
In their case report, “Sudden Headache in a Woman With Hypertension” (CONSULTANT,July 2002, page 1049), Drs Gary Quick and Maggie Law describe apatient with uncharacteristically severe headache and very high blood pressure.

In their case report, “Sudden Headache in a Woman With Hypertension” (CONSULTANT,July 2002, page 1049), Drs Gary Quick and Maggie Law describe apatient with uncharacteristically severe headache and very high blood pressure.

Calcium channel blockersare commonly prescribedto treat severalcardiovascular diseasesand may be helpful inother conditions, such as migraineand bipolar disorder.1 These agentsare associated with numerous clinicallysignificant drug interactions.1-3While some of these interactions,such as the effect of verapamil onserum digoxin concentrations, arewell-known, others are not widely recognized-yet warrant attention.

A 77-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after severaldays of illness that began with fever, nausea, emesis, and headache. Muscleweakness and associated myalgia developed; the weakness became so severethat the patient needed help to get out of bed and walk to the bathroom.The day before he came to the hospital, he slept much of the time and wasdifficult to arouse.

A 69-year-old retired accountant presents with a 2-month history of daily headaches. The pain is moderate, constant,global, pressure-like, and occasionally pulsating; it is sometimes exacerbated when the patient lies down. He denies nauseaor vomiting, ocular symptoms, weakness, or sensitivity to light. His wife reports that years ago he experienced throbbingheadaches regularly.
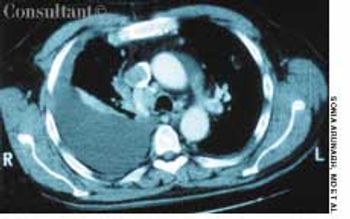
A 64-year-old woman with a history of diabetes, hypertension, and lymphoma was admitted to the hospital with a dull headache, conjunctival congestion, and slight dyspnea. Her pulse rate was 96 beats per minute; blood pressure, 146/68 mm Hg; and respiration rate, 22 breaths per minute. She also had increased jugular venous distention; cardiovascular and chest examination findings were normal. Edema of both arms and dilated blood vessels on the anterior chest wall were noted.

A bright, active 10-year-old boy has been experiencing recurrent bouts ofabdominal pain with nausea and occasional vomiting for 3 years. Although hehas had 1 or 2 attacks at school, the pain usually occurs at home-frequentlyon weekends. His mother has been unable to correlate these episodes with particularfoods or activities. She notes that her son has experienced motion sicknessduring long auto trips and during a family holiday in the mountains ofColorado.
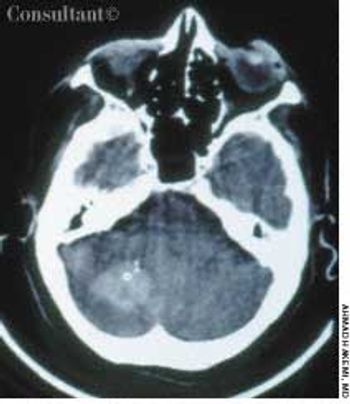
A 65-year-old woman with a long history of hypertension treated with metoprolol and felodipine complained of dizziness, headache, nausea, and vomiting of acute onset. Her blood pressure was 220/110 mm Hg. She was drowsy and unable to stand or walk.

A 28-year-old man presents tothe emergency departmentwith high fever; progressive, severe,generalized, throbbing headache;blurred vision; and increasingconfusion. These symptoms started3 days earlier.

A 37-year-old woman presents to the emergency departmentwith a diffuse, sharp, pounding headache,which started 2 hours earlier. She rates her discomfort as4 on a scale of 1 to 10. Neck muscle soreness is also present,but the pain does not radiate.

Is there a meaningful percentage of patients who contract Lyme disease but havenone of the early symptoms-neither the rash nor the flu-like symptoms (eg, fever,myalgia, headache, and stiff neck)-and in whom the disease only becomes clinicallyevident in a later stage when it is much harder to treat?

Migraine is an episodic, often debilitatingcondition that affects women moreoften than men. Twenty-eight millionAmericans suffer from migraineheadaches-and nearly 75% of theseare women.1 Unlike other chronic painconditions, migraine has its peakprevalence during the years of greatestproductivity, when most women arejuggling family responsibilities andcareers.2 Many women are particularlysusceptible to migraine attacks justbefore and during menses.