
Newer anti-obesity drugs aren't your mother's Fen-Phen, but they also don't come without their own potential downsides.

Newer anti-obesity drugs aren't your mother's Fen-Phen, but they also don't come without their own potential downsides.

Questions you were afraid to ask about weight-loss modalities in the context of obesity and type 2 diabetes are answered here.
Nonalcoholic steatosis is the most common cause of liver disease in the USA. Try your hand at our half dozen questions on the hepatic cousins NAFL and NASH.

A new study estimates that 67.6 million Americans age >25 years are obese and an additional 65.2 million are overweight.

In these half-dozen slides, we look at this dangerous combination and the particular challenges it poses to diagnosis and disease management.
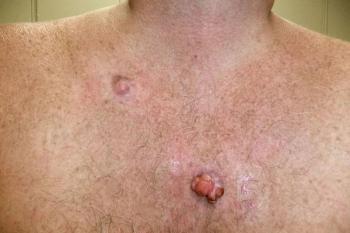
Two lesions have been slowly expanding on an older man’s chest for 2 years. What is the problem? This and questions on 3 other topics in this quiz.
Diabetes, obesity, hyperlipidemia, hypothyroidism-these endocrine disorders and others are major reasons why patients come to you. Find out what you know, and don’t know, here.

Should calcium supplementation be SOP? Are all high-fat foods bad? Does the “3500 calorie rule” work? Noodle these and other nutrition questions.

Obesity was declared a hormone-based disease in 2012, creating the need for a structured approach to obesity medicine. The AACE has taken the lead.

Researchers discover new evidence about the interplay between environment and health.

Only one-third of patients with eating disorders are ever asked about their problems with food. Screening in primary care is essential.
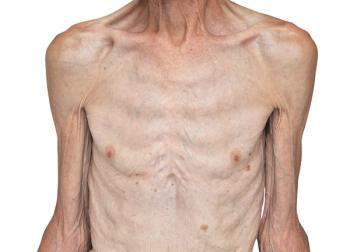
Underweight means highest risk, say researchers.
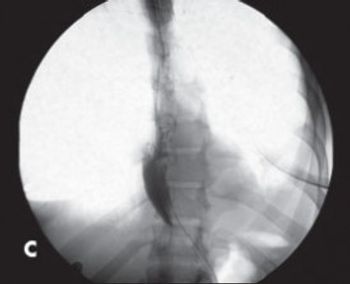
The development of a standardized treatment that simultaneously addresses achalasia and obesity is becoming more imperative as obesity becomes epidemic in the US. Here’s a case in point.

Evidence-based recommendations on the intake of free sugars to reduce the risk of noncommunicable diseases are the ingredients of a new WHO guideline. Find the recipe in these slides.

The odds of children becoming overweight go up with sleep-disordered breathing and short sleep duration, underscoring the need for early identification of these risk factors.

A new study shows that the risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease increases with obesity. Yet, the risk was increased in underweight persons as well.

The prediction of more shallow sleep in overweight and obese men with high testosterone levels is useful because poor sleep quality has been linked to an increased risk of diabetes and hypertension.
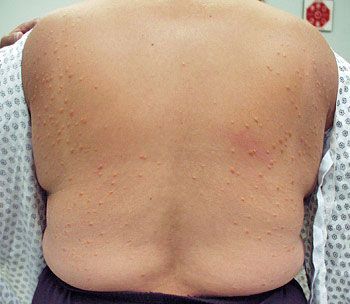
Obesity increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, hypertension, diabetes, and cancer, and it is associated with an array of complications, as the following cases attest.

Persons with a genetic predisposition to obesity who eat fried foods are at higher risk for obesity than those without a genetic predisposition.

The connections between obesity and depression in young women are strengthened by the results of a new study.

They breathe in more air than do normal-weight persons, exposing them to more air pollutants and making them more vulnerable to asthma and other pulmonary diseases.

Diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia, heart disease, congestive heart failure, osteoarthritis, low back pain, GERD, obstructive sleep apnea? What does it take?

Obese children in this study were nearly 3 times as likely to have asthma as nonobese children.

Being overweight increases a woman’s risk of ovarian cancer, according to a new comprehensive report. The finding offers a way to reduce the risk.

Here: factors that can affect home BP readings . . .when to start antiretroviral therapy . . . coping strategies for the challenges of aging . . . triggers to avoid in hyperthyroid patients . . . insights into causes of childhood obesity.