
The authors describe a patient who presented with episodic hemoptysis and other respiratory symptoms. His chest radiograph showed a diffuse reticulonodular pattern. Bronchoscopy led to the diagnosis of pulmonary blastomycosis.

The authors describe a patient who presented with episodic hemoptysis and other respiratory symptoms. His chest radiograph showed a diffuse reticulonodular pattern. Bronchoscopy led to the diagnosis of pulmonary blastomycosis.

Abstract: Patients who have aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease (AERD) usually experience upper and lower respiratory tract symptoms about 1Z|x to 2 hours after taking aspirin or another NSAID that inhibits the enzyme cyclooxygenase-1. In addition to symptoms such as nasal congestion, rhinorrhea, paroxysmal sneezing, periorbital edema, laryngospasm, and intense flushing, patients may have severe--often life-threatening--exacerbations of asthma. AERD occurs in about 10% to 20% of patients with asthma and in about 30% of asthmatic patients with nasal polyposis. However, AERD also occurs in patients who do not have any of these predispos- ing conditions. In patients with AERD, aspirin desensitization can improve asthma control, reduce the need for corticosteroids, and reduce the need for sinus surgery. (J Respir Dis. 2006;27(7):282-290)

A 37-year-old man presents with new-onset fever and abdominal pain of several days' duration. What does the PA film show, and what further action would you take to arrive at a diagnosis?

Rates of gonorrhea and chlamydial infection are highest among females 15 to 24 years old. Annual screening of all sexually active adolescents is warranted.

A painful, vesicular eruption; an asymptomatic red macule; a rapidlyspreading erythematous plaque--can you identify the disorderspictured here?
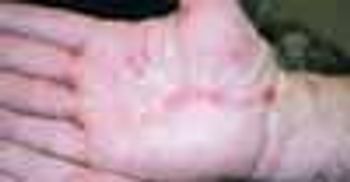
Painful, 1- to 1.5-cm macules and papules had developed on the palms and dorsal hands and wrists of a 60-year-old man 2 weeks earlier, after a deer-hunting trip. He had not seen any ticks on his skin or clothing. The lesions persisted despite self-treatment with over-the-counter topical corticosteroids. The patient had general malaise but denied fever, chills, and arthralgia. He was not taking any medications.

A review of the environmental determinants of allergic rhinitis and asthma, including house dust mites, cats, dogs, and cockroaches.

Avoidance of allergens and irritants known to cause or aggravate allergic rhinitis and asthma is a key component in the management of these disorders.

Early diagnosis enables patients to derive maximum benefit from highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART). Primary care practitioners can play a key role in the timely identification of HIV infection.

Which of the rashes pictured here is cellulitis?

A 40-year-old man complains of worsening lower extremity discomfort.

ROCKVILLE, Md. - The FDA has approved a label revision for the antibiotic Ketek (telithromycin) warning of possible severe and sometimes fatal liver injury during or immediately following treatment with the drug.

ROCKVILLE, Md. - The FDA has given accelerated approval to Prezista (darunavir), a novel protease inhibitor for salvage treatment of patients with HIV.

LOS ANGELES, June 26 - An anti-seizure agent can reduce the frequency of chronic migraine events, according to a researchers here.

ATLANTA, June 23 ? Americans returning after the World Cup in Germany should be wary of measles, according to the CDC, which issued a measles warning today aimed at soccer fans.

ATLANTA - Six unrelated clusters of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection involving 44 people in three states have been linked to 13 unlicensed street-corner tattoo artists.

ROCHESTER, Minn. - Heartburn is mainly a phenomenon of western culture, according to a systematic review of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).

SEATTLE - Among newly sexually active women, consistent condom use by their partners reduced the risk of human papilloma virus (HPV) infection, researchers reported.

LONDON - If the fates of former cannibals in New Guinea are an accurate indicator, British citizens may have a half-century to worry about whether they ate beef in the 1990s tainted with prion proteins that will lead one day to variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease.

BALTIMORE - Reports of paralyzed rats made to walk come and go, all claiming to be new and different. That said, this one is based on coaxing mouse embryonic stem cells into forming functional motor neuron circuits that extend to skeletal muscle, and it may well be different.

CINCINNATI - When it comes to inducing allergies in young children, not all types of airborne fungal spores are created equal, researchers here said.

UTRECHT, The Netherlands - Oral swabbing with antiseptics may be an inexpensive and effective way to prevent bacterial pneumonia in patients on mechanical ventilators, according to a study here.

OAKLAND, Calif. ? Coffee may help protect the livers of heavy alcohol drinkers. In a cohort study of Kaiser Permanente members, drinking one to three cups of coffee a day was associated with a 40% decrease in the risk of alcoholic cirrhosis versus drinking less than one cup.

ATLANTA ? After 25 years, the AIDS pandemic has killed more than 25 million people round the world. Today, nearly 40 million people live with HIV.

AMSTERDAM, The Netherlands ? A short course of antibiotics is just as effective as seven to 10 days for patients with uncomplicated community-acquired pneumonia who improve substantially, researchers here reported.