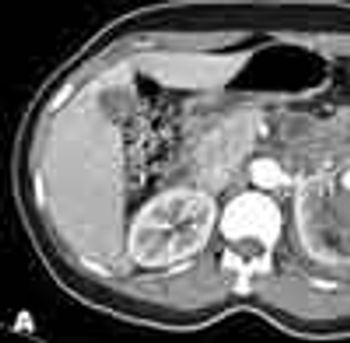
Abstract: In the assessment of community-acquired pneumonia, an effort should be made to identify the causal pathogen, since this may permit more focused treatment. However, diagnostic testing should not delay appropriate empiric therapy. The selection of empiric therapy can be guided by a patient stratification system that is based on the severity of illness and underlying risk factors for specific pathogens. For example, outpatients who do not have underlying cardiopulmonary disease or other risk factors can be given azithromycin, clarithromycin, or doxycycline. Higher-risk outpatients should be given a ß-lactam antibiotic plus azithromycin, clarithromycin, or doxycycline, or monotherapy with a fluoroquinolone. If the patient fails to respond to therapy, it may be necessary to do bronchoscopy; CT of the chest; or serologic testing for Legionella species, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, viruses, or other pathogens. (J Respir Dis. 2006;27(2):54-67)