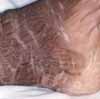
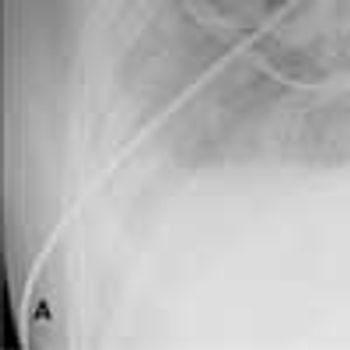
A 57-year-old woman presents with swelling of the hands that began several weeks earlier and is now worsening. She denies joint pain, and she has no history of trauma or significant vascular disease. She has had pneumonia several times; each episode was successfully treated with antibiotics. She has smoked 2 packs of cigarettes a day for the past 20 years