
LEIDEN, The Netherlands -- The risk of symptomatic venous thrombosis for healthy individuals is low after an airflight of four or more hours, but increases with more and longer flights, researchers reported.

LEIDEN, The Netherlands -- The risk of symptomatic venous thrombosis for healthy individuals is low after an airflight of four or more hours, but increases with more and longer flights, researchers reported.

HONG KONG -- What's bad for the heart may also be bad for the colon, according to investigators here.

BOSTON -- It sounds like an old wives' tale, but a boy is significantly more likely to be the second child if a woman gains weight after a first pregnancy, found researchers here.

PITTSBURGH -- Preventive care services such as mammography and cholesterol screening are much more likely to be delivered outside the realm of the annual well-patient checkup than as part of it, found researchers here.

AMSTERDAM -- Patients with type 1 diabetes who used insulin detemir (Levemir) for two years had better glycemic control and less nocturnal hypoglycemia than patients on NPH insulin, investigators reported here.

ROCKVILLE, Md. -- The FDA said bottles of Baby's Bliss Gripe Water, which is marketed as a remedy for "colic, hiccups, and teething," may be contaminated with a parasite that causes severe diarrhea.

AMSTERDAM -- Type 2 diabetes may be linked to mental health disorders, but age and gender may be contributing factors, according to two separate studies.

AMSTERDAM -- Men are up to two and a half times more likely to have newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes than women, but once a woman is diagnosed, the disease is just as deadly for them as for men.

CHICAGO -- Obesity in older age appears not to be the risk factor for cognitive decline that it is in middle age, researchers found.

AMSTERDAM -- Inflammation in patients with type 2 diabetes is independent of obesity, an observation that may partly explain the increased risk of cardiovascular disease among patients with diabetes.

CALGARY, Alberta -- Exercise strengthens glycemic control for type 2 diabetes patients whether they walk on a treadmill or pump iron, but combining aerobic and resistance exercise appears to have the greatest benefit.
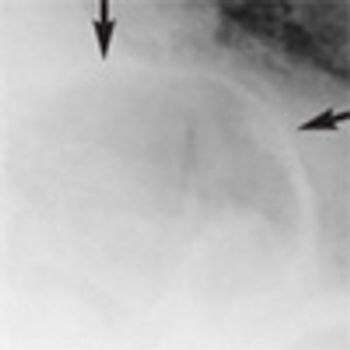
An 88-year-old woman was brought to the emergency department after she choked on a piece of meat. She had dysphagia of many years' duration and progressive weight loss over the past 5 years.

DALLAS -- Patients with elements of metabolic syndrome are more likely to develop highly acidic urine, increasing their risk of forming uric-acid kidney stones, researchers reported.

ATLANTA -- A prostate cancer diagnosis should be a cardiovascular wake-up call, said researchers here.

BILTHOVEN, The Netherlands -- Pounds weigh heavily on the risk of developing coronary heart disease, independent of traditional risk factors, according to a meta-analysis

DALLAS -- A fatty heart, cardiac steatosis, can occur in patients on the road to type 2 diabetes and in the presence of normal left ventricular dysfunction, investigators here have determined.

ABSTRACT: Low-density lipoproteins are the most common atherogenic particles in diabetic dyslipidemia; therefore statins, which dramatically reduce low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, are first-line therapy for patients with diabetes. These agents produce equivalent relative risk reductions in those with and without diabetes but confer greater absolute risk reduction because of the increased incidence of ischemic cardiovascular events in those with diabetes. The LDL cholesterol goal for patients with diabetes who do not have coronary heart disease is below 100 mg/dL. For secondary prevention, the goal is below 70 mg/dL. High-dose statin therapy may be required to achieve these goals. Fibric acids are a reasonable initial option for patients with triglyceride levels above 200 mg/dL and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels below 40 mg/dL; in such patients they reduce risk as effectively as statins. Intermediate-release niacin raises HDL cholesterol levels; the effect is enhanced when niacin is combined with a statin.

For 2 weeks, a 67-year-old obese woman has had episodes of diffuse, nonradiating abdominal pain that last for several hours and are slightly relieved by famotidine/antacid. She rates the pain as 7 on a scale of 1 to 10.

abstract: Common causes of poorly controlled asthma include nonadherence to long-term inhaler therapy; environmental exposures; and uncontrolled comorbidities, such as allergic rhinitis. Adherence can be limited by many factors, including inadequate patient education, medication cost, prior failed treatment, poor physician-patient relationship, unrealistic expectations for therapy, and depression. For patients who have a poor perception of their symptoms, emphasizing the "disconnect" between symptoms and pulmonary function can help motivate them to monitor themselves with a peak flow meter and to adjust their medication accordingly. For patients with allergic triggers, instituting allergen-specific environmental controls can decrease symptoms and urgent care visits for asthma. Chronic rhinosinusitis and gastroesophageal reflux disease can also contribute to difficult-to-control asthma, and treatment of these comorbidities can help reduce asthma symptoms. (J Respir Dis. 2007;28(9):365-369)

A 47-year-old woman who recently completed adjuvant chemotherapy for colon cancer has painless cervical lymphadenopathy of 1 to 2 cm. She has no fever, sore throat, cough, or unexplained weight loss, and she denies exposure to ill persons or animals.

Respondents to a MedPage Today poll were almost equally split over whether bariatric surgery should be first-line therapy in the treatment of obesity, but most of those who said Yes did so with reservations.

BETHESDA, Md. -- Emphasizing that asthma affects different patients in different ways, the National Asthma Education and Prevention Program has issued new evidence-based guidelines on the disease.

SEATTLE -- ZIP codes and property values will provide a better handle on the scope of the nation's obesity problem than income, race, or education, investigators here reported.

BOSTON -- Whole grains may help prevent type 2 diabetes, with consistent results across studies, researchers said.

BOSTON -- The development of type 2 diabetes -- or at least part of it -- may be in your head, researchers here said.