
Aspergillus species are ubiquitous molds to which humans are commonly exposed. Of approximately 180 species, it is estimated that 34 are medically significant. Most persons who come in contact with the fungus remain asymptomatic.

Aspergillus species are ubiquitous molds to which humans are commonly exposed. Of approximately 180 species, it is estimated that 34 are medically significant. Most persons who come in contact with the fungus remain asymptomatic.

Symptomatic primary HIV infection occurs in an estimated 50% to 90% of patients. A constellation of symptoms that most closely resembles those of acute infectious mononucleosis characterizes the syndrome.

In the preface to the third edition of this comprehensive reference on AIDS therapy, the editors proclaim that their book is a “one-stop resource for busy clinicians in busy practice settings.” And this textbook serves that purpose well. But first, you will need to lift it. This hardcover edition weighs in at a hefty 7 pounds!

A 92-year-old woman presents with sharp abdominal pain of 1 day's duration, accompanied by 1 episode of emesis. The pain is neither relieved nor exacerbated by food ingestion.

Kaposi sarcoma (KS), AIDS-related non-Hodgkin lymphoma (AIDS-NHL), and anal squamous cell carcinoma/anal intraepithelial neoplasia (SCC/AIN) are malignancies that commonly involve the GI tract in patients who have HIV/AIDS.1 Oncogenic viruses have been implicated in the etiology of each of these neoplasms-specifically, human herpes virus 8 (HHV8) in KS, Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in AIDS-NHL, and human papillomavirus in SCC/AIN.
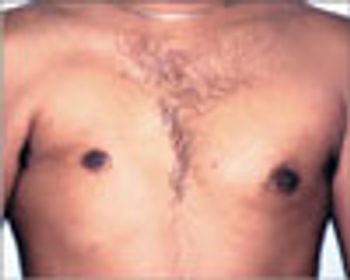
A 23-year-old man's right chest shows a common congenital muscle anomaly-partial absence of the pectoralis major muscle. The abnormality was noted during a routine preemployment physical examination. The clavicular origin seemed to be intact. There was no apparent decrease in shoulder internal rotation or adduction strength, and the patient had not noticed any shoulder weakness or limitation in motion.

The numerous symptom domains of fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS) include pain, fatigue, sleep disturbance, mood disturbance, function impairment, irritable bowel syndrome, tension and migraine headache, and cognitive dysfunction. Its pathophysiology is rooted in neural dysregulation in the spinal cord and brain.

When diagnosing vitamin B12 deficiency, we routinely include a measurement of the methylmalonic acid (MMA) level in all patients whose B12 values are under 400 pg/mL. An elevated MMA level confirms B12 deficiency.

A patient of mine recently had an extensive allergy workup after a rash developed, apparently following exposure to wheat products.

What amount-and type-of alcohol is most effective in lowering cardiovascular risk? A recent paper suggests that drinking wine responsibly reduces the risk of heart disease to a greater extent than moderate consumption of beer or spirits, such as whiskey.

The features of acromegaly (frontal bossing, enlarging hands and feet, changes in the prominence of the lower jaw) are so subtle and progress so slowly that patients and family members often miss them.

Primary HIV infection refers to the earliest stages of infection, or the interval from initial infection to seroconversion (when antibody to HIV is detectable). During this stage, many patients have symptoms of acute HIV seroconversion illness, are viremic with very high HIV RNA levels, and have negative or indeterminate findings on HIV antibody tests.

UNICEF has reported that there have been some improvements for children facing AIDS, but progress is still far short of goals set for 2010 (Worsnip P. Reuters. April 3, 2008).

Apart from clinical trials that provide highly active antiretroviral therapy shortly after the recognition of an acute seroconversion reaction-an intervention that some believe could be a prelude to eradicating HIV -there has long been debate over the optimal time to initiate antiretroviral therapy.

Metronidazole, the prototype nitroimidazole, was originally released in 1959 for the treatment of Trichomonas vaginalis infections. It has since been used to treat a variety of infections caused by anaerobic and facultative anaerobic bacteria and protozoa. Here we discuss the need for dosing adjustments in patients with hepatic disease.

Shapiro discussed the numerous studies that reiterate- despite a troubling grassroots opinion among lay Lyme disease advocates and a select group of physicians- that the term "chronic Lyme disease" is a misnomer for other symptom complexes and that long-term antibiotic therapy provides no benefit.1,2 "Patients with these symptoms have been studied at many different scientific centers," explained Shapiro, extrapolating from an article he coauthored that appeared in the October 14, 2007, issue of the New England Journal of Medicine.1 "The majority have no evidence of ever having been infected with the bacteria that causes Lyme disease, either by clinical history or by laboratory tests.

PREVALENCE OF ANAL humanpapillomavirus (HPV) infection was24.8% among a study population of222 heterosexual men who confirmedthat they had never engagedin male-male sexual intercourse. Thestudy is scheduled to appear in TheJournal of Infectious Diseases and canbe viewed ahead of print at the journal'sWeb site.

Life-threatening heart failure associated with itraconazoleantifungal therapy developed in a patient with disseminatedCoccidioides immitis infection. This was documented bycardiac studies that demonstrated a deterioration of cardiacfunction during therapy and an improvement after itraconazoletherapy was discontinued. Heart failure associatedwith itraconazole can be missed by those unfamiliar with thiscomplication. In any patient with a fungal infection who isbeing treated with itraconazole, this serious complication canoccur; however, it can be reversible with discontinuation ofthe drug. [Infect Med. 2008;25:292-293]

Postsurgical endophthalmitis caused by Rhizobium radiobacterdeveloped in a 62-year-old man. The patient was treatedwith empiric intraocular therapy. On identifying the causativeorganism, systemic ciprofloxacin was added to the treatmentregimen. Therapy resulted in complete resolution of visualchanges caused by the infection. [Infect Med. 2008;25:274-276]

A66-year-old white man with tuberculosis of the shoulderjoint had a severe hypersensitivity reaction to antituberculosismedications. Symptoms included development of pulmonaryinfiltrates, hepatic dysfunction, renal insufficiency, andneutropenia. The patient improved after the medicationswere withdrawn. [Infect Med. 2008;25:287-291]