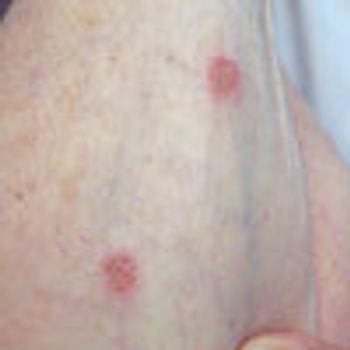
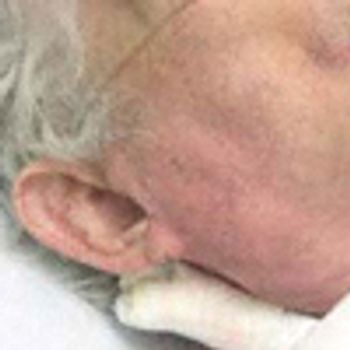
A 76-year-old woman presents with chest pain-which she describes as“muscle tightness”- that began when she awoke in the morning. Thepain is constant, exacerbated by deep inspiration, and accompanied by asubjective sense of slight dyspnea; she rates its severity as 3 on a scale of1 to 10. She denies pain radiation, nausea, diaphoresis, palpitations, andlight-headedness. Her only cardiac risk factors are hypertension and a distanthistory of smoking.