hospital at low doses as inotropic therapy is tapered. Angiotensin II receptor blockers may be a suitable alternative for patients who cannot tolerate ACE inhibitors. For patients who cannot tolerate either class of drug, a combination of hydralazine and a nitrate is recommended. ß-Blockers are first-line therapy for patients with current or previous symptoms of HF and reduced left ventricular function, as well as all patients hospitalized for HF. An aldosterone antagonist may be added to the regimen of patients with moderately severe to severe symptoms and reduced ejection fraction whose renal function and potassium concentration can be monitored.

ABSTRACT: Heel pain that occurs with the first several steps in the morning and diminishes as walking continues is the classic symptom of plantar fasciitis. Assessment of risk factors, such as improper footwear, a change in physical activities, and a new running surface, is important. Radiographs are rarely useful. Plantar fasciitis is generally self-limited; symptoms typically take 6 to 18 months to resolve. Conservative measures may include relative rest, stretching, strengthening, shoe modifications, orthoses, night splints, NSAIDs, and ice therapy. A corticosteroid injection may be warranted in resistant cases. If extensive conservative treatment is unsuccessful, referral to an orthopedic surgeon may be indicated.

A 48-year-old woman is evaluated for transfer to the ICU. She presented to the emergency department 48 hours ago with severe abdominal pain and emesis. The pain had started several days earlier and was located in the upper abdomen with some radiation to the back. No position--even the fetal position--provided relief. After admission, she was given intravenous fluids and analgesics; in the last several hours, her condition has deteriorated. She now complains of thirst and is somewhat agitated.
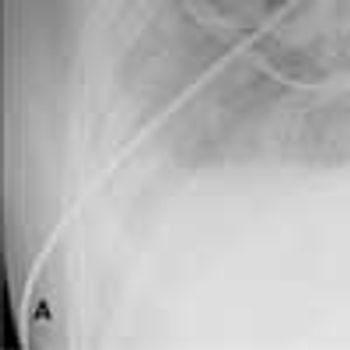
For a week, a 39-year-old woman with a history of intravenous heroin use had generalized pain, fever, chills, and a nonproductive cough. She rated the pain at 10 on a scale of 1 to 10; it was sharp, constant, and unrelieved by heroin. She also reported dyspnea at rest, pleuritic chest pain, and a 15-lb weight loss over the past month. She had no significant medical history or drug allergies, smoked a half pack of cigarettes per day, and denied alcohol use.
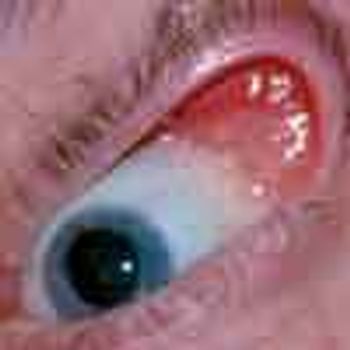
For several days, the left eye and eyelids of a 60-year-old obese man had been red and irritated. The symptoms were worse in the morning after waking. The patient had recently started wearing a nighttime continuous positive airway pressure mask for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). He slept exclusively on his left side.

SEATTLE -- Fine-particulate air pollution over time significantly increased the risk of a first heart attack or stroke, as well as cardiac mortality, in postmenopausal women, researchers here reported.

BOSTON -- Insofar as pain-free knees are concerned, recreational exercise is orthopedically irrelevant to middle-age and older persons, researchers here reported.

SAN DIEGO -- Although computed tomography angiography showed striking results in a small study reported here among patients with known heart disease, the decision to proceed with a coronary bypass still seems to need a visit by a catheter.

PORTLAND, Ore. -- A single bone mineral density scan to predict future fracture risk may be good for life for healthy older women, according to a large study.

ANN ARBOR, Mich. -- People who are cynically distrustful tend to have higher levels of inflammatory markers associated with atherosclerosis than those who believe the best of others' motives, investigators here suggested.

ANN ARBOR, Mich. -- Fatter, poorer, and less educated breast cancer patients are more likely to get partial-dose chemotherapy, which may jeopardize their survival, researchers reported.

LEICESTER, England -- Lifestyle changes appear to be at least as effective as drugs to prevent type 2 diabetes among patients with impaired glucose tolerance, according to a meta-analysis.

CAMBRIDGE, England -- Defects in the receptor for leptin are rare but should be considered when diagnosing obese patients with uncontrolled appetites, according to researchers here.