
More than 5.5 million US adults, or nearly 2% of the adult population, have some type of paralysis,

More than 5.5 million US adults, or nearly 2% of the adult population, have some type of paralysis,

The objective of this study was to estimate the annual cost burden of Parkinson disease (PD) in the United States. Resource use and cost profiles were developed using all-payer statewide hospital discharge data from 6 states; emergency department visit, long-term–care, and national survey data; fee schedules; and published study findings. (Average direct and indirect costs per patient were calculated in 2007 US dollars.) The annual cost per patient was $21,626 (direct cost: $12,491). When applied to the US PD population (N = 500,000), the annual average cost was approximately $10.78 billion (direct costs, $6.22 billion; indirect costs, $4.56 billion). PD has substantial economic consequences for patients and their families, insurers, and society. (Drug Benefit Trends. 2009;21:179-190)

Mortality rates from heart disease and stroke are falling in the United States, but cardiovascular disease remains the leading cause of death, according to a report by the American Heart Association (AHA). An estimated 869,724 persons died of heart disease in 2004 compared with 911,603 persons in 2003. When considered separately from other cardiovascular diseases, stroke was the third leading cause of death in 2004. The number of deaths attributable to stroke that year was estimated to be 150,074, a decrease from 157,689 deaths in 2003.
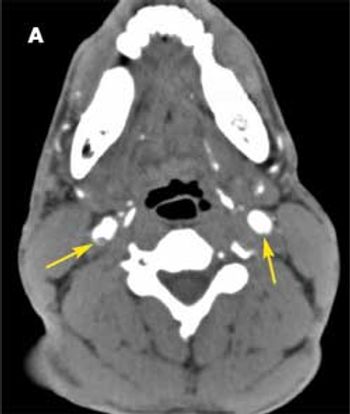
A 37-year-old man was brought to the emergency department (ED) after he had 2 near-syncopal events. The first occurred in the morning and rapidly resolved; the second occurred later in the day at work. The night before he had a headache and neck pain. In the ED, he reported left arm and leg weakness and was noted to have left facial droop.

An analysis of 1274 patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS) admitted to a single Colorado medical center over a 2-year period found that application of any acute stroke treatment strategy improved the patients’ NIH Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score.

Thirteen years have passed since intravenous tissue plasminogen activator was approved for treating patients with acute ischemic stroke, but some experts think hospitals-even those designated as primary stroke centers-have been slow to implement the strategy.

Many persons with chronic conditions are not getting the care and support they seek from the health care system, according to findings of a survey of 1109 persons aged 44 years and older with at least 1 chronic condition, stratified as baby boomers (aged 44 to 63) and seniors (aged 65 and older). Among their biggest complaints, persons with chronic health conditions say their physicians do not spend enough time with them. They also report having had to put off care because of cost.
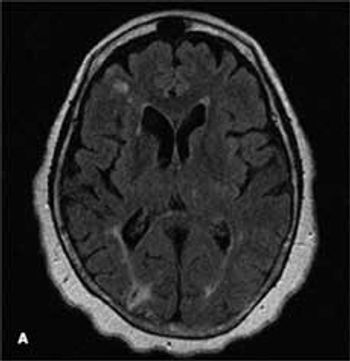
A 68-year-old woman with a history of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and tobacco use presented with her third stroke in the past 7 years. Neurological deficits included dysarthria and left-sided motor and sensory loss. A previous transthoracic echocardiogram with a bubble study did not reveal any cardiac source of embolism. Axial MRI of the brain on admission showed an abnormal signal in the bilateral hemispheres representative of multiple subacute infarcts

Clinicians often override electronic medication safety alerts, according to study findings published in the February issue of the Archives of Internal Medicine, indicating that such systems need to be more selective to be truly useful.

When medical professionals think of the health consequences of obesity, we usually think of increased prevalence of coronary artery disease, stroke, some cancers, diabetes, and hypertension. If we think a bit more, osteoarthritis, gallstones, asthma, and sleep disorders come to mind.1 How many of us are aware of the connection between obesity and the increased risk of various mental illnesses and conditions?

I have a healthy 16-year-old patient who needs a preparticipation physical examination. The family history is significant for the father’s sudden death from a thoracic aortic aneurysm at 42 years of age. How far should I pursue the workup?

