
Listen to 2 obesity experts discuss and analyze the role of insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes and obesity.


SURMOUNT-2: Tirzepatide Treatment Leads to Average 15% Weight Loss in Adults with T2D, Obesity

Global Diabetes Prevalence Will Double by 2050, Affecting 1.3 Billion People: New Predictions

Listen to 2 obesity experts discuss and analyze the role of insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes and obesity.

ENDO 2023. The pattern of intermittent fasting improved glycemic measures in a weight-independent fashion after just 7 days, according to the study abstract.
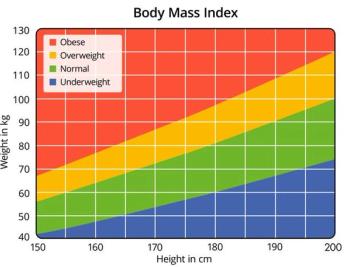
Acknowledging the historical harm caused by sole reliance on the measure for decisions in clinical practice, the AMA urges clinicians to incorporate other valid measures.
Nearly half of responding medical professionals said patients without T2D have asked for an Ozempic Rx and about 18% of them have provided one, avoiding significant backlash for a denial.

Compounded versions of semaglutide, often sold online, may contain salt versions of the molecule and are not evaluated by the FDA for safety or efficacy.

Your daily dose of clinical news you may have missed.

Findings highlight the need to develop strategies to improve weight management in primary care, according to study authors.

Efficacy of the daily pill met the standard now established by the once-weekly injection of 15% loss of baseline bodyweight in adults with overweight or obesity, says Novo Nordisk.

A nationally recognized obesity expert discusses mental health in women with obesity.

Your daily dose of clinical news you may have missed.

Dr Caroline Apovian reminds primary care clinicians who care for patients with obesity that diet and lifestyle counseling are essential for maximum results.

Participants with overweight or obesity had lower testicular volume than their healthy peers, putting them at risk for infertility later in adulthood.

The dual GIP/GLP-1 receptor agonist was associated with a nearly 15% reduction in body weight in adults with overweight/obesity and without type 2 diabetes.

GLP-1 RA side effects such as nausea and vomiting can be minimized by starting at the lowest available dose and titrating slowly; Dr Caroline Apovian explains why.

GLP-1 receptor agonist-based medications for obesity modify gut hormone imbalances, making diet and lifestyle change far more effective, explains Caroline Apovian, MD.

The American College of Physicians announced an initiative that renews and expands its focus on equitable access to obesity care, including new resources for physicians.

Your daily dose of clinical news you may have missed.
Dubbed the "twincretin," the GLP-1/GIP RA met weight and HgbA1c reduction endpoints, with nearly half of tirzepatide-treated patients achieving weight loss of at least 15%.

For persons diagnosed with obesity, a prescription antiobesity medication is just one part of optimal care that includes significant lifestyle change as well, says Caroline Apovian, MD.

Apovian: GLP-1 receptor agonists are the first antiobesity medications to simulate human physiology, which is why they sustain weight loss and are meant for long-term use.

In our latest episode, an obesity medicine physician explains the importance of a comprehensive plan to manage chronic pain in patients with obesity.

In persons with biopsy-confirmed NASH, the probability of disease resolution was more than 3X greater after RGB or SG vs lifestyle intervention at 52 weeks.

Caroline Apovian, MD, highlights how drugs like semaglutide 2.4 mg treat the chronic relapsing disease of obesity and why a distinction from "weight-loss drugs" is critical.

A family physician and obesity medicine physician talks about chronic pain in patients with obesity.

Your daily dose of clinical news you may have missed.