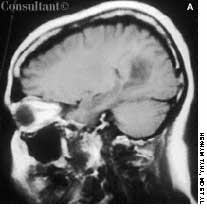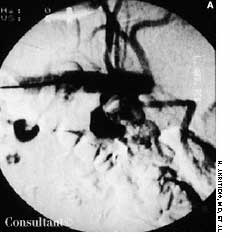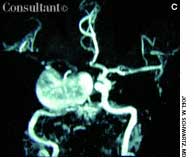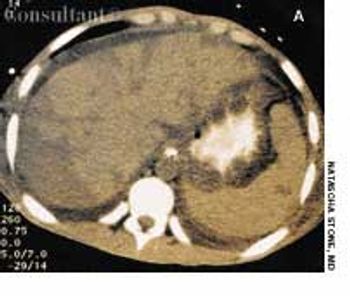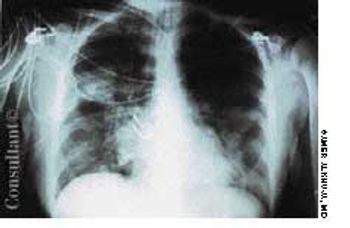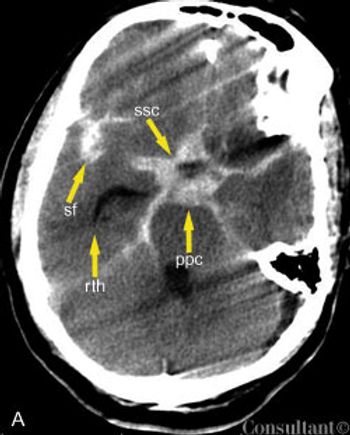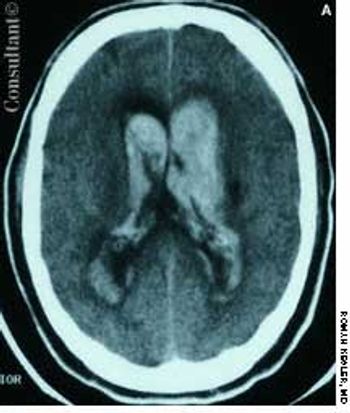
A 57-year-old man complained of a severe headache of sudden onset while he was lifting heavy boxes. Within minutes, he collapsed and became unconscious. On arrival at the emergency department, the patient was deeply comatose. His pupils were 7 mm, fixed, and unreactive to light; brainstem reflexes were absent, and he was unresponsive to noxious stimulation. His blood pressure was 210/120 mm Hg; he had no known history of hypertension.