Coronary artery disease (CAD), the most common form of cardiovascular disease in the United States, is the most costly type of cardiovascular condition to manage, according to the American Heart Association. Of the estimated $448.5 billion in total costs for cardiovascular diseases and stroke in 2008, CAD accounted for $156.4 billion, more than twice the cost of hypertension ($69.4 billion) and stroke ($65.5 billion) (Figure 1). Direct costs associated with CAD were $87.6 billion in 2008, of which prescription drug costs alone were $9.7 billion (Figure 2). Of the $68.8 billion in indirect costs for CAD in 2008, $58.6 billion were associated with lost productivity caused by increased mortality.
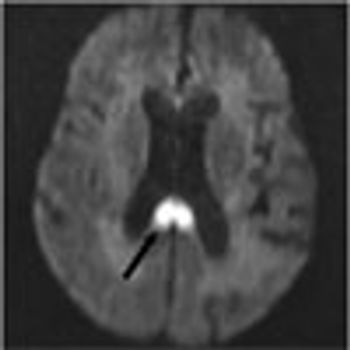
A 68-year-old woman was hospitalized because of confusion and agitation of sudden onset. Her history included dementia and multiple infarcts of both cerebellar hemispheres, bilateral basal ganglia, bilateral parietal lobes, and the right occipital lobe.

Selecting the most effective stroke prevention strategy for patients with cerebrovascular disease is an acknowledged challenge. In addition to decisions about the appropriateness of carotid surgery or angioplasty and stenting, there is the often tricky matter of designing the most effective medical regimen.

Selecting the most effective stroke prevention strategy for patients with cerebrovascular disease can be challenging.

As part of his preparation for retirement, a 66-year-old executive undergoes a complete physical examination. He is in good health and has no symptoms to report. Along with other age-appropriate screening studies, you discuss testing for vascular disease with him.

A neurologist prescribed a combination pill of dipyridamole and aspirin (2 tablets daily) for secondary stroke prevention in my patient, a 74-year-old woman. However, this patient also has increased cardiac risk.

Each year about 700,000 Americans sustain a stroke, and about 29% of those patients who are aged 65 years or older die within 1 year. Worldwide, stroke is the third leading cause of death and the leading cause of severe disability in adults.

Systolic hypertension is an independent risk factor for coronary artery disease, stroke, and end-stage renal disease. Nonpharmacological interventions for systolic hypertension include limitation of dietary sodium and alcohol intake along with weight reduction and aerobic exercise.

Major depression is twice as likely to develop in post-stroke patients (approximately 20%) than in nonstroke patients of the same age.1 Other psychiatric symptoms that are also more common in post-stroke patients include minor depression, anxiety, anger, and inappropriate or excessive laughing or crying (emotional incontinence).2

A 57-year-old woman presents for follow-up several months after a series of thrombotic episodes. Four days after she underwent ankle fusion to relieve pain and edema associated with a leg fracture that had occurred 40 years earlier, she sustained a massive myocardial infarction (MI).

Mortality data released by the CDC in January show that between 1999 and 2005, the age-adjusted death rate for coronary heart disease decreased by 25.8%, from 195 to 144 deaths per 100,000 persons per year. The new data also indicate that since 1999, the death rate for stroke has decreased by 24.4%, from 61 to 47 deaths per 100,000 persons per year. The reduction in mortality rates in 2005 resulted in approximately 160,000 fewer deaths from coronary heart disease and stroke, 2 of the 3 leading causes of death in the United States.

Diabetes is a destructive disease that kills thousands eachyear in the United States and disables thousands more, and its incidence hasbeen rising dramatically. Glycemic control is imperative to forestallcomplications; however, it can be difficult for patients to achieve glycemicgoals.

Consumer-directed health plans (CDHPs) are attracting new interest as a result of a ruling by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) over what constitutes preventive services. CDHP benefit designs take various forms, but in general, these are low-premium, high-deductible plans that provide full or close to full coverage for enrollees once the deductible is met and are typically tied to a health savings account (HSA).
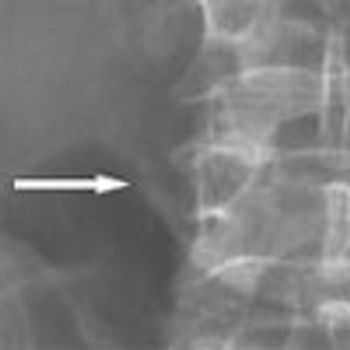
An obese 61-year-old man with a history of heroin abuse was brought to the hospital after he had fallen onto his buttocks on a sidewalk. He was able to stand initially, but weakness and numb-ness in his legs rendered him suddenly unable to walk or prevent himself from voiding. He denied abdominal or back pain. His medical history included asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and hypertension.